
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
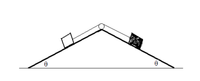
Two blocks are positioned on surfaces, each inclined at the same angle of 53.7 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The blocks are connected by a rope which rests on a frictionless pulley at the top of the inclines as shown, so the blocks can slide together. The mass of the black block is 6.98 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction for both blocks and inclines is 0.420. Assume static friction has been overcome and that everything can slide. What is must be the mass of the white block if both blocks are to slide to the RIGHT at an acceleration of 1.5 m/s^2?
a. 5.19 kg
b. 2.46 kg
c. 2.34 kg
d. 3.02 kg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- wo blocks are positioned on surfaces, each inclined at the same angle of 52.3 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The blocks are connected by a rope which rests on a frictionless pulley at the top of the inclines as shown, so the blocks can slide together. The mass of the black block is 3.16 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction for both blocks and inclines is 0.440. Assume static friction has been overcome and that everything can slide. What is must be the mass of the white block if both blocks are to slide to the LEFT at an acceleration of 1.5 m/s^2? 2.34 kg 1.66 kg 10.38 kg 5.97 kgarrow_forwardA small block with mass m is set on the top of an upside-down hemispherical bowl. If the coefficient of static friction between the block and the bowl is μs and the block is slowly repositioned at different points down the surface of the bowl, at what angle measured from the vertical will the block begin to slide? Write your answer in terms of the mass, m; the gravitational acceleration on Earth, g; and the coefficient of static friction, μs. (Assume the +y axis is vertically upward.)arrow_forwardTwo blocks are positioned on surfaces, each inclined at the same angle of 42.6 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The blocks are connected by a rope which rests on a frictionless pulley at the top of the inclines as shown, so the blocks can slide together. The mass of the black block is 5.49 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction for both blocks and inclines is 0.420. Assume static friction has been overcome and that everything can slide. What is must be the mass of the white block if both blocks are to slide to the RIGHT at an acceleration of 1.5 m/s^2? 1.55 kg 3.55 kg 1.37 kg 1.04 kgarrow_forward
- Two blocks are positioned on surfaces, each inclined at the same angle of 40.9 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The blocks are connected by a rope which rests on a frictionless pulley at the top of the inclines as shown, so the blocks can slide together. The mass of the black block is 2.37 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction for both blocks and inclines is 0.500. Assume static friction has been overcome and that everything can slide. What is must be the mass of the white block if both blocks are to slide to the LEFT at an acceleration of 1.5 m/s^2? 0.87 kg 22.68 kg 11.66 kg 0.96 kgarrow_forwardTwo blocks are positioned on surfaces, each inclined at the same angle of 43.0 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The blocks are connected by a rope which rests on a frictionless pulley at the top of the inclines as shown, so the blocks can slide together. The mass of the black block is 6.15 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction for both blocks and inclines is 0.260. Assume static friction has been overcome and that everything can slide. What is must be the mass of the white block if both blocks are to slide to the LEFT at an acceleration of 1.5 m/s^2?arrow_forwardTwo blocks are positioned on surfaces, each inclined at the same angle of 40.9 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The blocks are connected by a rope which rests on a frictionless pulley at the top of the inclines as shown, so the blocks can slide together. The mass of the black block is 6.53 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction for both blocks and inclines is 0.210. Assume static friction has been overcome and that everything can slide. What is must be the mass of the white block if both blocks are to slide to the RIGHT at an acceleration of 1.5 m/s^2? 3.15 kg 5.48 kg 2.65 kg 2.32 kgarrow_forward
- Two blocks are positioned on surfaces, each inclined at the same angle of 51.0 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The blocks are connected by a rope which rests on a frictionless pulley at the top of the inclines as shown, so the blocks can slide together. The mass of the black block is 4.15 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction for both blocks and inclines is 0.260. Assume static friction has been overcome and that everything can slide. What is must be the mass of the white block if both blocks are to slide to the LEFT at an acceleration of 1.5 m/s^2? 6.28 kg 4.07 kg 2.65 kg 9.85 kgarrow_forwardTwo blocks are positioned on surfaces, each inclined at the same angle of 55.4 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The blocks are connected by a rope which rests on a frictionless pulley at the top of the inclines as shown, so the blocks can slide together. The mass of the black block is 7.71 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction for both blocks and inclines is 0.600. Assume static friction has been overcome and that everything can slide. What is must be the mass of the white block if both blocks are to slide to the LEFT at a constant velocity? 18.60 kg 7.71 kg 13.16 kg 3.20 kgarrow_forwardPlease help with this question, it comes with a few subparts. PLEASE HELP.arrow_forward
- A block of mass 1.96kg is accelerated across a rough surface by a rope passing over a pulley, as shown in the figure below. The tension in the rope is 14.0N, and the pulley is 10.8cm above the top of the block. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.350. Calculate the value of x at which the acceleration becomes zero.arrow_forwardYou are playing stuffleboard and you must slide your weighted disk 8m across the floor where it will come to rest on the target. You give it an initial push of 4 m/s but then it slides on its own to a stop. The disk is 0.8 kg. What is the coefficient of friction if your shot is perfect a bull's eye?arrow_forwardTwo blocks are positioned on surfaces, each inclined at the same angle of 55.4 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The blocks are connected by a rope which rests on a frictionless pulley at the top of the inclines as shown, so the blocks can slide together. The mass of the black block is 4.36 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction for both blocks and inclines is 0.290. Assume static friction has been overcome and that everything can slide. What is must be the mass of the white block if both blocks are to slide to the LEFT at a constant velocity? 2.91 kg 6.54 kg 4.36 kg 5.45 kgarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON