Question

Transcribed Image Text:Problem 1
=
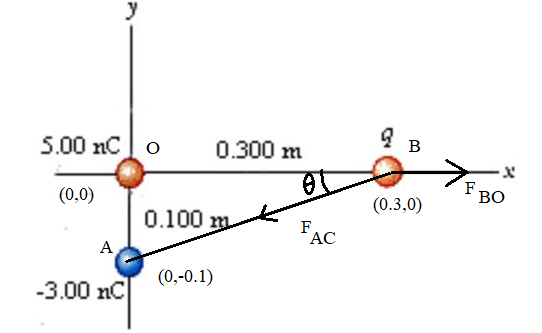
Two source charges (5.0 nC and -3.0 nC) are located on the y-axis respectively at y
-0.10 m, as shown below. A test charge q is located on the x-axis at x = 0.30 m.
charge is repelled by the 5.0-nC source charge and attracted to the -3.0-nC source charge.
(a)
(b)
(c)
5.00 nC
y
-3.00 nC
0.300 m
0.100 m
X
0 and y
-
The test
First, indicate whether the test charge is positive or negative. Then, letting || = 9.0 nC,
find the magnitude and direction of the net electric force on the test charge. (Specify the
direction as an angle measured counterclockwise from the +x axis.)
Now suppose the test charge q is removed, and only the two source charges remain.
Consider three regions along the y-axis: (i) above 5.0 nC, (ii) between 5.0 nC and -3.0
nC, and (iii) below -3.0 nC. In which region(s), other than infinity, is it possible for the
net electric potential to be zero? Justify your answer(s) qualitatively, but do not perform
any calculations.
The net electric field produced by the two source charges is zero at a certain point on the
y-axis below the -3.0-nC charge. Determine the (finite) y coordinate of this point. (Note:
The solution does not require use of the quadratic formula. If your equation appears
quadratic, take the square root of both sides to obtain a linear equation that can be solved
more easily.)
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given that:
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Solve the following problem by writing complete solutions with corresponding units and by using the constant value.arrow_forward11:09 d G M O 图“ Ritesh Sah 2. A uniform rod of length L lies on the x-axis as shown. The rod has a net charge of Q that is uniformly spread alongits length. Q=+5.00e-9 C L= 5.00 meters A uniformly charged rod of length L on the x-axis. Point P is at (5,2) meters on the x,y plane. Use the methods shown in class to: • Calculate the magnitude/size of the electric field at point P due to the rod. Calculate the Trig Angle, measured counter-clockwise from the +x-axis in degrees, of the electric field at point P due to the rod.arrow_forwardThe magnitude of the electrostatic force between two identical ions that are separated by a distance of 7.7 x 10-10 m is 263.1 x 10° N. (a) What is the charge of each ion? (b) How many electrons are "missing" from each ion (thus giving the ion its charge imbalance)? (a) Number Units (b) Number i Unitsarrow_forward
- Two test charges are located in the ?x–?y plane. If ?1=−4.70 nCq1=−4.70 nC and is located at ?1=0.00 m,x1=0.00 m, ?1=0.680 m,y1=0.680 m, and the second test charge has magnitude of ?2=3.00 nCq2=3.00 nC and is located at ?2=1.20 m,x2=1.20 m, ?2=0.550 m,y2=0.550 m, calculate the ?x and ?y components, ?xEx and ?y,Ey, of the electric field ?⃗ E→ in component form at the origin, (0,0). The Coulomb force constant is 1/(4??0)=8.99×109 N·m2/ C2.arrow_forwardThere are two point charges q1=(7.000x10^0) µC and q2=(-3.0000x10^0) µC. q1 is located at origin (0, 0). q2 is located at (4.00x10^0) m,(5.000x10^0) m). Now we place another point charge q3 = (1.0000x10^1) µC at ((4.00x10^0) m, 0), i.e. q3 is right underneath of q2. Please calculated the X-component of the electrostatic force on q3 . Give your answer in the unit of N with 3 sf. Note: Use the sign to represent the direction, for example -2.11x10^-4 means the force is on the negative x direction.arrow_forwardA point charge, q = -5.0 nC, and m = 2.0 x 10-18 kg, is shot vertically upward with an initial speed of 3.0 x 105 m/s from a thin, infinite, planar sheet of uniform charge with surface charge density of σ = +4.0 nC/m^2 . To what vertical elevation will q rise above the sheet of charge? Neglect gravityarrow_forward
- A charge of 7 µC is on the y axis at 5 cm, and a second charge of –7 µC is on the y axis at –5 cm. 507 µC 4 3 2 + 1 3 μC +++++ -1 + 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 -2 -3 -5 0-7 µC Find the force on a charge of 3 µC on the a axis at x = 3 cm. The value of the Coulomb constant is 8.98755 × 10º N · m²/C². Answer in units of N.arrow_forwardIt is 15 km from downtown bozeman, Montana, to the Ridge, atop the Bridger bowl Ski area. If 1 C positive charge is placed on the top the ridge and a 1C positive charge is place atop the Baxter hotel in downtown Bozeman, what will be the force of repulsion between the two charges?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios