
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
topic: Bradford Assay
There are numerous methods of protein determination in use, but this module focuses on the Bradford assay.
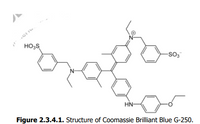
The Bradford assay is a dye-binding method that employs Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250, whose structure
is shown in Figure 2.3.4.1. Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 is a dye that interacts with proteins through
hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions.
What are the identities and functions of the components of the Bradford reagent in protein content
determination?
Transcribed Image Text:GI I
HO;S
-SO
HN-
Figure 2.3.4.1. Structure of Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- What is the function of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) in SDS-PAGE? stabilizes the gel matrix, improving resolution during electrophoresis SDS solubilizes proteins to give them uniformly negative charges, so the separation is based purely on size. SDS raises the pH of the gel, separating multiunit proteins into individual subunits. SDS solubilizes proteins to give them uniformly positive charges, so separation is based purely on pH.arrow_forward4arrow_forward3. a. Estimate the molecular weight of sphingosine kinase in kiloDaltons. b. Interpret the results of the experiment with the reducing agent. What does the result of Lane 2 and Lane 3 migrations tell you about the primary, secondary or tertiary structure of the sphingosine kinase?arrow_forward
- You are studying a protein-protein interaction in 2 proteins. You decide to test both these proteins in different buffers and see if the interaction is preserved. You run the assay in the following buffers, pH 7.4, pH 7.4 with BME, pH 4.5, pH 3.5, pH 11, pH 12.5. The SDS gels from the assays are attached. a. What type of protein-protein interaction do these results suggest? b. What amino acids are most likely involved in this interaction? (Guess based on assay)arrow_forward8L.Part Iarrow_forwardA decapeptide was analyzed and the following information obtained. Determine the primary structure of the peptide. Edman's Degradation: PTH-Ala Trypsin produces 3 peptides of the following composition: 1. Gly, His 2. Ala, Leu, Lys, Val 3. Arg (2), Phe, Pro Chymotrypsin produces 2 peptides of the following composition: 1. Ala, Leu, Lys, Phe, Val 2. Arg (2), Gly, His, Pro Elastase produces 1 amino acids and 3 peptides 1. Ala 2. Leu, Val 3. Arg (2), Lys, Phe, Pro, Gly, His Arg Gly His Leu Phe Pro Valarrow_forward
- Marker Proteins Molecular Weight (daltons) Distance 132,000 66,000 43,000 14,400 Serum Albumin (Dimer) Serum Albumin (Monomer) 23mm 32mm Ovalbumin 39mm 60mm Lysozyme Unknown 1 26mm Unknown 2 58mm Rabbit serum (albumin) 33mm 1.On semilog paper (provided below) plot the distance migrated by each standard protein as a function of molecular weight. Determine the molecular weight of the unknown proteins and the major protein found in rabbit serum (albumin) from this calibration curve. ii) Interferon is a protein of 25,000 Dalton. How far would it have migrated, land it been included in this experiment? iii) The average amino acid residue in a protein has a molecular weight of 120 Daltons. Assuming that your unknowns are average, how many amino acid residues do they containarrow_forwardPlease help me with this question. How many amino acid residues are in the heavy and light chains of the Fab fragment, and how many amino acid residues are in lysozyme?arrow_forwardH CH₂ H₂C HC-CH3 CH₂ H H₂C (S) H₂C H CH₂ CH₂ CH₂ NH O C NH NH₂ a) Which of the following statements about this peptide are correct? Group of answer choices Treatment of this peptide with trypsin generates two products. This peptide is a substrate for carboxypeptidase A Treatment of this peptide with cyanogen bromide generates a pentapeptide and a tripeptide. Treatment of this peptide with chymotrypsin generates three products. Treatment of this peptide with elastase generates 2 products. None of the above statements are correct. b) What is the sequence of this peptide using one letter abbreviations? c) What is the pH which would correspond to the ionization of the peptide as drawn above? 1, 5, 7, 10, 14arrow_forward
- Can I get a visual (drawn on paper or on a software; like chem draw or chem sketch)? Illustrate detailed chemical scheme for how you will functionalize your biomolecule to the surface of the sensor (e.g. if you wanted to functionalize a protein to a gold SPR chip, you should could show the assembly of an amine-terminated SAM, followed by carbodiimide coupling of. the protein). These schemes should be drawn using a chemical illustration software package (ChemDraw / ChemSketch).Your chemical schemes should be as detailed as necessary to accurately depict the chemical design of your system, DO NOT INCLUDE a step-wise mechanism, it is not necessary. You should include at least one literature reference to support your conjugation strategy.arrow_forwardFind a method that uses some form of HPLC for the analysis of proteins. What was the stationary phase used? How does this kind of stationary phase separate the proteins? What kind of mobile phase was used? Was the method isocratic or was a gradient used? How were the proteins detected?arrow_forwardMaintaining the proper structure of high value biopharmaceutical proteins like monoclonal antibodies throughout downstream processing is critical to process economics. What factors (at least 3) should be considered/controlled to maintain proper 3-dimensional configuration?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON