
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
This position time graph describes an object's motion. Use it to predict the position (in m) of the object at a time of 24.0 seconds.
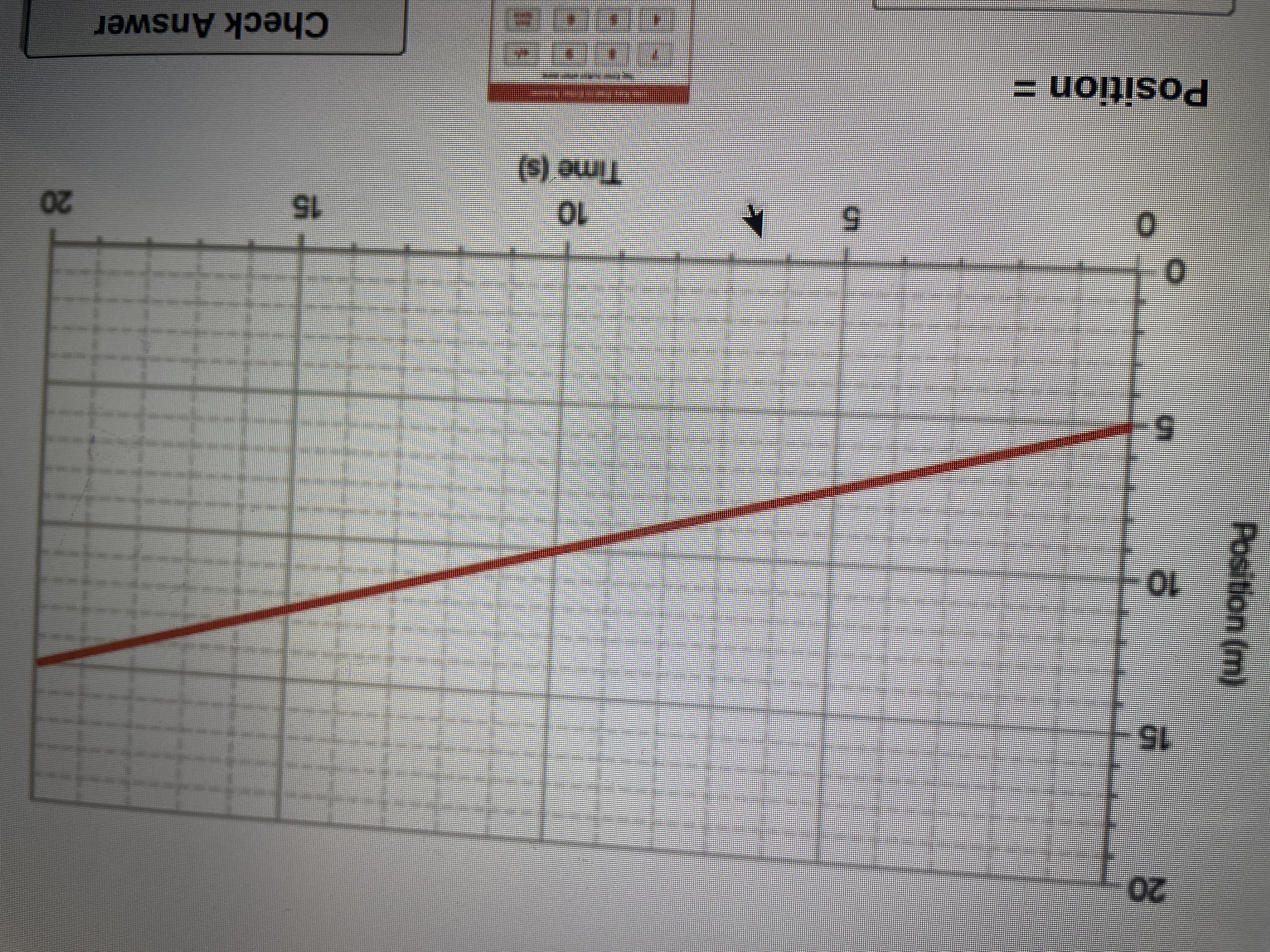
Transcribed Image Text:**Graph Description for Educational Website**
This image displays a line graph illustrating the relationship between position and time in an object's motion.
**Axes:**
- The x-axis represents time, measured in seconds (s), and ranges from 0 to 20 seconds.
- The y-axis represents position, measured in meters (m), and ranges from 0 to 20 meters.
**Graph Features:**
- The red line displays a linear, upward trend, indicating a constant velocity.
- At time \(t = 0\) seconds, the position starts at approximately 5 meters.
- The object steadily increases its position, reaching around 18 meters by 20 seconds.
This graph demonstrates the concept of constant velocity, where an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time.
**Interactive Components:**
- Beneath the graph, there is an input section labeled "Position = " for users to enter their calculations.
- A "Check Answer" button is visible, suggesting an interactive aspect for educational purposes.
This tool can be used in learning environments to teach concepts of linear motion and graph interpretation.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A pilot flies in a straight path for 1 h 30 min. She then makes a course correction, heading 10 degrees to the right of her original course, and flies 2 h in the new direction. If she maintains a constant speed of 660 mi/h, how far is she from her starting position? Your answer is _______________ mi Enter your answer rounded to two decimal places.arrow_forwardA ball is thrown straight down at 1.29 m/s and hits the ground 1.07 seconds later. How many meters did the ball travel before hitting the ground? Type your answer.arrow_forwardA cat is being chased by a dog. Both are running in a straight line at constant speeds. The cat has a head start of 3.8 m. The dog is running with a speed of 9.1 m/s and catches the cat after 6.6 s. How fast did the cat run? m/sarrow_forward
- A physics teacher walks 5 km East, 2.5 km South, 5 km West, and finally 2.5 km North. The entire motion lasted for 3 hours. Determine the average speed and the average velocity.arrow_forwardAn Australian magpie (Gymnorhina tibicen) flies 53 m south and then 47 m west, in a total time of 35 minutes. What is its displacement from the starting position? Enter only the numerical part of your answer (in m) to the nearest integer.arrow_forwardChapter 02, Problem 10 In reaching her destination, a backpacker walks with an average velocity of 1.26 m/s, due west. This average velocity results, because she hikes for 6.62 km with an average velocity of 2.54 m/s due west, turns around, and hikes with an average velocity of 0.381 m/s due east. How far east did she walk (in kilometers)? dw VE West East dɛ Number Units the tolerance is +/-2% Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Workarrow_forward
- 1) You recorded your position with respect to the front door of your house as you walked to the mailbox. Examine the data presented in the table provided in the book and answer the following questions: (a) What instruments might have you used to collect data? (b) Represent your motion using a position-versus-time graph. (c) Tell the story of your motion in words. (d) Show on the graph the displacement, distance, and path length.arrow_forwardTwo kids are racing towards a toy somewhere between them. Albert has 3.90 times further to run than Betty. Albert is to the West of the toy and Betty is to the East of the toy. Albert runs at a constant speed of 1.60 m/s. It takes him 2.90 s to reach the toy.How far did Albert run to reach the toy?arrow_forward(a) Calculate the height (in m) of a cliff if it takes 2.30 s for a rock to hit the ground when it is thrown straight up from the cliff with an initial velocity of 8.07 m/s. (Enter a number.) m (b) How long (in s) would it take to reach the ground if it is thrown straight down with the same speed? (Enter a number.) s †arrow_forward
- An airplane flies eastward and always accelerates at a constant rate. At one position along its path, it has a velocity of 34.9 m/s . It then flies a further distance of 49300 m , and afterwards, its velocity is 42.7 m/s . Find the airplane's acceleration. acceleration: Calculate how much time elapses while the airplane covers those 49300 m. elapsed time:arrow_forwardSome experimental researcher tells us that the position of an object as a function of time is given by x(t) = at3 - bt2 + ct - d, where the constants are a = 3.6 m/s3, b = 4.0 m/s2, c = 60 m/s and d = 7.0 m. Find the average acceleration over the first 2.4 seconds. A) 18 m/s/s B) 54 m/s/s C)36 m/s/s D) 76 m/s/sarrow_forwardFor the following function models the position s(t)s(t) of an object moving along a stright line, where tt is in seconds and ss is in meters. s(t)=t2-6t Find the simplified expression for the average velocity from t=7t=7 to t=7+ht=7+h. s(t+h)-s(t)/h=?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON