
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
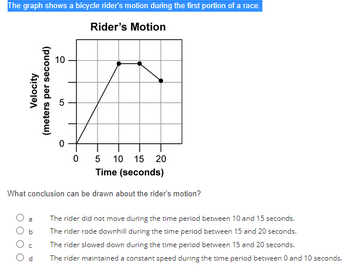
Transcribed Image Text:The graph shows a bicycle rider's motion during the first portion of a race.
Rider's Motion
Velocity
(meters per second)
b
с
10
#
05 10 15 20
Time (seconds)
What conclusion can be drawn about the rider's motion?
d
10
0
The rider did not move during the time period between 10 and 15 seconds.
The rider rode downhill during the time period between 15 and 20 seconds.
The rider slowed down during the time period between 15 and 20 seconds.
The rider maintained a constant speed during the time period between 0 and 10 seconds.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3.) graph is given. The following position -vs- time +40 +30 Position +20 x (m) +10 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Time t(s) A.) Determine the instantaneous velocity at t = 2 s. B.) velocity at t = 16 s. C.) Determine the instantaneous Draw a velocity -vs-time graph.arrow_forwardH4.arrow_forwardHicham El Guerrouj of Morocco holds the world record in the 1500 m running race. He ran the final 400 m in a time of 51.9 s. What was his average speed in mph over the last 400 m?A. 14.2 mph B. 15.5 mphC. 17.2 mph D. 23.9 mpharrow_forward
- Help me pleasearrow_forwardA swimmer pushes off a wall from rest where she has a constant acceleration of 2m/s2 for 1.5 seconds. She then continues for 10 seconds at constant velocity. At this point, a) How far away from the wall is she if the pool is 50m? b) If she then glides to a stop, what was her deceleration rate? c) Draw the position verse time graph, velocity verse time graph, and acceleration verse time graph. You can assume all accelerations are constant. d) Now take your velocity verse time graph and re calculate the distance covered by the swimmer.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements are true regarding velocity-time graphs?I. The slope of a velocity-time graph is acceleration. II. The graph has a slope of zero if the object is at rest. III. A line with negative slope indicates that the object is slowing down.arrow_forward
- x (m) 100 50 t (s) 40 10 20 30 Gyge Pearson Ecton inc.pubting A graph of position versus time for a certain object moving along the x-axis is shown on the graph. a. Find the object's velocity in the time interval from 0 s to 20 s. S b. Find the object's velocity in the time interval from 30 s to 40 s.arrow_forwardAn object moves so that its position depends on time as x=−10m+(5m/s)t+(2.5m/s2)t2. Which statement below is not true? a) The object never stops moving. b) The object first moves in the negative direction and then in the positive direction c) The object is accelerating d) The speed of the object is always increasing Which answer is correct and why?arrow_forwardA car traveling at an initial speed of 16 m/s to the left (negative direction) slows down to a speed of 4.0 m/s (still moving to the left) over a distance of 40.0 m. 1) What is the acceleration? Is it positive or negative? 2) How much time went by? 3) What is the car's average velocity during this time?arrow_forward
- Two books are on a shelf 1.3 m from one another. Book A has a mass of 2.2 kg. Book B hasa mass of 1.7 kg. A very naughty student sees the books while walking by. She tears somepages out of book A so that its new mass is 2.0 kg and sets it back on the same spot on theshelf.What effect does this have on the gravitational force between the books.AThe gravitational force increases because the mass of one book decreases.BThe gravitational force remains constant because the books remain in the same place.CThe gravitational force on book B decreases because the mass of book A decreases.DThe gravitational force on both books decreases because the mass of book A decreases.arrow_forwardA sprinter reaches his maximum speed in 2.6 seconds from rest with constant acceleration. He then maintains that speed and finishes the 100 yards in the overall time of 10.02 seconds. Determine his maximum speed Vmax- t = 0 - 100 yd t = 2.6 sec t = 10.02 secarrow_forwardThe position vs. time graph for an object is shown here. Is the object's acceleration positive, negative, or zero? 10 ne (s) O negative zero O positive It is impossible to tell w) udgsodarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON