
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
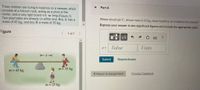
Transcribed Image Text:Three children are trying to balance on a seesaw, which
consists of a fulcrum rock, acting as a pivot at the
center, and a very light board 4.6 m long (Figure 1).
Two playmates are already on either end. Boy A has a
mass of 45 kg, and boy B amass of 35 kg.
Part A
Where should girl C, whose mass is 25 kg, place herself so as to balance the seesaw?
Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Figure
< 1 of 1
HA
Value
Units
Submit
Request Answer
m = 45 kg
m = 35 kg
< Return to Assignment
Provide Feedback
m 25 kg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A diver comes off a board with arms straight up and legs straight down, giving her a moment of inertia about her rotation axis of 18 kg-m². She then tucks into a small ball, decreasing this moment of inertia to 3.6 kg m². While tucked, she makes two complete revolutions in 1.0 s. Part A If she hadn't tucked at all, how many revolutions would she have made in the 1.7 s from board to water? Express your answer using two significant figures. 15] ΑΣΦ N= ? revarrow_forwardPlease answer it within 30 minutes. I will upvote!arrow_forwardA meter stick balances horizontally on a knife-edge at the 50.0 cm mark. With two 5.04 g coins stacked over the 18.2 cm mark, the stick is found to balance at the 41.8 cm mark. What is the mass of the meter stick? Number i Unitsarrow_forward
- Hello can somone please help me with part a,,b,c of this question. I've submitted it 2 times and waited for over 2 hours. thanks means alotarrow_forwardTwo identical 20.0-kg balls, each 25.3 cm in diameter, are suspended by two 35.0-cm wires as shown in the figure (Figure 1). The entire apparatus is supported by a single 18.0-cm wire, and the surfaces of the balls are perfectly smooth. Find the tension in the top wire. Find the tension in each of two bottom wires.arrow_forwardShown in the figure below is a system of two blocks. One of these blocks is resting on a surface tilted left and the other one is on a surface tilted right. The strings and the pulley have no mass. There is no friction anywhere in the problem.The characteristics of the system are given here: m1 = 4.14 kg m2 = 6.69 kg ?1 = 23.0 ?2 = 57.7 Answer all the following:What is the normal force, N1, on mass m1? What is the normal force, N2, on mass m2? What is the acceleration, a of the system? What is the tension, T?arrow_forward
- FA b b Pivot F, In the figure above, 4 forces of equal magnitude act on a uniform thin metal plate. The plate has a hinge (pivot) set up at one corner as shown. Rank the four forces in order, from the least amount of torque to the greatest amount of torque generated about the pivot point. Note: Dashed lines are merely drawing aids. F3, F2, F1, F4 F3, F1, F2, F4 F4, F3, F2, F1 F2, F1, F3, F4 F4, F3, F1, F2arrow_forwardPlease assist with question 2 with details on how to do it. Thank you.arrow_forwardDirections: Select the best answer for the following questions. Use g = 9.80 m/s? and assume all numbers are accurate to 3 significant figures unless otherwise indicated. 1. An 900 N billboard worker stands on a 3 m scaffold supported by vertical ropes at each end. If the scaffold weighs 400 N and the worker stands 1 m from one end, what is the tension in the two ropes that support the scaffold at either end?arrow_forward
- Three children are trying to balance on a seesaw, which consists of a fulcrum rock, acting as a pivot at the center, and a very light board 3.4 m long (Figure 1). Two playmates are already on either end. Boy A has a mass of 45 kg, and boy B a mass of 35 kg. ▼ Part A Where should girl C, whose mass is 25 kg, place herself so as to balance the seesaw? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. for Part A for Part Addo for Part redo for Part A reset for Part A keyboard shortcuts for Part A help for Part A x= Value Unitsarrow_forwardIn this assignment, the radius refers to the distance between the location where the force is applied and the axis of rotation. A ruler is initially at rest when a student briefly exerts a downward force on the right end, as shown. The magnitude of the force exerted by the student is less than the weight of the ruler. Assume that the pivot point is frictionless. Answer the following questions based on this description. Part A: 1. While the hand is pushing, but before the ruler begins to move, the tangential acceleration of the ruler is 2. While the hand is pushing, but before the ruler begins to move, the centripetal acceleration of the ruler is 3. While the hand is pushing, but before the ruler begins to move, the angular acceleration of the ruler is 4. At the instant the hand has stopped pushing, the tangential acceleration of the ruler is 5. At the instant the hand has stopped pushing, the centripetal acceleration of the ruler is 6. At the instant the hand has stopped pushing, the…arrow_forwardYou have a summer internship at NASA and are working on plans for a new space station to be launched into orbit around the Earth. The design of the space station is shown. i It is to be constructed in the shape of a hollow ring of mass 52,000 kg. The structures other than the ring shown in the figure have negligible mass compared to the ring. Members of the crew will walk on a deck formed by the inner surface of the outer cylindrical wall of the ring, with radius r = 140 m. The thickness of the ring is very small compared to the radius, so we can model the ring as a hoop. At rest when constructed, the ring is to be set rotating about its axis so that the people standing inside on this deck experience an effective free-fall acceleration equal to g. The rotation is achieved by firing two small rockets attached tangentially to opposite points on the rim of the ring. Your supervisor asks you to determine the following: (a) the time interval during which the rockets must be fired if each…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON