
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
How would you determine the pKa1 and Ka1 from graph. Please show calculation steps to finding the Ka
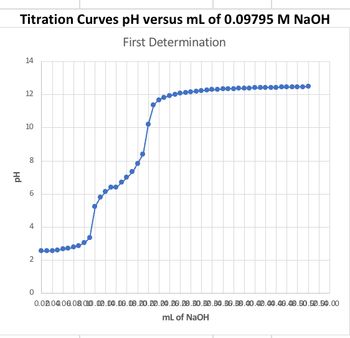
Transcribed Image Text:**Titration Curves: pH versus mL of 0.09795 M NaOH**
**First Determination**
This graph represents a titration curve, demonstrating the relationship between pH and the volume of 0.09795 M NaOH added.
- **X-axis:** This axis represents the volume of NaOH added, measured in milliliters (mL), ranging from 0.0 to 5.0 mL.
- **Y-axis:** This axis represents the pH level of the solution, ranging from 0 to 14.
**Description of the Curve:**
1. **Initial Phase:**
- The pH starts at a low value, around 2, indicating an acidic solution.
- As small amounts of NaOH are added, the pH remains relatively stable until approximately 0.2 mL of NaOH is added.
2. **Rising Phase:**
- Beyond 0.2 mL, there is a noticeable increase in pH, which continues as more NaOH is added.
- The curve shows a sharp rise, indicating the neutralization of acid by the base.
3. **Equivalence Point:**
- The steepest part of the curve signifies the equivalence point, where the solution is neutralized.
4. **Final Phase:**
- After the equivalence point, the curve levels off, with the pH stabilizing around 12 to 13.
- This indicates an excess of NaOH, giving the solution a basic character.
This titration curve is typical for strong acid-strong base titrations, illustrating how pH changes in response to the addition of a base to an acidic solution.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Breaking which bond results in the peaks at 105 and 198 amu? in the peak at 272 amu?arrow_forwardtext fs % Questions: S T Calibri 1 f6 - Key Words: global warming 1. Why is oxygen NOT a greenhouse gas? ☐ 18 12 6 Y G + & BIUA 7 Lesson 2: Greenhouse Gases SYMPIREH 2. Why is the effect of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere similar to the effect of glass surrounding greenhouse? 3. The atmosphere on the planet Venus is almost 96 % carbon dioxide. What effect might its concentration of carbon dioxide have on the average surface temperature on Venus? fB 3 Page 3: The Structure of Greenhouse Gases Questions 4. What effect does an increase in the atmospheric carbon dioxide levels (and therefore rising temperatures) have on the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere? Why? U 漫 5. Both coal and natural gas can be burned to generate electricity. However, burning natural gas produces about half the carbon dioxide emissions as burning coal to provide the same amount of energy. Why is it better for the environment to phase out coal-burning power plants in favor of natural gas-burning power…arrow_forwardQuestion 11 Which of the indicated protons would have the smallest pKa value? C. H. a. CH3 .C. CC-H C H- H. d. b. a by O darrow_forward
- Part A Classify each of the following as ionic or molecular. Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. MgCO3 FePO3 AsCl3 N₂O3 Ba3(PO4)2 Al(ClO2)3 Co(C₂H3O2)2 lonic Submit Request Answer Reset Help Moleculararrow_forwardHow are the two BRs related and how are the OH figures relatedarrow_forwarda. Rubidum chloride, RbCl, and sulfuric acid, H₂SO4 Rule 4: an exception to the rule for sulfates; RbCl(aq) + H₂SO4 (aq) → Rb₂SO4(s) + HCl(aq) Rule 4: an exception to the rule for sulfates; 2RbCl(aq) + H₂SO4 (aq) → Rb₂SO4 (8) + 2HCl(aq) Rule 4: an exception to the rule for sulfates; 2RbCl(aq) + H₂SO4 (aq) → Rb2SO4 (aq) + 2HCl(aq) O No precipitate: both Rb₂SO4 and HCI are soluble RbCl(aq) + H₂SO4 (aq) → no precipitate b. Potassium carbonate, K₂CO3, and barium chloride, BaCl₂ O Rule 6: Most carbonate salts are only slightly soluble; K₂CO3(aq) + BaCl₂ (aq) → BaCO3(s) + 2KCl(aq) O Rule 6: exeption to rule for carbonates; 2K₂CO3(aq) + BaCl₂ (aq) → BaCO3(s) + 2KCl(aq) O Rule 6: Most carbonate salts are only slightly soluble; K₂CO3(aq) + BaCl₂ (aq) → BaCO3(aq) + 2KCl(aq) O Rule 6: Most carbonate salts are only slightly soluble; K₂CO3(aq) + BaCl2 (aq) → BaCO3 (8) + KCl(aq) c. Sodium sulfate, Na2SO4, and barium nitrate, Ba(NO3)2 O Rule 4: an exception to the rule for sulfates; Na₂SO4 (aq) +…arrow_forward
- Acetic acid has a Ka value of 1.8×105, what is its Kb value? Section а. 5.6×10-10 b. 1.8×10-19 c. 5.6×10-5 d. 1.8×10° С. Sectionarrow_forwardhelp me pleasearrow_forward(d) For the following reaction: OH Na O a. draw the products and label the acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate base with pk, values b. show your work for calculating the Kea of the reaction in the forward directionarrow_forward
- Solve correctly please. (Gpt/Ai wrong answer not allowed)arrow_forwardCalculate the pką of an acid with Ka = 7.77 x 10-4. %3D O A. 2.230 О в. 3.110 O C. 4.147 D. 7.160 O E. 10.089arrow_forwardShop Trendy CHEM 1032Cengage S19 34 https://ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/evo/index.html?elSBN-9781305657571 &id-430934266&isnapshotld-10652508 s19 3.4 Cengage MInbox (112) DTAP Q Search this course L ions Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. The rate constant of the elementary reaction H2(g) +Br2(g) 2HBr(g) is k 4.45x10 L mol s at 250°C, and the reaction has an activation energy of 170 kJ mol (a) Compute the rate constant of the reaction at a temperature of 289°C L mol , 1 (b) After e (b) After equal concentrations of H, and Bry are mixed at 250o C, 6,03 10' s is required for half of them to be consumed. How long will itke to consume half of the reactants if an identical experiment is performed at 289°C? Submit Answer 3 question attempts remaining Autosaved at 9:31 AM Back 9:31 2/28arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY