
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
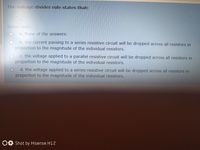
Transcribed Image Text:The voltage divider rule states that:
Select one:
a. None of the answers.
b. the current passing to a series resistive circuit will be dropped across all resistors in
proportion to the magnitude of the individual resistors.
C. the voltage applied to a parallel resistive circuit will be dropped across all resistors in
proportion to the magnitude of the individual resistors.
d. the voltage applied to a series resistive circuit will be dropped across all resistors in
proportion to the magnitude of the individual resistors.
OE Shot by Hisense H12
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How did you calculate 3/8.8 from the current divider rule in step 3?arrow_forwardProblem 3.14 Consider two voltage dividers shown in (Figure 1). Suppose that v=361 V. Figure 75 k w Figure a 75 kn 25k0 b'e 25 kn 40 kn Consider two voltage dividers shown in (Figure 1). Suppose that V=361 V. 60 kn 1 of 2 40 ΚΩ www 25.000/60 ΚΩΣ 2 of 2 VAarrow_forwardFor the circuit given below: Calculate the equivalent resistance, RAB. as seen across termimals A and B using R113 2, R241 2, R326 2, R444 2, R511 2, R647 2. Write your answer up to 3 decimal places. Do not use unit in the answer. Just write your calculated answer with up to 3 decimal places, R1 R4 ww R6 R5 3R3 R2 RABarrow_forward
- Questions and Problems: | 1. What are the identifying characteristics of a series circuit? 2. What are the identifying characteristics of a parallel circuit? 3. What changes occur in the total resistance of a circuit as additional resistances are added (a) in series? (b) in paraliel? 4. What are the different types of resistances and their purpose? 5. Why are lamps in a house lighting circuit not conhected in series? 6. A small lamp is designed to draw 300mA in a 6V circuit. What is the resistance of the lamp filament? 7. A battery with an internal resistance of 1.50 is connected in series with resistors R1 = 32 and R2 = 3.52 if the potential difference across the 32 resistor is 9v. What is the emf of the battery? 8. Determine the ideal voltage source needed by three resistors connected in series R1 = 62, R2 in the circuit. 9. Determine the total resistance of the circuit of the circuit below. 82 and R3 = 102 if a required current of 0.5A flows 140 4.50 3 40 250 180 1.50 5n 40n 100 20…arrow_forwardWhich statement is correct about a series circuit? The sum of currents in each load multiplied by the total resistance determines t voltage. The sum of the individual resistances equals the total resistance. The sum of all the voltage drops equals the source voltage. The voltage drops are equal to the input source. In a series circuit, the current, I, is Different in each resistor The highest near the positive and negative terminals of the voltage source The same everywhere Different at all points along the circuitarrow_forwardCould you please explain why is a voltage divider used in this circuit? What does vth,rth,gm and the symbol that is equal to B/gm mean? Thank you so mucharrow_forward
- Three identical 12 Q resistors are connected to a variable source in a mixed circuit. The circuit includes a 6.0 A fuse. R2 R Vo R3 Which of the following statements describes the potential difference across the resistors?arrow_forwardQuestion 12) attatched Delmars electricity 7th edition.arrow_forwardPlease show all work and highlight or circle your answers for parts d, e and f. Thank youarrow_forward
- Resistors R1 and R2 are connected in parallel. The total current drawn from a 30V source is 6A. WHen the value of resistor R2 is doubled, the current drop to 4A. Determine the resistances of R1 and R2arrow_forward3. Source transformationarrow_forwardThe following questions refer to the circuit represented by the diagram at right. Think of R2 as the internal resistance of the inductor. a) Immediately after the switch is closed, find the magnitude and direction of the conventional current (if any) through the battery, and find the potential difference across the inductor. b) A long time after the switch is closed, find the magnitude and direction of the conventional current (if any) through the battery, and find the potential difference across the inductor. c) After the switch has been closed for a long time it is suddenly opened. Immediately after the switch is opened, find the magnitude and direction of the conventional current (if any) through the resistor R1 and the potential difference across the inductor.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,