
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
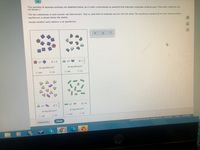
Transcribed Image Text:Tiny samples of aqueous solutions are sketched below, as if under a microscope so powerful that individual molecules could be seen. (The water molecules are
not shown.)
The two substances in each sample can interconvert. That is, each kind of molecule can turn into the other. The equilibrium constant K for each interconversion
equilibrium is shown below the sketch.
Decide whether each solution is at equilibrium.
K=4
K =
At equilibrium?
At equilibrium?
O yes
O no
O yes
O no
K=-
K= 9
At equilibrium?
At equilibrium?
O yes
O no
O yes
O no
Explanation
Check
0 2021 McGrawH Education Al Rights Reserved. Terms of Use I Pvacy I Accessibility
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following equilibrium system at 355 K. 2NOBr(g) -----> 2NO(g)+Br2(g). If an equilibrium mixture of the three gases at 355 K contains 3.21x10^-2 M NOBr, 2.01x10^-2 M NO,and 3.98x10^-2 M Br2 what is the value of the equilibrium constant Karrow_forward8) Consider the system below. When equilibrium is restored, how will the number of each type of molecule and the concentration of each substance compare to those before the stress was introduced? Complete the following table using the words "decrease," "same," or "increase." 2 NH,(g) = N,(g) + 3 H,(g) AH = 92.4 kJ/mol Decrease Volume Decrease Temperature N, Equilibrium Concentration Н, NH, N, Equilibrium Number Н, NH,arrow_forwardA gaseous mixture contains 0.27 mol CO, 0.12 mol H2, and 0.022 mol H,O, plus an unknown amount of CH4, in each liter. This mixture is at equilibrium at a certain temperature. CO(9) + 3H, (9) = CH4 (9) + H,O(9) What is the concentration of CH4 in this mixture? The equilibrium constant K, equals 3.99.arrow_forward
- At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant K for the following reaction is ×2.0510−7 : Br2g + OCl2g BrOCl g+BrClg Use this information to answer the following question. What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Round your answer to 3 significant digits. K= 3Br2 (g) +3OCl2 (g) 3BrOCl (g) +3BrCl (garrow_forwardFor the chemical equation 2SO2(g) + NO2(g) 2SO3(g) + NO(g) The equilibrium constant at a certain temperature is 5.50. At this temperature, calculate the number of moles of NO2(g) that must be added to 1.20 mol SO2(g) in order to form 0.80 mol SO3(g) at equilibrium.arrow_forwardTrue/False. Explain your answer in one sentence or less. In an equilibrium process, the concentrations of products and of reactants are equal. The value of the equilibrium constant for a given reaction depends on the initial concentrations of reactants. Large value for equilibrium constant K means the reaction will be less complete at the equilibrium point. The concentration of a pure solid is left out of an equilibrium constant expression but a pure liquid is included.arrow_forward
- Consider the combustion of methane (as represented by the following equation). This is the reaction that occurs for a Bunsen burner, which is a source of heat for chemical reactions in the laboratory. CH 4(9) +20 2(g) =CO2(g) + 2H 20(g) For the system at chemical equilibrium, which of the following explains what happens if the temperature is reduced? O a. The equilibrium position is shifted to the left and the value for K increases. O b. The equilibrium position is shifted to the right and the value for K increases. O c. The equilibrium position is shifted to the right and the value for K decreases. O d. The equilibrium position is shifted but the value for K stays constant. Oe. The equilibrium position is shifted to the left and the value for K decreases.arrow_forwardA chemist is studying the following equilibirum, which has the given equilibrium constant at a certain temperature: 2 CH₂(g)3H₂(g) + C₂H₂ (g) K₂=6. x 108 He fills a reaction vessel at this temperature with 11. atm of methane gas. Use this data to answer the questions in the table below. Can you predict the equilibrium pressure of H₂, using only the tools available to you within ALEKS? If you said yes, then enter the equilibrium pressure of H₂ at right. Round your answer to 1 significant digit. yes no at atm x10 Xarrow_forwardConsider the equilibrium system described by the chemical reaction below. Determine the concentration of O, at equilibrium by writing the equilibrium constant expression and solving it. Complete Parts 1-2 before submitting your answer. = 2 H₂O(g) 2 H2(g) + O̟₂(g) 1 2 NEXT At this temperature, the Kc = 2.4 × 103 and the equilibrium concentrations of H2O and H2 are 0.11 M and 0.019 M, respectively. If [x] represents the equilibrium concentration of O2, set up the equilibrium expression for Kc to solve for the concentration. Each reaction participant must be represented by one tile. Do not combine terms. Кс = 2' = 2.4 × 103 > RESET [0.11] [0.019] 2[0.11] 2[0.019] [0.11]² [0.019]² [x] [x]² [2x] [2x]²arrow_forward
- A chemist is studying the following equilibirum, which has the given equilibrium constant at a certain temperature: N2(g) + 2H2O(g) 2 NO(g) + 2 H2(g) K=2.x 10 -10 He fills a reaction vessel at this temperature with 6.0 atm of nitrogen gas and 11. atm of water vapor. Use this data to answer the questions in the table below. Can you predict the equilibrium pressure of H2, using only the tools available to you within ALEKS? ○ yes x10 O no If you said yes, then enter the equilibrium pressure of H₂ at right. Round your answer to 1 significant digit. atm 5arrow_forward1. What conditions of temperature and pressure favor products in the following reaction: PCl5(g) ⇌ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) ΔH = 238 kJ/mol 2. Consider the system below. When equilibrium is restored, how will the number of each type of molecule and the concentration of each substance compare to those before the stress was introduced? Complete the following table using the words “decrease,” “same,” or “increase.” 2 NH3(g) ⇌ N2(g) + 3 H2(g) ΔH = 92.4 kJ/mol Decrease Volume Decrease Temperature Equilibrium Concentration N2 H2 NH3 Equilibrium Number N2 H2 NH3 3. Nitric acid is produced commercially by the Ostwald process. The first step of the Ostwald process is: 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2(g) ⇌ 4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g) + energy In which direction will the above system shift in the following situations: 3. (a) Some NO is added.arrow_forwardCalculating an equilibrium constant from a partial equilibrium.. Sulfur dioxide and oxygen react to form sulfur trioxide during one of the key steps in sulfuric acid synthesis. An industrial chemist studying this reaction fills a 2.0 L flask with 3.9 atm of sulfur dioxide gas and 0.74 atm of oxygen gas, and when the mixture has come to equilibrium measures the partial pressure of sulfur trioxide gas to be 1.2 atm. Calculate the pressure equilibrium constant for the reaction of sulfur dioxide and oxygen at the final temperature of the mixture. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K, = [ %3D do x10 Ar Eplanation Check O 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accessibility FEB tv 23 30 MacBook Air DII DD F12 F11 F10 F9 80 888 F8 F7 F5 F6 F4 F3 esc F2 F1 $ % @ 8. 3 4 5 6 2 Uarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY