
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
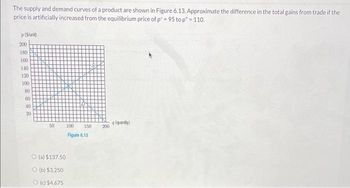
Transcribed Image Text:The supply and demand curves of a product are shown in Figure 6.13. Approximate the difference in the total gains from trade if the
price is artificially increased from the equilibrium price of p = 95 to p*= 110.
p(Sunit)
200
180
888888888
160
140
120
100
50
100 150 200
Figure 6.13
O(a) $137.50
Ⓒ (b) $3,250
O (c) $4,675
(quantity)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 25 20 15 10 5 d(q) = 20-9/20 s(q) = 11+q/40 40 80 120 160 200 (a) Find a price where the supply and demand curve would predict a surplus in the marketplace for the produce. Explain how you know there would be a surplus using using data from the supply and demand curve. (b) Estimate the price where the consumers would completely stop buying the product. Explain how you found your answers by referring to the above graph.arrow_forwardAssuming a $9 per unit subsidy is implemented, the new quantity traded will be ______. a) 12 b) 14 c) 16 d) 19 e) 21 f) 22.5 g) 45 h 66 i) 82.5 j) 148.5 k) 171arrow_forwardAssume that the actual price of the tv is 2096 lower than what you are willing to pay. Consumer surplus is the difference between what you are willing to pay and the actual price of the product. What is the consumer surplus in this situation? Sceptre 65" Class 4K UHD LED TV HDR U650CV-U Average Rating (4.1)out of 5stars1529 ratings, based on1529reviews Please see the provided rubric. O Focus hp inbrt sc & 8 {arrow_forward
- The US demand curve for transporting freight by truck is а° - 580B - 60в "Р, where B denotes billion. Here, P is the price to transport a standard shipping container one mile, and quantity Q is the number of shipping-container-miles transported in a year. The marginal cost of transport is $1/mile (i.e., fuel and driver costs). Each truck can drive up to a maximum of 100,000 miles/year. Assume each truck carries one shipping container. The annual fixed cost of operating a truck is $200,000. Consequently, the average cost of a truck that drives q miles a year is ($200,000/q) +$1. All trucks have the same costs. There are no barriers to setting up a new trucking firm and/or acquiring additional trucks, and there are large numbers of people capable of running a trucking firm. Part (a) Sketch average and marginal costs for a truck, as a function of miles driven. Part (b) (i) (ii) (ii) (iv) (v) What is the price-per-mile of transporting freight by truck? How many miles does the combined US…arrow_forwardPrice per Constant- Quality Unit $1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00 5.00 Quantity Demanded of Constant-Quality Units per Year 1,000 800 600 400 200 According to the above table, at a price of $1 per unit, which of the following would exist? A) a surplus of 200 units Quantity Supplied of Constant-Quality Units per Year 200 400 600 800 1,000 OB) a shortage of 200 units OC C) a shortage of 800 units ⒸD) a surplus of 800 unitsarrow_forwardConsider the market for good x for which there is one firm controlling the market.D(q)=165-10qMC(q)=5q+15MR(q)=165-20qC(q)=2.5q^2+15q+8 (a) Find the point of equilibrium. (b) How many units must the firm produce and sell to maximize its profits? (c) What will be the price the firm will charge to consumers?arrow_forward
- Price(per bottle) Quantity supplied Normal timesquantity demanded Hurricanequantity demanded $6 100 25 75 $5 85 35 85 $4 70 45 95 $3 55 55 105 $2 40 65 115 $1 25 75 125 Concerned with citizen complaints of price gouging during past hurricanes, Florida's state government passes a law setting a price ceiling for a bottle of water equal to the market equilibrium price during normal times. After all, it seems unfair that sellers of water gain because of a hurricane. During a hurricane, there would be a shortage of bottles of water. Without the antiprice gouging law, consumers would have to pay $ more than the ceiling price, but they would be able to buy more bottles of water.arrow_forwardAssuming a $9 per unit subsidy is implemented, the new price to the buyers will be $______. a) 12 b) 14 c) 16 d) 19 e) 21 f) 22.5 g) 45 h 66 i) 82.5 j) 148.5 k) 171arrow_forwardPrice Quantity Supplied Quantity Demanded $10 100 295 11 150 275 12 190 250 13 220 220 14 245 .180 15 265 135 If a technological advance lowers production costs such that the quantity supplied increases by 60 units of this product at each price, the new equilibrium price would be O A) $13. B) $12. C) $11. D) $14.arrow_forward
- help please answer in text form with proper workings and explanation for each and every part and steps with concept and introduction no AI no copy paste remember answer must be in proper format with all workingarrow_forwardPrice ($/unit) 150 120 70 40 10 100 $2,500 $1,500 $4,000 $1,000 200 300 Supply Demand Quantity (thousands) Referring to the above figure, and as a result of the price increasing from $70 to $120, total deadweight loss to consumers and producers would be:arrow_forwardQ6 The demand and supply functions for two interdependent commodities are given by: Qp, = 120 – 2P, + P;; Qs, = -7 + 7P, Qp, = 168 + 3P, – 7P;; Qs, = -3 + 20P, %3D (a) Explain whether these goods are complementary or substitutable. (b) Determine the equilibrium price and quantity. (c) The government decides to provide a subsidy of $4 on each unit of good 1 only. What effect does this subsidy have on the equilibrium prices of each good?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education