
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course List)
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781305627734
Author: Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. Anderson
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
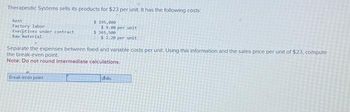
Transcribed Image Text:Therapeutic Systems sells its products for $23 per unit. It has the following costs
Rent
Factory labor
Executives under contract
Raw material
$ 195,000
$9.00 per unit
$365,500
$ 2.20 per unit
Separate the expenses between fixed and variable costs per unit. Using this information and the sales price per unit of $23, compute
the break-even point.
Note: Do not round intermediate
calculations.
Break-even point
hits
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Grand Canyon Manufacturing Inc. produces and sells a product with a price of 100 per unit. The following cost data have been prepared for its estimated upper and lower limits of activity: Overhead: Selling and administrative expenses: Required: 1. Classify each cost element as either variable, fixed, or semi-variable. (Hint: Recall that variable expenses must go up in direct proportion to changes in the volume of activity.) 2. Calculate the break-even point in units and dollars. (Hint: First use the high-low method illustrated in Chapter 4 to separate costs into their fixed and variable components.) 3. Prepare a break-even chart. 4. Prepare a contribution income statement, similar in format to the statement appearing on page 540, assuming sales of 5,000 units. 5. Recompute the break-even point in units, assuming that variable costs increase by 20% and fixed costs are reduced by 50,000.arrow_forwardRooney Company produces a product that sells for $36 per unit and has a variable cost of $12 per unit. Rooney incurs annual fixed costs of $151,200. Required a. Determine the sales volume in units and dollars required to break even. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. b. Calculate the break-even point assuming fixed costs increase to $235,200. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. a. Sales volume in units a. Sales in dollars b. Break-even units b. Break-even salesarrow_forwardGibson Company produces a product that sells for $29 per unit and has a variable cost of $11 per unit. Gibson Incurs annual fixed costs of $97,200. Required a. Determine the sales volume in units and dollars required to break even. Note: Do not round Intermediate calculations. b. Calculate the break-even point assuming fixed costs Increase to $160,200. Note: Do not round Intermediate calculations. a. Sales volume in units a. Sales in dollars b. Break-even units b. Break-even salesarrow_forward
- Brissett Corporation makes three products that use the current constraint, which is a particular type of machine. Data concerning those products appear below: GK LQ XK Selling price per unit $ 326.11 $ 543.37 $ 519.00 Variable cost per unit $ 252.05 $ 420.86 $ 397.71 Time on the constraint (minutes) 4.00 8.00 8.00 Required: a. Rank the products in order of their current profitability from the most profitable to the least profitable. In other words, rank the products in the order in which they should be emphasized. b. Assume that sufficient constraint time is available to satisfy demand for all but the least profitable product. Up to how much should the company be willing to pay to acquire more of the constrained resource? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) A. GK LG QX B. Maximun Amountarrow_forwardYeti sells a product for $560, variable cost per unit of $330, and total fixed costs of $262,890. Compute break-even sales in units and in sales dollars. (Do not use commas or dollar signs in your responses.) Break-even point (in units) units Break-even point (in dollars) $arrow_forwardCrane Manufacturing Ltd. has provided you with the following CVP income statement. Sales (1,460 units) Variable costs: Cost of goods sold Selling expenses Administrative expenses Contribution margin Fixed costs: Cost of goods sold Selling expenses Administrative expenses Operating income $1,022,000 454,060 81,760 67,160 419, 20 153,300 52,560 33,580 $179,580 a. Calculate the contribution margin ratio. b. Calculate the break-even point in sales dollars and number of units.arrow_forward
- Brissett Corporation makes three products that use the current constraint, which is a particular type of machine. Data concerning those products appear below: GK LQ XK Selling price per unit $ 326.09 $ 543.35 $ 518.00 Variable cost per unit $ 252.04 $ 420.85 $ 397.70 4.10 8.10 8.00 Time on the constraint (minutes) Required: 1. Rank the products in order of their current profitability from the most profitable to the least profitable. In other words, rank the products in the order in which they should be emphasized. 2. Assume that sufficient constraint time is available to satisfy demand for all but the least profitable product. Up to how much should the company be willing to pay to acquire more of the constrained resource? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardPlease do not give solution in image format ?.arrow_forwardS Munoz Corporation sells products for $44 each that have variable costs of $19 per unit. Munoz's annual fixed cost is $560,000. Required Use the per-unit contribution margin approach to determine the break-even point in units and dollars. Break-even point in units Break-even point in dollars Marrow_forward
- Analyzing Income under Absorption and Variable Costing Variable manufacturing costs are $86 per unit, and fixed manufacturing costs are $193,200. Sales are estimated to be 6,900 units. If an amount is zero, enter "0". Round intermediate calculations to the nearest cent and your final answers to the nearest dollar. a. How much would absorption costing operating income differ between a plan to produce 6,900 units and a plan to produce 9,200 units? X b. How much would variable costing operating income differ between the two production plans? ✓arrow_forwardShock Electronics sells portable heaters for $49 per unit, and the variable cost to produce them is $29. Ms. Amps estimates that the fixed costs are $100,800. a. Compute the break-even point in units. Break-even point b. Fill in the following table (in dollars) to illustrate that the break-even point has been achieved. Sales Fixed costs Total variable costs Net profit (loss) units $ 0arrow_forwardJamison Company uses the total cost method of applying the cost-plus approach to product pricing. Jamison produces and sells Product X at a total cost of $800 per unit, of which $540 is product cost and $260 is selling and administrative expenses. In addition, the total cost of $800 is made up of $460 variable cost and $340 fixed cost. The desired profit is $168 per unit. Determine the markup percentage on total cost. %arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning

Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305627734
Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. Anderson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Cengage Learning