
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781285869759
Author: Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
The values of the dissociation constants for H3PO4 are given in the table above. If a solution has a pH of 1, which of the following chemical species would have the lowest concentration?
a) H+
b) H2PO4-
c) HPO42-
d) PO43-
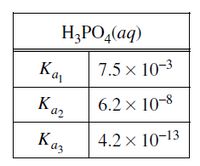
Transcribed Image Text:(bv)*
H;PO,(aq)
7.5 × 10-3
Ka
Kaz
6.2 × 10-8
Kaz
4.2 x 10-13
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1-1. The raw water supply for a community contains 18 mg/L total particulate matter. It is to be treated by addition of 60 mg alum (Al2(SO4)3-14H;O) per liter of water treated. Essentially, all the added alum precipi- tates represented by the following reaction: Al2(SO4)3 · 14H20 → 2 Al(OH);(s) + 3So,- + 6H* + 8H2O For a total flow of 7500 m/d, compute the daily alum requirement, the total concentration of suspended sol- ids in the water following alum addition, and the daily load of particulate solids requiring disposal (including both those initially present and those formed during treatment).arrow_forward(i) H3C CI (ii) HO OHarrow_forward1597 59 S ||| 2 O CHEMICAL REACTIONS Calculating ion molarity using solute mass A chemist prepares a solution of magnesium bromide (MgBr₂) by measuring out 2.1 g of MgBr, into a 300. mL volumetric flask and filling to the mark with distilled water. V Calculate the molarity of Br anions in the chemist's solution. Be sure your answer is rounded to the correct number of significant digits. Microsoft O W Microsoft Microsoft 6.52.210... esc mol L Explanation 18 ! 1 Check 9,206 2 # 3 103 NOV 6 X $ 4 O 67 5⁰ % 5 stv 6 Y 2 & 7 © 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. U * CO 66 8 A 9 I 1 Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility W 0 0 P { [ do F }arrow_forward
- Give the correct standard line notation.arrow_forward(The ? stands for a number the student is going to calculate.) Fill in the missing part of this equation. Note: your answer should be in the form of one or more fractions multiplied together. (-5.1 x 10' Pa cm' 3 3 = ? kPa·m x10arrow_forwardWhat is the pH of (3.21x10^-1) M C5H5NHBR? Enter your answer in scientific notation with 3 sig figs. Do not include any units in your answer. Do not round any intermediate calculations. Note: Your answer is assumed to be reduced to the highest power possible. Your Answer: х10 Answerarrow_forward
- (a) Iz(s) + 5 Cu²* (aq) + 6 H;O(I) –→ 2 103"(aq) + 5 Cu(s) + 12 H*(aq) (b) Hg²*(aq) + 21 (aq) → Hg(1) + Iz(s) (c) H2SO3(aq) + 2 Mn(s) + 4 H¯ (aq) · S(s) + 2 Mn²*(aq) + 3 H2O(I)arrow_forward2-12. What is the mass in milligrams of solute in (a) 26.0 mL of 0.150 M sucrose (342 g/mol)? (b) 2.92 L of 5.23 X 10-3 M H,O2?arrow_forwardo i MeO XS HCI 3. 40° C A A A 1. Br₂ 2. 2x t-Buo K* CN A CN CNarrow_forward
- (a) Iz(s) + 5 Cu²* (aq) + 6 H2O(1) (b) Hg²*(aq) + 21 (aq) (c) H2SO3(aq) + 2 Mn(s) + 4 H*(aq) → S(s) + 2 Mn²* (aq) + 3 H,O(I) 2 10;"(aq) + 5 Cu(s) + 12 H*(aq) - Hg(1) + I2(s) - -arrow_forwardWhen a Vitamin C (ascorbic acid; MM = 176.12 g mol-1) tablet is crushed, dissolved and titrated with 0.0377 M KIO3(aq) to a purple/blue endpoint (given by a starch indicator), the volume of KIO3 used is 40.01 mL. How many mg of Vitamin C were in the tablet? KIO3(aq) + 5 KI + 6 H+ → 3 I2(aq) + 3 H2O I2 (aq) + ascorbic acid → 2 I- + dehydroascorbic acidarrow_forward(a) A student carries out a titration to find the concentration of some sulfuric acid. The student finds that 25.00 cm of 0.0880 mol dm aqueous sodium hydroxide, NaOH, is neutralised by 17.60 cm of dilute sulfuric acid, H2SO4. -3 H2SO4(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) → Na2SO,(aq) + 2H2O(1) (i) Calculate the amount, in moles, of NaOH used. answer = mol (ii) Determine the amount, in moles, of H2SO4 used. answer mol (ii) Calculate the concentration, in mol dm3, of the sulfuric acid. answer = mol dm3 (b) After carrying out the titration in (a), the student left the resulting solution to crystallise. White crystals were formed, with a formula of Na2SO4•x H2O and a molar mass of 322.1 g mol. What term is given to the x H2O' part of the formula? Using the molar mass of the crystals, calculate the value of x. answer =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning