
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
Two balls, of masses mA= 42 g and mB = 60 g, are suspended as shown in the figure. The lighter ball is pulled away to a 66 angle with the vertical and released. Assume that the positive x-axis is directed to the right.
b)What is the velocity of each ball after the elastic collision?
Transcribed Image Text:Two balls, of masses ma = 42 g and mB = 60 g, are
suspended as shown in the figure. The lighter ball is pulled
away to a 66 ° angle with the vertical and released. Assume
that the positive x axis is directed to the right. (Figure 1)
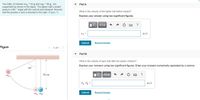
Part A
What is the velocity of the lighter ball before impact?
Express your answer using two significant figures.
Π ΑΣφ
VA =
m/s
Submit
Request Answer
Figure
< 1 of 1
Part B
What is the velocity of each ball after the elastic collision?
Express your answers using two significant figures. Enter your answers numerically separated by a comma.
66°
30 cm
?
m/s
= 4a Ya
A B
Submit
Request Answer
ma mB
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A block of wood, with mass 1.50 kg, rests stationary on horizontal ground.The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the ground is 0.933.A bullet, with mass 0.250 kg, moving horizontally, hits and sticks into the block of wood.We find that the speed of the block of wood, with the bullet embedded in it, just after the collision is 11.5 m/s. a) Calculate the speed of the bullet before hitting the block of wood. m/s(b) Calculate how far the block slides along the ground before coming to rest. Also include a diagram showing physical situation and coordinatesarrow_forwardA bullet is fired into a block of wood sitting on a block of ice. The bullet has an initial velocity of 500m/s and a mass of 0.005kg. The wooden block has a mass of 1.2kg and is initially at rest. The bullet remains embedded in the block of wood afterward. a) Assuming that the momentum is conserved, find the velocity of the block of wood and bullet after the collision. b) What is the magnitude of the impulse that acts on the block of wood in this process? c) Does the change in momentum of the bullet equal that of the block of wood?arrow_forwardTwo identical pucks have an elastic collision on a frictionless horizontal table, as shown in the figure. Ꮎ B A Puck A has a speed of v A = 4.4 m/s before the collision, while puck B is stationary. After the collision puck B is seen to move off at an angle of 0 =44° from the line of A's initial velocity. What is the angle between the velocities of the two pucks after the collision in degrees? Number degrees. What is the speed of A after the collision? Number Unitsarrow_forward
- Two billiard balls of equal mass move at right angles and meet at the origin of an xy coordinate system. Initially ball A is moving upward along the y axis at 2.0m/sm/s, and ball B is moving to the right along the x axis with speed 3.7m/sm/s. After the collision (assumed elastic), the second ball is moving along the positive y axis. What is the final direction of ball A? Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forwardTwo vehicles approach a right angle intersection and then collide. After the collision, they become entangled. If their mass ratios were 1:4 and their respective speeds as they approached were both 13 m/s, find the magnitude and direction of the final velocity of the wreck. 12.5 m/s at 79° 13.1 m/s at 79° 15.7 m/s at 79° 16.3 m/s at 79° Correct.arrow_forwardTwo shuffleboard disks of equal mass, one orange and the other green, are involved in a perfectly elastic glancing collision. The green disk is initially at rest and is struck by the orange disk moving initially to the right at voi = 3.00 m/s as in Figure a, shown below. After the collision, the orange disk moves in a direction that makes an angle of 0 = 35.0° with the horizontal axis while the green disk makes an angle of o 55.0° with this axis as in Figure b. Determine the speed of each disk after the collision. Vof = m/s Vaf = m/s After the collision Before the collision Need Help? Watch It Read Itarrow_forward
- Two shuffleboard disks of equal mass, one orange and the other green, are involved in a perfectly elastic glancing collision. The green disk is initially at rest and is struck by the orange disk moving initially to the right at vo- 7.75 m/s as in Figure a, shown below. After the collision, the orange disk moves in a direction that makes an angle of e = 39.0° with the horizontal axis while the green disk makes an angle of 9 = 51.0° with this axis'as in Figure b. Determine the speed of each disk after the collision. Vof= m/s Vof- m/s After the collision Before the collisionarrow_forwardTwo shuffleboard disks of equal mass, one orange and the other green, are involved in a perfectly elastic glancing collision. Voi = 3.15 m/s as in Figure The green disk is initially at rest and is struck by the orange disk moving initially to the right at v a, shown below. After the collision, the orange disk moves in a direction that makes an angle of 0 = 38.0° with the horizontal axis while the green disk makes an angle of = 52.0° with this axis as in Figure b. Determine the speed of each disk after the collision. X V of Vgf= 1.66 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m/s m/s a Before the collision After the collision barrow_forwardTwo billiard balls of equal mass move at right angles and meet at the origin of a xy coordinate system. Ball A is moving upward along the y axis at vAvAv_A = 2.3 m/s, and ball B is moving to the right along the x axis with speed vB= 5.5 m/s. After the collision, assumed elastic, ball B is moving along the positive yy axis a)What is the final direction of ball A? b) What are their two speeds?arrow_forward
- Two clay balls collide and stick. Ball 1 has a mass of 3 kg and an initial velocity of 10 m/s in the positive x direction. Ball 2 has a mass of 10 kg and an initial velocity of 12 m/s in the negative x direction. What is the final velocity of the combined mass?arrow_forwardTwo billiard balls of identical mass move toward each other as shown in the figure. Assume that the collision between them is perfectly elastic. If the initial velocities of the balls are v1i = +34.3 cm/s and v2i = −20.1 cm/s, what are the velocities of the balls after the collision? Assume friction and rotation are unimportant. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) v1f = cm/s v2f = cm/sarrow_forwardA cue ball of mass m1 = 0.365 kg is shot at another billiard ball, with mass m2 = 0.595 kg, which is at rest. The cue ball has an initial speed of v = 5.5 m/s in the positive direction. Assume that the collision is elastic and exactly head-on. Write an expression for the horizontal component of the billiard ball's velocity, v2f, after the collision, in terms of the other variables of the problem. What is this velocity, in meters per second? Write an expression for the horizontal component of the cue ball's velocity, v1f, after the collision. What is the horizontal component of the cue ball's final velocity, in meters per second?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON