Question
thumb_up100%
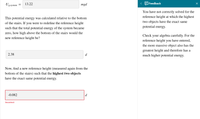
Now, find a new reference height (measured again from the bottom of the stairs) such that the highest two objects have the exact same potential energy.
The answer was not 0.082 or the negative of that, I tried both and no luck. Both were marked wrong.
Transcribed Image Text:13.22
mgd
< Feedback
´g,system
You have not correctly solved for the
reference height at which the highest
This potential energy was calculated relative to the bottom
of the stairs. If you were to redefine the reference height
two objects have the exact same
potential energy.-
such that the total potential energy of the system became
zero, how high above the bottom of the stairs would the
Check your algebra carefully. For the
new reference height be?
reference height you have entered,
the more massive object also has the
greatest height and therefore has a
much higher potential energy.
2.38
d
Now, find a new reference height (measured again from the
bottom of the stairs) such that the highest two objects
have the exact same potential energy.
-0.082
d
Incorrect

Transcribed Image Text:Three different objects, all with different masses, are
initially at rest at the bottom of a set of steps. Each step is
of uniform height d. The mass of each object is a multiple
of the base mass m: object 1 has mass 3.10m, object 2 has
mass 1.46m, and object 3 has mass m. When the objects
are at the bottom of the steps, define the total gravitational
potential energy of the three-object system to be zero. If
the objects are then relocated as shown, what is the new
total potential energy of the system?
d
Each answer requires the numerical coefficient to an
3
algebraic expression. Each algebraic expression is given
using some combination of the variables m, g, and d,
where g is the acceleration due to gravity. Enter only the
numerical coefficient. (Example: If the answer is 1.23mgd,
just enter 1.23)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- In the figure, a frictionless roller coaster car of mass m = 992 kg tops the first hill with speed v0 = 16.7 m/s at height h = 40.7 m. How much work does the gravitational force do on the car from that point to (a) point A, (b) point B, and (c) point C? If the gravitational potential energy of the car-Earth system is taken to be zero at C, what is its value when the car is at (d) B and (e) A? I know the first one is 0 J.arrow_forwardA 9.00-kg particle moves from the origin to position ©, having coordinates x = 4.50 m and y = 4.50 m as shown in the figure. One force on the particle is the gravitational force acting in the negative y direction. Using the equation (W = FAr cos e = F . Ař), calculate the work done by the gravitational force in going from O to © along the following paths. у (m) C) (x, y) х (m) (a) the purple path (o0© (b) the red path (OB© (c) the blue path (O© (d) Your results should all be identical. Why?arrow_forwardIn the figure, a frictionless roller coaster car of mass m - 992 kg tops the first hill with speed vo- 11.9 m/s at heighth-47.0 m. How much work does the gravitational force do on the car from that point to (a) point A, (b) point B, and (c) point C? If the gravitational potential energy of the car-Earth system is taken to be zero at C, what is its value when the car is at (d) Band (e) A? Firstarrow_forward
- A cat's crinkle ball toy of mass 28 g is thrown straight up with an initial speed of 5 m/s. Assume in this problem that air drag is negligible. (a) What is the kinetic energy of the ball (in J) as it leaves the hand? (b) How much work is done (in J) by the gravitational force during the ball's rise to its peak? (c) What is the change in the gravitational potential energy of the ball (in J) during the rise to its peak? (d) If the gravitational potential energy is taken to be zero at the point where it leaves your hand, what is the gravitational potential energy (in J) when it reaches the maximum height? (e) If the gravitational potential energy is taken to be zero at the maximum height the ball reaches, what would the gravitational potential energy (in J) be when it leaves the hand? (f) What is the maximum height the ball reaches (in m)? marrow_forwardA particle moves along a curved path y(x) = (10 m){1+cos[(0.1 m−1)x]} , from x = 0 to x = 10π m, subject to a tangential force of variable magnitude F(x) = (10 N)sin[(0.1 m−1)x]. How much work does the force do? (Hint: Consult a table of integrals or use a numerical integration program.)arrow_forwardYou drop a 2.50 kg book to a friend who stands on the ground at distance D-13.0 m below. If your friend's outstretched hands are at distance d-1.60 m above the ground (see the figure), (a) how much work W, does the gravitational force do on the book as it drops to her hands? (b) What is the change AU in the gravitational potential energy of the book-Earth system during the drop? If the gravitational potential energy U of that system is taken to be zero at ground level, what is U (c) when the book is released and (d) when it reaches her hands? Now take U to be 100 J at ground level and again find (e) W. (f) AU, (g) U at the release point, and (h) U at her hands. 10000 Elarrow_forward
- A cat's crinkle ball toy of mass 15 g is thrown straight up with an initial speed of 3 m/s. Assume in this problem that air drag is negligible. (a) What is the kinetic energy of the ball as it leaves the hand? (b) How much work is done by the gravitational force during the ball's rise to its peak? (c) What is the change in the gravitational potential energy of the ball during the rise to its peak?arrow_forwardYou go for a walk one afternoon down a level street to a park where there is a hill. If the hill is 62 meters above street level and 4.6 km from home , how much work in the physics sense do you do in order to get to the top of the hill? Assume your mass is 65 kg and the acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s. Give your answer in joules (J).arrow_forwardA tennis ball of mass m = 0.091kg is thrown straight up with an initial speed v_{0} = 14m / s Let the gravitational potential energy be zero the initial height of the tennis ball a.what is the maximum height , h in meters the ball reaches B. What is the work done by gravity W_{g} Joules, during the ball's flight to its maximum height?arrow_forward
- A dock worker pushes am = 2.20 kg bin a distance d = 2.40 m along the floor by a constant force of magnitude F = 16.0 N directed at an angle 0 = 20.0° below the horizontal as shown in the figure. Assume the floor is frictionless. (Enter your answers in joules.) (a) Determine the work done on the bin by the applied force (the force on the bin exerted by the dock worker). (b) Determine the work done on the bin by the normal force exerted by the floor. (c) Determine the work done on the bin by the gravitational force. (d) Determine the work dong by the net force on the bin.arrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardProblem Thirteen. A potential energy function is given by U(r)=U2 where o = 2.00 m r r and U, = 1.00 J. Find the magnitude of the force at r= 1.00 m. Give an answer in kN. 25.) (A) 280 (В) 106 (С) 420 (D) 470 (E) 530arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios