Question
thumb_up100%
Water enters a house (Fig. ) through a pipe with an inside diameter
of 2.0 cm at an absolute pressure of 4.0 * 10^5 Pa (about 4 atm). A
1.0-cm-diameter pipe leads to the second-floor bathroom 5.0 m above.
When the flow speed at the inlet pipe is 1.5 m/s, find the flow speed,
pressure, and volume flow rate in the bathroom.
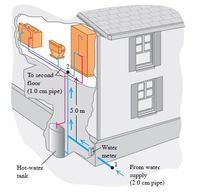
Transcribed Image Text:To second
floor
(1.0 cm pipe)
5.0 m
Water
meter
Hot-water
From water
supply
(2.0 cm pipe)
tank
2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A water pipe having a 2.59 cm inside diameter carries water into the basement of a house at a speed of 0.770 m/s and a pressure of 213 kPa. If the pipe tapers to 1.31 cm and rises to the second floor 6.71 m above the input point, A) What is the speed of the water at the second floor? B) What is the water pressure at the second floor?arrow_forwardWater is carried through a pipe. At point A, the diameter is 20 cm and the pressure is 130 kPa. At point B, which is 4.0 m higher than point A, the diameter is 30 cm. If the flow is 0.08 m^3/s, what is the pressure at the second point? 9.3 kPa Not any of the choices listed 93 Pa 0.92 atm 930 mmH20arrow_forwardFind the pressure difference required between the ends of a 2.00 m long, 1.00 mm diameter horizontal tube for 40° C water to flow through it at an average speed of 4.0 m/s. Water at 40° has a viscosity of 0.7 x 10-3 Pa s. The pressure difference is equal to ______x105 Pa. Recall the equation for volume flow rate with viscosity: Δ?Δ?=??4Δ?8??arrow_forward
- If a kitchen sink has a volume of 20 L. Water flows in the sink with a mass flow rate of 0.5 kg/s. If the drain is closed, how long, in seconds, does it take for the sink to fill up? Density of water = 1000 kg/m3arrow_forwardA sealed tank containing seawater to a height of 12.0 m also contains air above the water at a gauge pressure of 3.05 atm. Water flows out from the bottom through a small hole. Calculate the speed with which the water comes out of the tank. Express your answer in meters per second.arrow_forwardA container of cross-sectional area 107 cm2 contains liquid of density 1.75 g/cm3 to a height of 6.80 cm above a small hole of area 1.00 cm2 in the side. (a) Find the speed of the fluid as it leaves the hole.(b) Find the flow rate through the hole.arrow_forward
- A liquid of density 1350 kg/m3 flows steadily through a pipe of varying diameter and height. At Location 1 along the pipe, the flow speed is 9.83 m/s and the pipe diameter ?1 is 10.9 cm. At Location 2, the pipe diameter ?2 is 17.3 cm. At Location 1, the pipe is Δ?=9.47 m higher than it is at Location 2. Ignoring viscosity, calculate the difference Δ?between the fluid pressure at Location 2 and the fluid pressure at Location 1.arrow_forwardA beaker is filled with an unknown liquid up to a depth of 10.00cm . The gauge pressure at the bottom of the beaker is measured to be 1540.00Pa . What is the density of the liquid contained in the beaker?arrow_forwardA pumping station uses a Venturi tube to measure the flow rate of gasoline. The density of the gasoline is p = 7.40 x 102 kg/m3, the inlet and outlet tubes, respectively, have a radius of 2.80 cm and 1.40 cm, and the difference in input and output pressure is P, - P, = 1.20 kPa. (a) Find the speed (in m/s) of the gasoline as it leaves the hose. m/s (b) Find the fluid flow rate in cubic meters per second. m3/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios