
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
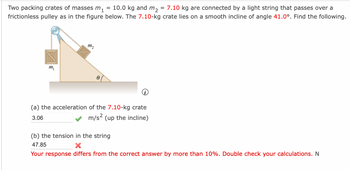
Transcribed Image Text:Two packing crates of masses m₁ 10.0 kg and m₂ = 7.10 kg are connected by a light string that passes over a
frictionless pulley as in the figure below. The 7.10-kg crate lies on a smooth incline of angle 41.0°. Find the following.
m₁
111₂
8
=
(a) the acceleration of the 7.10-kg crate
3.06
m/s² (up the incline)
(b) the tension in the string
47.85
X
Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Helparrow_forwardConsider the force shown in the figure below. If the y-component of the force is Fy = 16.0 N and the angle is θ = 22.0 ◦ , then the x-component and magnitude of the force are A. Fx = 0 and |F~ | = 16.0 N B. Fx = −16.0 N and |F~ | = 22.6 N C. Fx = −39.6 N and |F~ | = 42.7 N D. Fx = −6.46 N and |F~ | = 17.3 Narrow_forwardB h = 150 cm x = 50 cm L = 95 cm Mass = 0.8 kg at point G (so MMI = mL^2 about point A) At what acceleration (in m/s^2) will the object lift off the wall?arrow_forward
- A block of mass m = 1.85 kg is pushed a distance d = 3.15 m along a frictionless horizontal table by a constant applied force of magnitude F = 16.0 N directed at an angle ? = 32.0° below the horizontal as shown in the figure below. A block labeled m is on a horizontal surface. An arrow labeled vector F points downward and to the right at an angle ? above the horizontal, and acts upon the upper left corner of the block. A faded image of the block is a distance d to the right of the block. (a) Determine the work done on the block by the applied force.(b) Determine the work done on the block by the normal force exerted by the table.(c) Determine the work done on the block by the force of gravity.(d) Determine the work done by the net force on the block.arrow_forwardYou place a Box wing to 265.4 N on an inclined plane that makes a 43.5゚ angle with the horizontal. compute the component of the gravitational force acting down the inclined plane. answer in units of N.arrow_forwardWhen the load L is 4.7 m from point C, the tension T in the cable has a magnitude of 5.4 kN. Express T as a vector using the unit vectors i and j. Assume a = 4.7 m, b = 2 m, c = 4.3m. T x j) kN L b Answer: T = (i it iarrow_forward
- A block of mass m = 2.90 kg is pushed a distance d = 7.80 m along a frictionless horizontal table by a constant applied force of magnitude F = 16.0 N directed at an angle ? = 24.0° below the horizontal as shown in the figure below. A block labeled m is on a horizontal surface. An arrow labeled vector F points downward and to the right at an angle ? above the horizontal, and acts upon the upper left corner of the block. A faded image of the block is a distance d to the right of the block. (a) Determine the work done on the block by the applied force. J(b) Determine the work done on the block by the normal force exerted by the table. J(c) Determine the work done on the block by the force of gravity. J(d) Determine the work done by the net force on the block.arrow_forwardFigure x Part A - Moment due to a force specified by magnitude and endpoints F As shown, a member is fixed at the origin, point O, and has an applied force F, the tension in the rope, applied at the free end, point B. (Figure 1) VE ΑΣΦ ↓↑ vec Mo 0.013,97.9, - 196 Submit The force has magnitude F = 140 N and is directed as shown. The dimensions are x₁ = 0.450 m, x₂ = 1.70 m, y₁ = 2.60 m, and z₁ = 1.30 m. B What is the moment about the origin due to the applied force F? Express the individual components of the Cartesian vector to three significant figures, separated by commas. ► View Available Hint(s) Previous Answers X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining 1 of 3 ? i, j, k] N · marrow_forwardQ 5)A force vector F =3i + 3j N is applied on 5 kg mass of body on nonfrictionless horizontal surface. The velocity function of body is v = t + 2 . find the following : 1) frictional force (fs ) 2) the coefficient of friction of surface (μ) . (answer fs =1.7 N , u =0.34)arrow_forward
- Problem 9.35 - Enhanced - with Expanded Hints An 8.5 kg crate is pulled 5.1 m up a 30° incline by a rope angled 16° above the incline. The tension in the rope is 140 N and the crate's coefficient of kinetic friction on the incline is 0.25. For help with math skills, you may want to review: The Vector Dot Product ▼ SOLVE: Part B WT = T·Ar=TAx cos(16) = (140 N) (5.1 m) cos(16) = 690 J WG = FG Ar = mg▲x cos(120°) = (8.5 kg) (9.8 m/s²)(5.1 m) cos(120°) Wn=n· Ar=nAx cos(90°) = 0 J What is the increase in thermal energy of the crate and incline? Express your answer in joules to two significant figures. ► View Available Hint(s) VE ΑΣΦ ΔΕth = |105 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining ? 10 of 14 J Rearrow_forwardIn (Figure 1), F={300i-100j+550k}NF= (300i-100j+550k)N. Determine the magnitude of the projection of the force FF acting along the cable BA◆◆. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 2m 6m 1 of 1 3marrow_forwardConnected objects with inclined plane problem. Consider the figure where you have two boxes connected by a string over a pulley. The smooth (frictionless) ramp is inclined to a an angle of 35° with the flat ground, and the box on the ramp has a mass of 6.40 kg. The mass of the 6.4 kg hanging box is m = 3.05 kg. You don't need to consider significant figures in your answer, but don't round excessively partway through your calculations. 35° Find (a) the direction and (b) the magnitude of the hanging box's acceleration.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON