
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
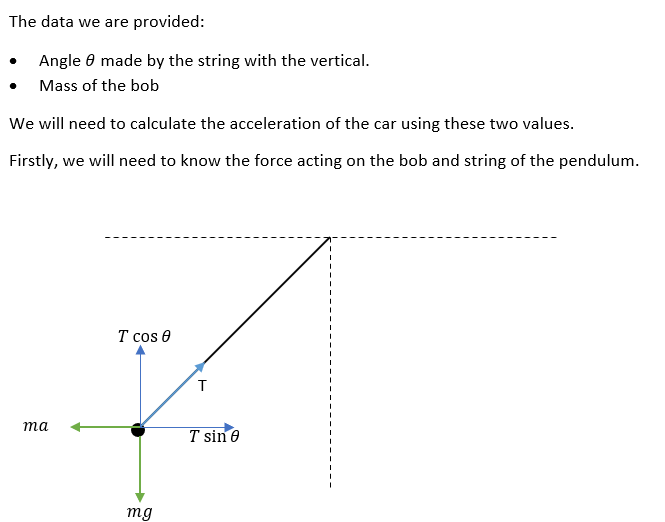
![A student is making an "accelerometer" by hanging a pendulum in a car. She wants
to determine the acceleration, a, of the car based on the angle, 0, the the
pendulum makes with the vertical. The pendulum has a bob of mass m. Assume
the windows are rolled up.
Hint: Solve in terms of variables then plug in.
e [°]
m [kg]
a [m/s*]
3.
14
28
6.0
28
check answers
21](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/18e5c811-cff1-48b8-a936-4c74d4925c39/0074d10f-a1ce-4bc6-b54b-0ab1f17523cb/1ymk5u2_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:A student is making an "accelerometer" by hanging a pendulum in a car. She wants
to determine the acceleration, a, of the car based on the angle, 0, the the
pendulum makes with the vertical. The pendulum has a bob of mass m. Assume
the windows are rolled up.
Hint: Solve in terms of variables then plug in.
e [°]
m [kg]
a [m/s*]
3.
14
28
6.0
28
check answers
21
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the attached Word file, a shape is on an x-y axis, beginning at x = 0. The bottom of the shape is 25 cm long and it reaches a height of 20 cm. The shape weights 450 g. The curved part of the shape is a parabola, i.e., it has the form y = ax2, where a is a constant to be determined. a) Determine the constant from the information given. b) If shape has a uniform density and a uniform width in the z-direction, find the x-component of the center-of-mass.arrow_forwardM = 2.2 kg, and the tension in the connecting string is 70 N. How long does it take the hanging mass to drop .5 m? Thecoefficient of kinetic friction between the top block and the incline is (μ = 0.13). Assume the pulley is frictionlessarrow_forwardA wedge with mass M rests on a frictionless horizontal table top. A block with mass m is placed on the wedge (the figure (Figure 1)(a)). There is no friction between the block and the wedge. The system is released from rest. Figure y M m 1 of 1 Part A Calculate the component of the acceleration of the wedge. Express your answer in terms of M, m, a, and constant g. IVE ΑΣΦ aw x = Submit Part B ab x = Calculate the component of the acceleration of the block. Express your answer in terms of M, m, a, and constant g. 15. ΑΣΦ Submit Part C Request Answer aby = ? Request Answer ? Calculate the y component of the acceleration of the block. Express your answer in terms of M, m, a, and constant g. IVE ΑΣΦΑΛΟ ?arrow_forward
- 3. An object is stuck at the origin. To get the object free, two forces are applied to the object. The first force, F, extends from the origin to position (-8,2). The second force, F2, acts on the object with a magnitude of 8 Newtons in the direction of 30°. You may assume units of distance are in meters. Represent the two force vectors, F and F2, in component form. Leave all answers in exact а. form. b. Draw a sketch of the two force vectors on the graph to the right. -5- с. If these two forces together free the object, in what direction and with what magnitude would the object travel? Round to one decimal -5 place as needed. -5arrow_forwardProblem 3: Amass is sliding on a frictionless surface with a speed v. It runs into a linear spring with a spring constant of k, which compresses from position x; to position xp. m ©theexpertta.com Write a general expression for the force that the spring exerts on the mass, in term of k and x. Choose the initial position of the front of the spring to be x=0. Fspring =-kx / Correct! Part (b) Select the