Question
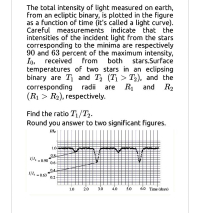
Transcribed Image Text:The total intensity of light measured on earth,
from an ecliptic binary, is plotted in the figure
as a function of time (it's called a light curve).
Careful measurements indicate that the
intensities of the incident light from the stars
corresponding to the minima are respectively
90 and 63 percent of the maximum intensity,
Io.
temperatures of two stars in an eclipsing
binary are T1 and T2 (T1 > T2), and the
corresponding radii
(R1 > R2), respectively.
received
from
both
stars.Surface
аге
R1
and R2
Find the ratio T1/T2.
Round you answer to two significant figures.
1.0-
0.8
1/1o =0.90
0.6-
04-
1|1. =0.63
0.2
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
6.0 Time (days)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- As we read in the book, a star that appears to be 1 magnitude brighter will have approximately 2.5 times as much flux hitting an observer's detector/telescope/eye (i.e. a star with an apparent magnitude of 4 has approximately 2.5 times more flux hitting the detector as a star with an apparent magnitude of 5). With this in mind what is the approximate ratio of the flux hitting the a detector for a star with an apparent magnitude of 3 compared to a star with an apparent magnitude of 7? (hint: remember that magnitudes follow a logarithmic scale, not a linear one)arrow_forwardYou measure a star to have a parallax angle of 0.04 arc-seconds. What fraction of a degree is this?arrow_forwardWhat is the parallax of a star that is 150 pc from Earth?arrow_forward
- Calculate by how many times Betelgeuse is brighter than the Sun, if its parallax is 0.006 arcsec, and its apparent magnitude is m = +.5. Can you first use the parallax to calculate the distance and then use the magnitude-distance formula to find the absolute magnitude of Betelgeuse and finally, compare it to the absolute magnitude of the Sun which is -26,74 because other experts used other methods and the answer was not correct.arrow_forwardA nearby star has a parallax of 0.317 arcseconds. How long does it take the light from this star to reach us?arrow_forwardFor a star with surface temperature 5,100 K, what is the peak frequency of light from the sun? Write your answer in THz (1012 Hz), to zero decimal places. Take the speed of light to be c=3 x 108 m/s.arrow_forward
- You measure a star to have a parallax angle of 0.12 arc-seconds What is the distance to this star in parsecs? 8.33 Hint: d = 1/p What is the parallax angle of a different star that is twice as far away as the star from the previous problems? [answer in arc-seconds without including the unit]arrow_forwardA Type Ia supernova is observed and achieves an apparent magnitude of m = 19.89 at peak brightness. The absolute magnitudes of Type Ia supernovae at peak brightness are known to be M=−19. Determine the distance to the supernovae in units of Mpc.arrow_forward(a) The figure shows the three stars and their velocities. Which star has the largest proper motion? Which star has the smallest proper motion? A B Eartharrow_forward
- Q3.2 The supergiant star has a surface temperature of about 2900 K and emits a power of approximately 4 x 1030 W. Assuming that is a perfect emitter and spherical, find its radius. (hint: Area of the sphere is A = 4πr²)arrow_forwardRefer to this table to determine the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. Then calculate the average speed of the Earth in its orbit in kilometers per second and meters per second?arrow_forwardThe brightness of a "young" star sometimes increases and decreases as a result of regional areas of "hot" and "cold" on the star's surface as well as variations in the density of the star's planet-forming debris, which can obstruct light. Suppose that for a particular star, the average magnitude (measure of brightness) is 4.3 with a variation of ±0.31 (on the magnitude scale, brighter objects have a smaller magnitude than dimmer objects). Furthermore, the magnitude of a star is initially observed to be 4.61, and the time between minimum brightness and maximum brightness is 6.4 days. Write a simple harmonic motion model to describe the magnitude Mof the star for day t.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios