
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
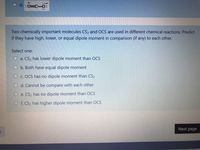
Transcribed Image Text:O d. :0=C-0:
Two chemically important molecules CS2 and OCS are used in different chemical reactions. Predict
if they have high, lower, or equal dipole moment in comparison (if any) to each other.
Select one:
O a. CS2 has lower dipole moment than OCS
O b. Both have equal dipole moment
O c. OCS has no dipole moment than CS2
O d. Cannot be compare with each other
e. CS2 has no dipole moment than OCS
O f. CS2 has higher dipole moment than OCS
Next page
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- O Macmillan Learning Introductory Chemistry Revell SECOND EDITION Which of these compounds does NOT have a net dipole? O sulfur dioxide, SO₂ water, H₂O carbon dioxide, CO₂ O hydrogen fluoride, HFarrow_forwardWhich is the lowest energy resonance structure? a. НО b. HO С. НО а но SH SH SH SHarrow_forward5. Which of the following covalent bonds is the LEAST polar? а. С - CI d. N-F е. О -Н f. 0-S b. С-Н С. Н-СI 6. Which of the following is the electron configuration of oxide, O?. a. 1s°2s°2p* b. 1s°2s°2p° c. 1s°2s°2p® d. 1s°2s°2p®3s?3p* e. 1s°2s°2p°3s°3p° f. 1s°2s°2p®3s°3p®arrow_forward
- Are the structures below polar or nonpolar? Circle the polar ones. Explain why the are polar and indicate the direction of all polar bonds.arrow_forwardClear my choice For the series methane, ammonia, and water, the bond angle increases in the following order: H,0 < NH3 < CH4. This trend is due to Select one: O a. a decreasing effective nuclear charge. O b. a decrease in the number of lone pairs. O c. an increase in atomic radius. d. an increase in the polarity of the molecules. O e. an increasing effective nuclear charge. Which bond angle is the largest? Select one: a. O-C-Sin COSarrow_forwardIn an alternate universe, these are types of electron cloud shapes a D cloud (shape in blue), and a E cloud (shape in gray). The nucleus is represented by a green circle. All other rules about orbitals and types of bonding are the same as our universe. A В E (one on top of the other) Answer the following questions below in Canvas A. Which orientation of clouds do you think would create the strongest bond and why B. Which orientation of clouds do you think represents a sigma bond and why C. Which orientation of clouds do you think represents a pi bond and why make sure you label which question you are answeringarrow_forward
- Answer the following questions about the Lewis structure for ammonium carbonate, (NH4)2CO3 ammonium ions and There are molecule. Each ammonium ion has In each ammonium ion, the central N has The single carbonate ion has The carbonate ion has covalent bonds. For the carbonate ion, the shape at the central C is a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 e. 4 f. 5 m. 20 o. 26 v. linear w. monoatomic ions cc. no bond angles, no central atom n. 24 p. 30 central atoms and REDs and single covalent bonds, q. 32 x. tetrahedral dd. 109.5° 8.8 r. 34 REDS, the shape is (x), and the bond angles are valence electrons. h. 10 carbonate ions. There are i. 12 valence electrons. and the bond angles are about j. 14 k. 16 I. 18 u. pyramidal aa. 120⁰ s. 36 t. diatomic y. trigonal planar z. bent ee. polar ff. nonpolar gg. ionic double covalent bonds, and bb. 180° hh. O and O ionic bonds in the triplearrow_forward21. Electrons in bonds remain localized between two atoms. Electrons in delocalized between more than two atoms Α. π, σ B. O, T C. π, π D. 0,0 E. ionic, o bonds can becomearrow_forwardConsider the structure below. What is the molecular geometry for the circled central atom? H. H H H H H. -CEC-Harrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY