
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781133104261
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Here a masses for 5 different objects. Each is dropped from rest, find which object (may be more than one) will have the greatest acceleration in free fall
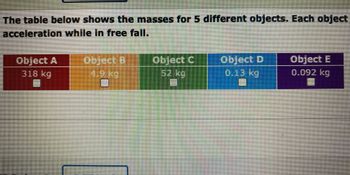
Transcribed Image Text:The table below shows the masses for 5 different objects. Each object experiences the same acceleration while in free fall.
| Object | Mass |
|----------|---------|
| Object A | 318 kg |
| Object B | 4.9 kg |
| Object C | 52 kg |
| Object D | 0.13 kg |
| Object E | 0.092 kg |
Each object listed is affected by gravity in the same way, which means they all accelerate at the same rate due to gravity regardless of their differing masses. This principle is a fundamental concept in physics, illustrating that the acceleration due to gravity is constant for all objects in free fall, assuming no air resistance.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two blocks, each of mass m, are hung from the ceiling of an elevator as in Figure P4.33. The elevator has an upward acceleration a. The strings have negligible mass. (a) Find the tensions T1 and T2 in the upper and lower strings in terms of m, a, and g. (b) Compare the two tensions and determine which string would break first if a is made sufficiently large. (c) What are the tensions if the cable supporting the elevator breaks? Figure P4.33 Problems 33 and 34.arrow_forwardWhat forces cause (a) an automobile, (b) a propeller-driven airplane, and (c) a rowboat to move?arrow_forwardAn object of mass m is dropped al t = 0 from the roof of a building of height h. While the object is falling, a wind blowing parallel to the face of the building exerts a constant horizontal force F on the object. (a) At what time t does the object strike the ground? Express t in terms of g and h. (b) Find an expression in terms of m and F for the acceleration ax of the object in the horizontal direction (taken as the positive x direction). (c) How far is the object displaced horizontally before hitting the ground? Answer in terms of m, g, F, and h. (d) Find the magnitude of the objects acceleration while it is falling, using the variables F, m, and g.arrow_forward
- Two objects are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless pulley as shown in Figure P4.30. Assume the incline is frictionless and take m1 = 2.00 kg, m2 = 6.00 kg, and = 55.0. (a) Draw free-body diagrams of both objects. Find (b) the magnitude of the acceleration of the objects, (c) the tension in the string, and (d) the speed of each object 2.00 s after it is released from rest. Figure P4.30arrow_forwardOn a single, light, vertical cable that does not stretch, a crane is lifting a 1 207-kg Ferrari and, below it, a 1 461 -kg BMW Z8. The Ferrari is moving upward with speed 3.50 m/s and acceleration 1.25 m/s2, (a) How do the velocity and acceleration of the BMW compare with those of the Ferrari? (b) Find the tension in the cable between the BMW and the Ferrari, (c) Find the tension in the cable above the Ferrari.arrow_forwardIn Figure P4.35, the man and the platform together weigh 950 N. The pulley can be modeled as frictionless. Determine how hard the man has to pull on the rope to lift himself steadily upward above the ground. (Or is it impossible? If so, explain why.) Figure P4.35arrow_forward
- A student takes the elevator up to the fourth floor to see her favorite physics instructor. She stands on the floor of the elevator, which is horizontal. Both the student and the elevator are solid objects, and they both accelerate upward at 5.19 m/s2. This acceleration only occurs briefly at the beginning of the ride up. Her mass is 80.0 kg. What is the normal force exerted by the floor of the elevator on the student during her brief acceleration?arrow_forwardAn object of mass m1 = 5.00 kg placed on a frictionless, horizontal table is connected to a string that passes over a pulley and then is fastened to a hanging object of mass m2 = 9.00 kg as shown in Figure P4.28. (a) Draw free-body diagrams of both objects. Find (b) the magnitude of the acceleration of the objects and (c) the tension in the string. Figure P4.28arrow_forwardA force F applied to an object of mass m1 produces an acceleration of 3.00 m/s2. The same force applied to a second object of mass m2 produces an acceleration of 1.00 m/s2. (a) What is the value of the ratio m1/m2? (b) If m1 and m2 are combined into one object, find its acceleration under the action of the force F.arrow_forward
- A 3.00-kg block starts from rest at the top of a 30.0 incline and slides a distance of 2.00 m down the incline in 1.50 s. Find (a) the magnitude of the acceleration of the block, (b) the coefficient of kinetic friction between block and plane, (c) the friction force acting on the block, and (d) the speed of the block after it has slid 2.00 m.arrow_forward(a) A cat with a mass of 850 kg in moving to the right with a constant speed of 1.44 m/s. What is the total force on the cat ? (b) What is the total force on the cat if it is moving to the left?arrow_forwardIn Figure P3.55, a spider is resting after starting to spin its web. The gravitational force on the spider makes it exert a downward force of 0.150 N on the junction of the three strands of silk. The junction is supported by different tension forces in the two strands above it so that the resultant force on the junction is zero. The two sloping strands are perpendicular, and we have chosen the x and y directions to be along them. The tension Tx is 0.127 N. Find (a) the tension Ty, (b) the angle the x axis makes with the horizontal, and (c) the angle the y axis makes with the horizontal.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning