The voltages v1, V2, V3, and v4 are the node voltages corresponding to nodes 1, 2, 3, and 4 in the below Figure. The value of node voltage vị is 25 V. Determine the values of v2, V3, and v4 node voltages. 10 2 3ip 20 2 b 25 V Va 30 2 2 A

In general, in a N node circuit, one of the nodes is chosen as reference or datum node, then it is possible to write N-1 model equations by assuming N-1 node voltages. We assume zero potential for the reference node. Let us take an example to illustrate the method.
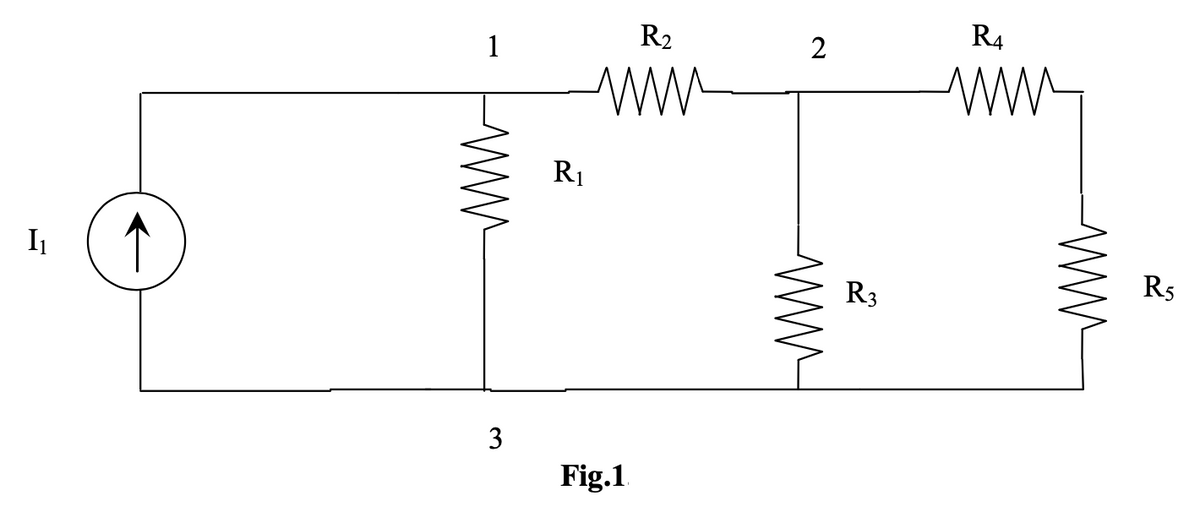
In the circuit shown in Fig. 1, node 3 is assumed as the reference node. The voltage at node 1 is the voltage at that node with respect to node 3. Similarly, the voltage at node 2 is the voltage at that node with respect to node 3.
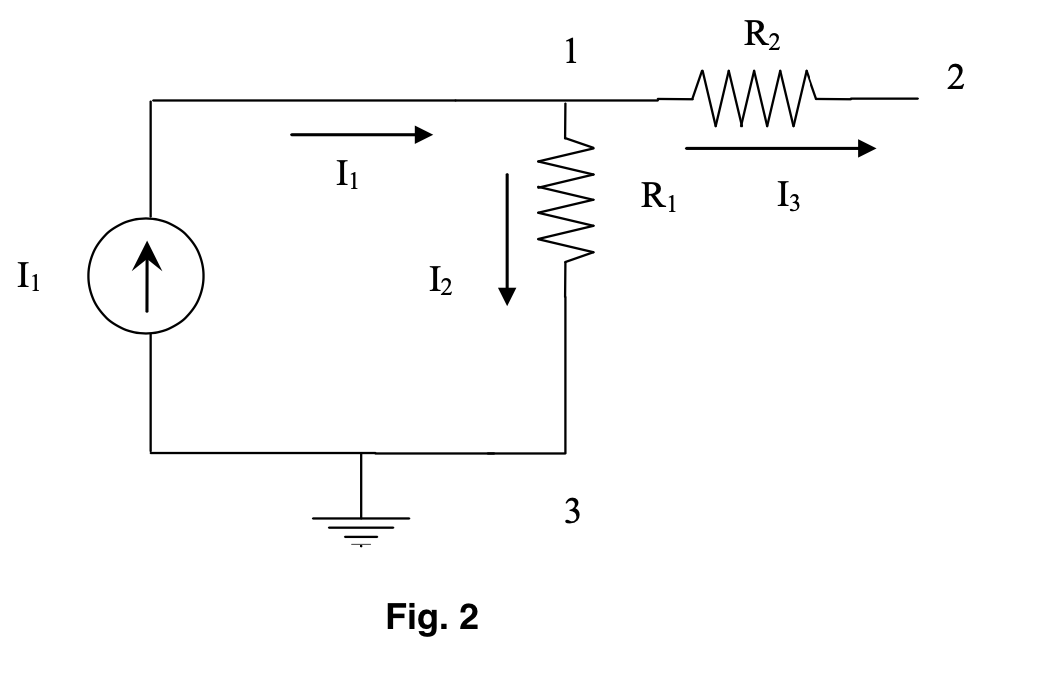
Applying KCL at node 1 ; the current entering is equal to the current leaving (refer Fig. 2)
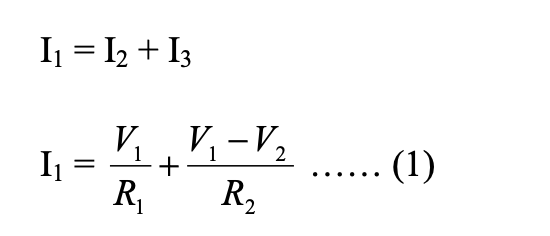
Where V1 and V2 are the voltages at node 1 and 2, respectively. Similarly, at node2, the current entering is
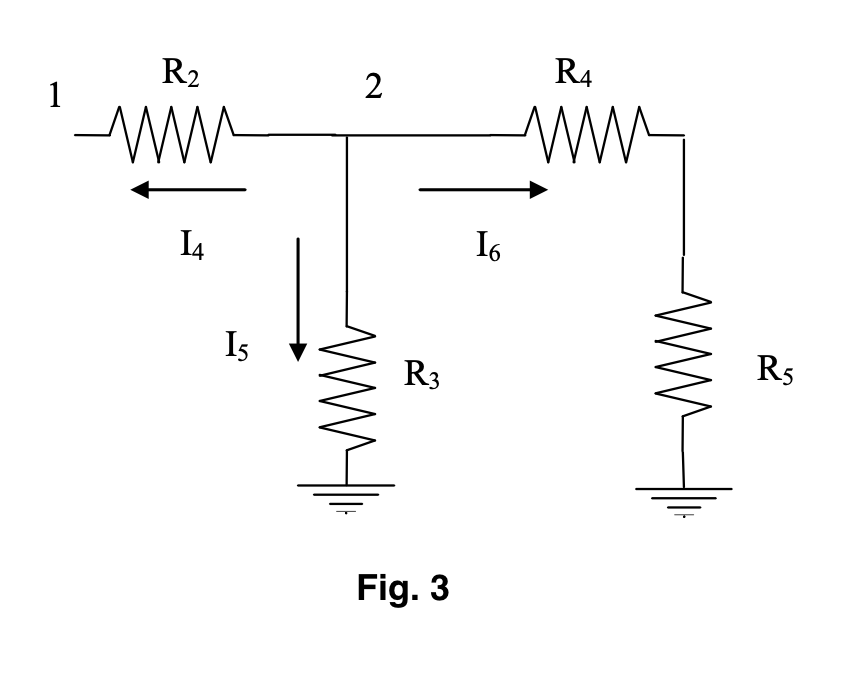
equal to the current leaving as shown in Fig. 3.
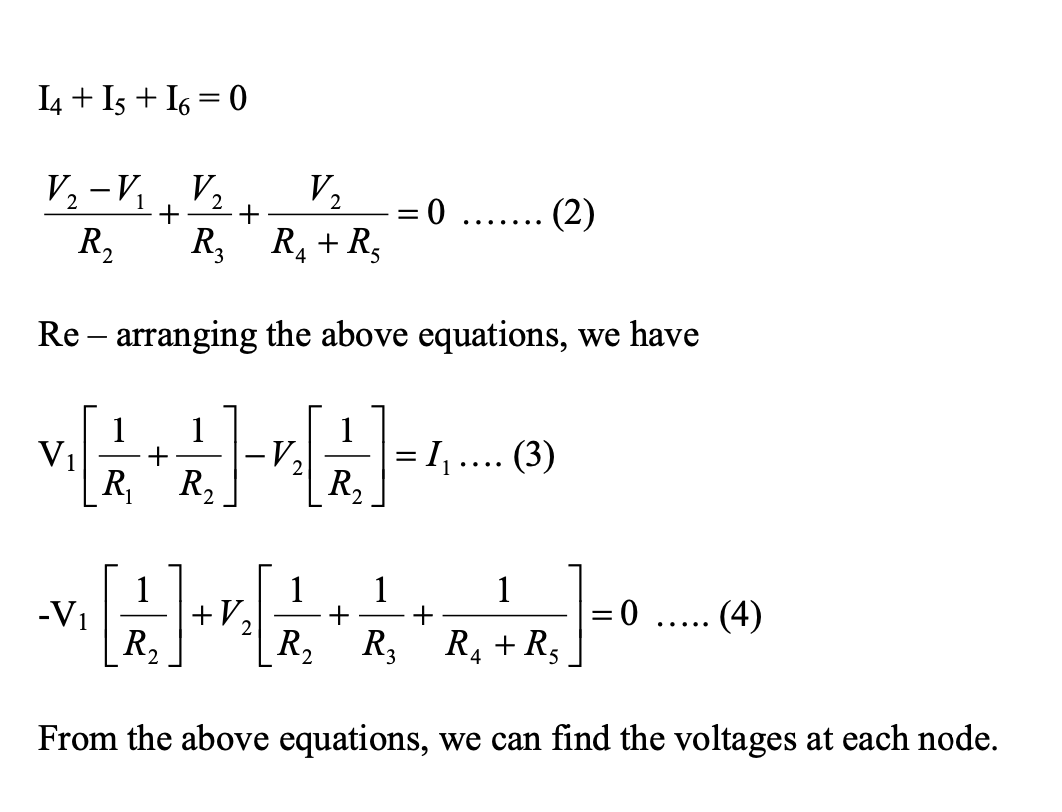
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 7 images