equation that correctly describes the work done by the spring to stop the mass. Ow=-kx? OW=- *fk x dx + , m v OW=-kx dx Ow= f *f k x dx OW= - *k x dx - , m v? OW = - * F x dx Submit Hint Feedback I give up! Hints: 0% deduction per hint. Hints remaining: 2 Feedback: 0% deduction per feedback. Part (c) Evaluate the relationship in part (b) to arrive at an expression for the work done in terms of known variables. Part (d) Solve for the numerical value of the work done in Joules given that x; = 0, x = 68 cm, and k= 145 N/m. W = - 33.5 W = -33.5 / Correct!arrow_forwardShown to the right is a block of mass m resting on a frictionless ramp inclined at an angle to the horizontal. The block is held by a spring that is stretched a distance d after the block is attached to it. E k= e wwwwww ▷ A Write an equation for the force constant of the spring in terms of the variables from the problem statement (m, 0, and d). Use g for the gravitational constant.arrow_forward
- The heaviest invertebrate is the giant squid, which is estimated to have a weight of about 0.20 tons spread out over its length of 36 feet. What is its weight in newtons? Incorrect: Your answer is incorrect. Your response differs significantly from the correct aarrow_forwardA hemispherical bowl having a radius of 6.2m is full of water. If the hemispherical bowl is made to rotate uniformly about the vertical axis at the rate of 30 rpm. a) Determine the volume of water that is spilled out. Answer in m3 b) Determine the remaining volume of water in the hemispherical bowl. Answer in m3arrow_forwardA baseball of mass m= 0.35 kg is spun vertically on a massless string of length L = 0.93 m. The string can only support a tension of Tmax= 10.6 N before it will break. Randomized Variables m = 0.35 kg L = 0.93 m Tmax= 10.6 N Part (a) What is the maximum possible speed of the ball at the top of the loop, in meters per second? Part (b) What is the maximum possible speed of the ball at the bottom of the loop, in meters per second?arrow_forward
- Two blocks of masses m, = 4.0 kg and mg = 8.0 kg are connected with a string that passes over a very light pulley (Figure 1). Friction in the pulley can be ignored. Block 1 is resting on a rough table and block 2 is hanging over the edge. The coefficient of friction between the block 1 and the table is 0.70 (assume static and kinetic friction have the same value). Block 1 is also connected to a spring with a constant 300 N/m. In the initial state, the spring is relaxed as a person is holding block 2, but the string is still taut. When block 2 is released, it moves down for a distanced until it stops (the final state). Figure 1 of 1arrow_forwardHelp. I cannot figure this out! A chandelier hangs h = 0.52 m down from two chains of equal length. The chains are separated from one another by a length L = 0.75 m at the ceiling. The chandelier has a mass of m = 19 kg. Write an expression for FT,y, the magnitude of the y-component of the tension in one chain, in terms of the given information and variables available in the palette.arrow_forwardFor part 1, assume m₁ =100 g, m2=90 g, m3 = 100 g, 01-27°, and 02=26°, what does T1x+T2x+T3x equal to? Enter your answer up to 1/1000 N accuracy. Pay attention to the sign of your answer. Your Answer: Answer units Question 9 (2 points) = For part 1, assume m₁ =100 g, m2=90 g, m3 100 g, 01-26°, and 02-27°, what does T1y+T2y+T3y equal to? Enter your answer up to 1/1000 N accuracy. Pay attention to the sign of your answer. Your Answer:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON