
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
This diagram shows an animal cell in meiosis I during crossing over and synapsis. A single tetrad is shown with a pair of homologous chromosomes that have been duplicated as sister chromatids. Red chromosomes indicate maternal DNA, and blue chromosomes indicate paternal DNA.
Use the passage to answer the question.
Once the animal cell has completed meiosis II:
-
A.
half of the gametes will contain recombinant chromosomes.
-
B.
none of the gametes will contain recombinant chromosomes.
-
C.
all of the gametes will contain maternal DNA.
-
D.
all of the gametes will contain paternal DNA.
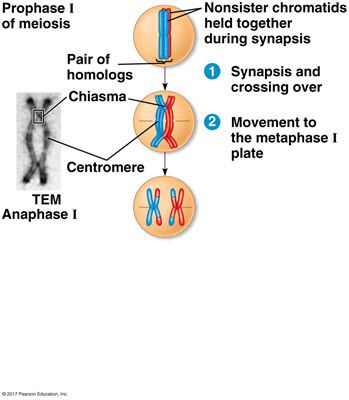
Transcribed Image Text:Title: Meiosis and Chromatid Behavior
**Diagram Explanation:**
The image illustrates key stages and structures involved during prophase I of meiosis and their transition to metaphase I. Here's a detailed breakdown:
1. **Prophase I of Meiosis:**
- This is the initial stage where homologous chromosomes pair up.
2. **Pair of Homologs:**
- Homologous chromosomes, or "homologs," align with each other.
3. **Chiasma:**
- The diagram highlights a chiasma, which is the point where homologs exchange genetic material through crossover.
4. **Centromere:**
- This is the constricted region of a chromosome that holds sister chromatids together.
5. **Nonsister Chromatids Held Together During Synapsis:**
- Synapsis is the process where homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange segments. Nonsister chromatids are parts involved in crossing over.
6. **TEM Anaphase I:**
- The Transmission Electron Micrograph (TEM) provides a detailed view of the chromosome structure during Anaphase I.
**Processes:**
1. **Synapsis and Crossing Over:**
- During this step, homologous chromosomes come together in a process called synapsis, allowing nonsister chromatids to exchange genetic material.
2. **Movement to the Metaphase I Plate:**
- Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate, preparing for the subsequent separation during Anaphase I.
This diagram provides a visual understanding of the physical and genetic interactions during the early stages of meiosis, crucial for genetic diversity.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The gamete is called a (n): The process of gamete production is called: The diploid reproductive cell destined to become a gamete is a (n): Gamete production occurs in the: Number of viable gametes produced per meiotic division: MALE 8. Explain how independent assortment leads to genetic diversity. 9. Explain why crossing over is observed in meiosis but not in mitosis. FEMALEarrow_forwardUse the following information as the basis for answering all questions: A diploid eukaryotic organism has 4 unique chromosomes. Chromosome I is metacentric, chromosome II is telocentric, chromosome III is a submetacentric, and chromosome IV is acrocentric. 16. How many total chromosomes are in a germ cell in the ovary of this organism that is in Metaphase of Meiosis I? 17. How many total chromatids are in a germ cell in the ovary of this organism that is in Metaphase of Meiosis I? 18. How many total telomeres are in a germ cell in the ovary of this organism that is in Metaphase of Meiosis I?19. How many total chromosomes are in a germ cell in the ovary of this organism that is in Anaphase of Meiosis I? 20. How many total chromatids are in a germ cell in the ovary of this organism that is in Anaphase of Meiosis I? 21. How many total telomeres are in a germ cell in the ovary of this organism that is in Anaphase of Meiosis I?arrow_forwardThese pictures represent cells in 2 different phases of meiosis. What are the differences between these 2 cells? Select all correct statements. Select ALL that apply: A. in 1, homologous chromosomes are being pulled apart, in the other sister chromatids are being pulled apart B. in one the sister chromatids are still attached, in the other they are not. C. 1 is in anaphase and 1 in metaphase D. following 1, you will get haploid cells but following the other you will still have diploid cells E. 1 contains homologous pairs the other does notarrow_forward
- Imagine a precursor germ cell (which will become a sperm or egg cell) from a diploid organism. Before the cell undergoes meiosis, it has a total of 40 chromosomes. Which of the following are true for this cell? Select all that apply The value of n is 40 After the first meiotic division, the cells will be haploid After the second meiotic division, there will be four cells When meiosis is complete, the sperm/egg will have 20 chromosomesarrow_forwardThe diploid number of chromosomes in the mustard plant, Arabidopsis thaliana, is 10. Knowing this, answer the following questions about the stages of mitosis.How many chromosomes will be found in each cell during prophase?arrow_forwardChoose the phase of meiosis in column 2 that best matches each event in column 1. one haploid set of replicated chromosomes at each spindle pole genetic recombination events take place shortest stage aligning of bivalents in the center of a spindle one haploid set of unreplicated chromosomes at each spindle pole aligning of monovalents in the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education