
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:이6
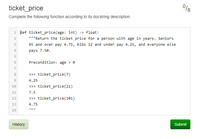
ticket_price
Complete the following function according to its docstring description.
1 def ticket_price(age: int) -> float:
"""Return the ticket price for a person with age in years. Seniors
65 and over pay 4.75, kids 12 and under pay 4.25, and everyone else
4
pays 7.50.
6.
Precondition: age > e
7
8.
>>> ticket_price(7)
9.
4.25
10
>> ticket_price(21)
11
7.5
12
>>> ticket_price(101)
13
4.75
14
History
Submit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Dice_Game.cpp #include <iostream>#include "Die.h" using namespace std; // a struct for game variablesstruct GameState { int turn = 1; int score = 0; int score_this_turn = 0; bool turn_over = false; bool game_over = false; Die die;}; // declare functionsvoid display_rules();void play_game(GameState&);void take_turn(GameState&);void roll_die(GameState&);void hold_turn(GameState&); int main() { display_rules(); GameState game; play_game(game);} // define functionsvoid display_rules() { cout << "Dice Game Rules:\n" << "\n" << "* See how many turns it takes you to get to 20.\n" << "* Turn ends when you hold or roll a 1.\n" << "* If you roll a 1, you lose all points for the turn.\n" << "* If you hold, you save all points for the turn.\n\n";} void play_game(GameState& game) { while (!game.game_over) { take_turn(game); } cout << "Game…arrow_forwardPrototype and functional call pleasearrow_forwardCodingarrow_forward
- Use C++ codingNested Structures: Define a structure for Student containing information about name, roll number, address. The Address is itself another structure containing house no., street no., sector no., phase no., city name. Using arrays declare two addresses for the student: one address is for temporary address and second one is for permanent address. Declare one student structure variable and using pointer to this structure variable take input from the user to enter the information about the student.arrow_forwardThe rules that apply to functions that have default arguments should be described.arrow_forwardC# program in Visual Studio Code. I need to be able to enter five integer values and then have the Unique values entered display. Private member variable to store 5 unique values (hint: use an Array or a List) Public function to get 5 unique values from the user and store them in the member variable loop to get the numbers, if a number is already stored, ignore it and keep looping until you have 5 unique numbers if a number is out of range, don't store the value, throw an exception and handle it in such a way that you don't break the loop but do message the user that the value was out of rangearrow_forward
- 10. When using a std::vector, what values do we expect to get from the size and empty member functions after calling the clear member function? Complete the table below with the expected values. member function value after donations.clear() donations.size() donations.empty()arrow_forwardWrite in c language please: write a statement that calls the function IncreaseItemQty with parameters computerInfo and addStock. Assign computerInfo with the returned value. #include <stdio.h> typedef struct ProductInfo_struct { char itemName[50]; int itemQty;} ProductInfo; ProductInfo IncreaseItemQty(ProductInfo productToStock, int increaseValue) { productToStock.itemQty = productToStock.itemQty + increaseValue; return productToStock;} int main(void) { ProductInfo computerInfo; int addStock; scanf("%s", computerInfo.itemName); scanf("%d", &computerInfo.itemQty); scanf("%d", &addStock); /* Your code goes here */ printf("Name: %s, stock: %d\n", computerInfo.itemName, computerInfo.itemQty); return 0;} thank you in advancearrow_forwardIt is necessary to outline the regulations that apply to functions with default parameters.arrow_forward
- Whether or not the order in which parameters are specified when invoking a function that accepts multiple arguments is critical.arrow_forwardQ1: Research Groups In response to popular demand, Dan’s established two research groups A and B composed of his n graduate students. Each of these students is a member of exactly one of the two groups at any given time. The students are numbered from 1 to n in some arbitrary order. To measure the success of his research groups, Dan assigns a citation score to each of them. Initially, both groups have citation score 0. Throughout the semester, events of the following two types happen: Student x publishes a paper in which they cite student y’s work (youcan assume all of the students have been around long enough to have prior research that can be cited). As a result, If x and y are in the same group, their group’s citation score increases by 1. If x and y are in different groups, y’s group’s citation score increases by 5. Dan changes student x’s group (from A to B or from B to A) to have them work on different projects. To assess the overall success of the research groups, Dan…arrow_forwardGame of Hunt in C++ language Create the 'Game of Hunt'. The computer ‘hides’ the treasure at a random location in a 10x10 matrix. The user guesses the location by entering a row and column values. The game ends when the user locates the treasure or the treasure value is less than or equal to zero. Guesses in the wrong location will provide clues such as a compass direction or number of squares horizontally or vertically to the treasure. Using the random number generator, display one of the following in the board where the player made their guess: U# Treasure is up ‘#’ on the vertical axis (where # represents an integer number). D# Treasure is down ‘#’ on the vertical axis (where # represents an integer number) || Treasure is in this row, not up or down from the guess location. -> Treasure is to the right. <- Treasure is to the left. -- Treasure is in the same column, not left or right. +$ Adds $50 to treasure and no $50 turn loss. -$ Subtracts…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education