
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Two vertical forces, each of magnitude P = 22 kips, are applied to a beam of the cross section shown. Determine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses in portion BC of the beam.
The maximum tensile stress is ksi.
The maximum compressive stress is ksi.
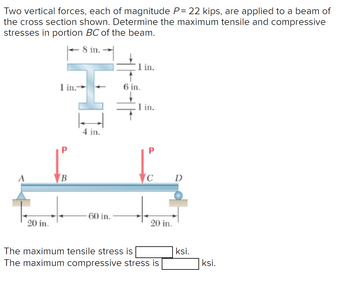
Transcribed Image Text:Two vertical forces, each of magnitude P= 22 kips, are applied to a beam of
the cross section shown. Determine the maximum tensile and compressive
stresses in portion BC of the beam.
8 in.
in.
1 in.-
6 in.
1 in.
4 in.
C
D
60 in.
20 in.
20 in.
The maximum tensile stress is
The maximum compressive stress is
ksi.
ksi.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Link AB, of width b = 2 in. and thickness t = 1414 in., is used to support the end of a horizontal beam. The average normal stress in the link is -18 ksi and the average shearing stress in each of the two pins is 12 ksi. Determine the average bearing stress (ksi). **The way I had solved it was that I used the given normal stress to first find the P force needed to plus into my bearing stress formula. I still however need the diameter. The answer key says to use the given shear stress equation to find the diamter, how do you know to use that and not the shear stress formula again?arrow_forwardA machine component is fabricated from a bent tube as shown below. One part of the tube lies along the z- axis, and the other part is parallel to the y-axis. The outside diameter of the tube is do 122 mm and its inside diameter is dį = 108 mm. A force F = 8.5 kN acts along a line from point to point D. Determine the principal stresses and the absolute maximum shear stresses at points A and B. Note that point A lies along the y-axis and point Blies along the x-axis. Given: • L₁ 258 mm L₂ = 118 mm • L -281 mm LA-602 mm 4 P (α₂₁)A- (₁2) A (Tmax) A L2 Z ²1 00 B L₁7 number (rtol=0,01, atol=1e-05) number (rtol-0.01, atol-1e-05) number (rtol-0.01 atol-le-057 F 0 MPA LA D L3 y 0 0arrow_forwardTwo vertical forces, each of magnitude P= 28 kips, are applied to a beam of the cross section shown. Determine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses in portion BC of the beam. 8 in.→ 1 in. 1 in.- 6 in. 1 in. B 4 in. P C D 60 in. 20 in. 20 in. The maximum tensile stress is ksi. The maximum compressive stress is ksi.arrow_forward
- 3- Calculate the total stresses and show the stress profiles in section A-A due to loading F1 and F2 subjected to the tip section of the arm with length L. A F2 F1arrow_forward3. The tensile member shown, 60 mm x 90 mm in cross section is subjected to a load P=300 kN. The plane A-A makes an angle of 14 degrees with the horizontal axis (x-axis). a. Determine the tensile stress at section A-A. b. Determine the shear stress at section A-A. 300 kN A 14° 300 kNarrow_forwardA simple pin-connected truss is loaded and supported as shown. The truss is constructed from three aluminum members, each having a cross-sectional area of A = 1480 mm2. Assume a = 1.3 m, b = 6.0 m, and c = 3.6 m. If P = 55 kN and Q = 75 kN, determine the normal stress in each member. P Q Answers: OAB = i овс= i JAC = i a B b с MPa (C) MPa (T) MPa (T)arrow_forward
- The main stress, the maximum shear stress, and the dead angle are obtained when the stress is given as shown in the picture below.Draw Mohr's circle.arrow_forwarda. Determine the principal stresses at point A on the cross section of the wrench at section a-a. Also Specify the orientation for this state of stress. b. Determine maximum in-plane shear stress at point A on the cross section of the wrench at section a-a. Also Specify the orientation for this state of stress.arrow_forwardProblem 2: A concentrated load P=36 kN is applied to the upper end of a pipe. The outside diameter of the pipe is D = 220 mm, and the inside diameter is d = 200 mm. Determine the vertical shear stress on the y-z plane of the pipe wall. 36 kN C Pipe cross section. Darrow_forward
- 16 mm 16 mm A M B |--40 mm-|--40 mm-| B D Couple-moment M is applied to the beam, which has a cross-section, as shown in the Figure. if M = 458 Nm and ß =62 Determine the stresses at points A, B and D. Also determine the orientation of neutral axis measured from z-axis.arrow_forwardCalculate non-zero stress components (normal and shear) at points A, B and C. Point C is located at the center of the cross section attached to the wall. Calculate non-zero strain components at point B. Neglect shear stress due to shear force. Given: loading F = 400 N, P-2000 N, and T = 75 N·m, Young's modulus E = 70 GPa, Poisson's ratio v = 0.25 15-mm D. -100 mmarrow_forwardThe couple M=129 kip-in. acts in a vertical plane and is applied to a beam oriented as shown. Determine the stress at point A 24 in. 24 in The stress at point A is 2.4 in 24 in. 2.4 in 2.4 in. kslarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY