
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
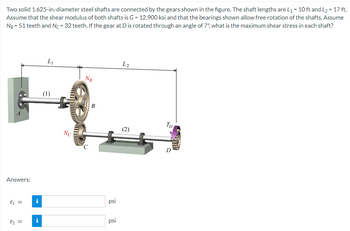
Transcribed Image Text:Two solid 1.625-in.-diameter steel shafts are connected by the gears shown in the figure. The shaft lengths are L₁ = 10 ft and L₂ = 17 ft.
Assume that the shear modulus of both shafts is G = 12,900 ksi and that the bearings shown allow free rotation of the shafts. Assume
NB = 51 teeth and Nc=32 teeth. If the gear at D is rotated through an angle of 7º, what is the maximum shear stress in each shaft?
A
Answers:
t₁ =
T₂ =
i
i
L₁
(1)
Nc
NB
C
B
psi
psi
L2
(2)
Tp
D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I really need help with this! Please answer it using the Maximum shear stress theory, and also be very clear with your explanation. Thank you!arrow_forwardA circular shaft of the dimensions shown in the following figure is subjected to three torques : T1 = 28 k-in, T2 = -8 k-in and T3 = 10 k-in. (a) What is the angle of twist of the right end due to the applied torque? (b) Plot the angle of twist diagram along the shaft. Let, G= 12×106 psi.arrow_forwardThe two solid shafts are connected by the gears shown. The motor constantly supplies 20 kW of power at 15 Hz to system at A. The yield shear stress is 140 MPa for shaft (1) and 220 MPa for the shaft (2), and over all factor of safety is 2. a) Find the diameter of both shafts. b) If the modulus of rigidity of shaft (2) G is 77.2 GPa, calculate the relative angle of twist D with respect to C. 30 teeth B (1) 48 teeth Tp 0.8 marrow_forward
- The shear modulus of the solid steel shaft is G = 11 x 10° ksi. Motor A is directly coupled to the shaft and delivers 3 hp while rotating at 1800 rpm (revolutions per minute). Gears B, C, and D remove the powers indicated in the figure. Given the following two criteria, determine the required diameter of the shaft to the nearest 1/s in. (1) The maximum shear stress must not exceed Tallow = 9 ksi. (2) In order to prevent binding or interference in the attached machin- ery, the angle of twist of gear B with respect to gear D must not exceed 1°. 1.25 ft 1.0 ft 3 hp 1.5 ft 1 hp 0.5 hp 1.5 hparrow_forwardA metal shaft ABCD with variable cross-section is subjected to three external torques (T₁=28 kip- in, T2=8 kip-in, and T3=10 kip-in) as shown in the figure below. Each torque is acting at the locations marked with circular points along the shaft. Note that a 16-inch long segment of the shaft at the free end (right) has a 1-inch diameter bore. The dimensions (lengths and diameters) of the shaft are given in the figure. Assume deformation is linear elastic and take G=12×106 psi. D [3" 16"- X C T₁ 2" -32"- T₂ 1" diam. bore B -16"- A T3 the bar has a uniform diameter d along its full length, but external torques remain the same and are applied at the same locations. If the failure shear stress for the material is equal to Tfail = 10 ksi, and the factor of safety is equal to 2, determine the required (uniform) diameter d for the bar. Assume that the bar is solid for its entire length.arrow_forwardThe splined ends and gears attached to the steel shaft are subjected to the torques shown in Figure 4. Take G = 75 GN/m². (i) (ii) Determine the location along the 40 mm diameter shaft where the shear stress is largest and plot the variation in shear stress from the shaft centre to its outer surface. Determine the angle of twist of sections C, D, and B relative to end A by producing a graphical plot of the variation of angle of twist from end A to end B (wind-up diagram). 300 N-m 500 N-m A www. 300 mm 200 N.m MAAN 400 mm Figure 4 500 mm 400 N-marrow_forward
- Gear shaft ABCDE is subjected to the torques shown in the figure. Find the internal torque in each seg- ment, and then plot the torsional moment diagram. Assume that the spacing between gears is constant, i.e., 10 in. T1 = T2 = 1000 lb-in. 500 lb-in. A B T3 = 800 Ib-in. C Ta = 500 lb-in. d = 1.0 in. D T; = 800 lb-in. Earrow_forward600 Nm An aluminum shaft with a constant diameter of 50 mm is loaded by torques applied to gears attached to it as shown in Figure. Using G = 28 GPa, determine the relative angle of twist of gear D relative to 900 Nm 1100 Nm 2 m 800 N-m gear A. 3m 2 marrow_forwardThe two solid steel shafts shown in the figure are connected together using gear wheels. The length of the CD shaft is Lcd=2 m and the length of the AB shaft is LAB= 1.5 m. The radius of gear C is rc=45 mm and the radius of gear B is rB= 90 mm. The CD and AB shafts rotate freely in the bearings on which they are supported. Also, shaft AB is fixed at point A. Each shaft has a diameter of 20 mm and a shear modulus of G=65 GPa. When a torque of T= 450 N.m is applied to the CD shaft from the D end;a) Calculate the torsion angle on shaft AB. (Write your result in radians.)b) Calculate the total rotation (torsion angle) of the D end of the CD shaft. (Write your result in radians.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY