
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
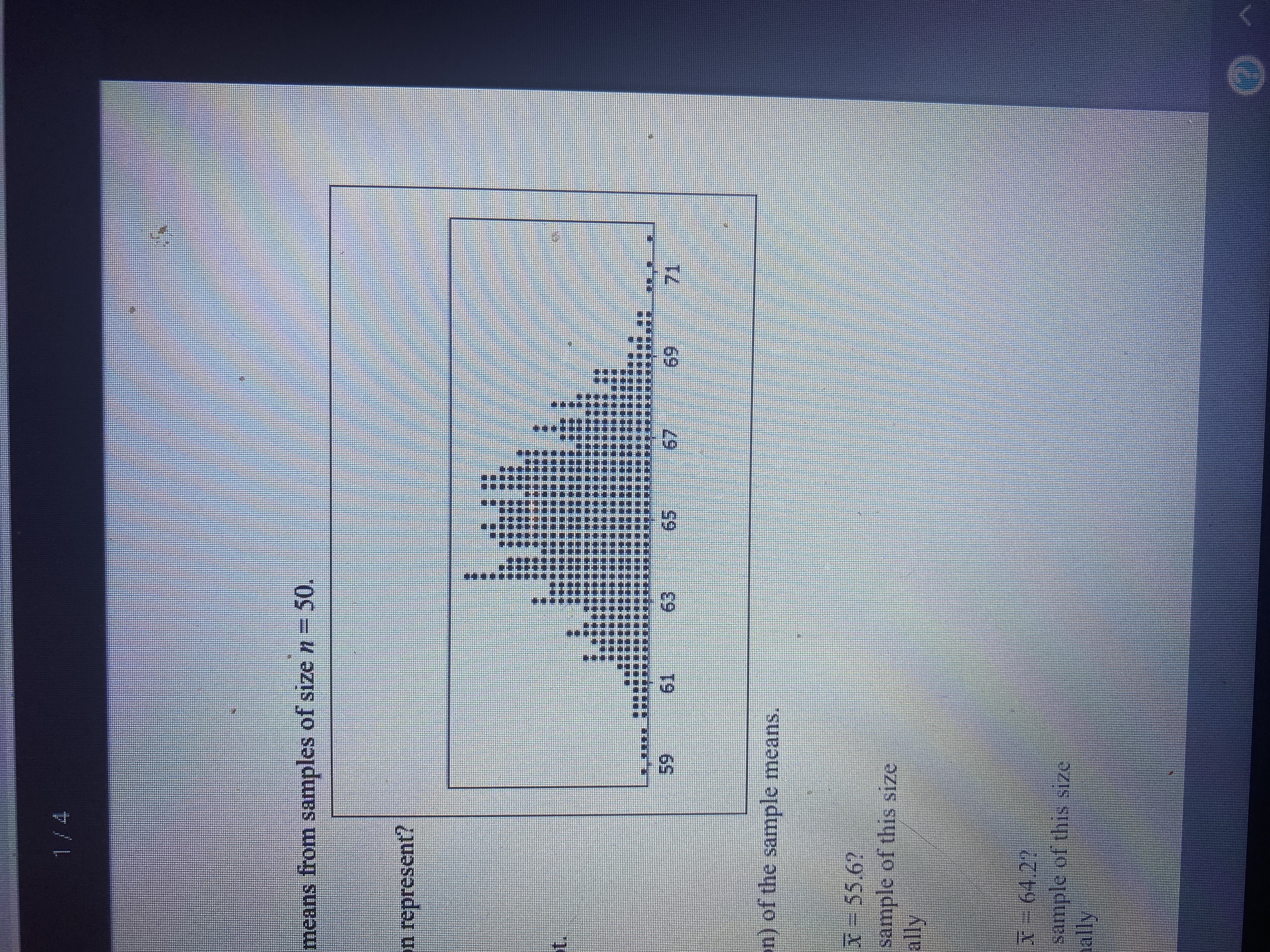
The sampling distribution attached shows sample
1. Using the sampling distribution, how likely is x-bar=55.6? Reasonably likely to occur from sample of this size, unusual but might occur occasionally, or extremely unlikely to occur.
2.using the sampling distribution, how likely is x-bar=64.2? Reasonably likely to occur from sample of this size, unusual but might occur occasionally, or extremely unlikely to ever occur.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose that the efficacy of a certain drug is 0.49. Consider the sampling distribution (sample size 166) for the proportion of patients cured by this drug. n = a. What is the mean of this distribution? b. What is the standard error of this distribution? Round the answer to three decimal places. ent Submit Question ry ent witharrow_forwardAccording to AC Lens, green eye color is one of the rarest with only 2% of the world's population having that eye color. A random sample of 1000 people from around the world are selected. Let p be the proportion of the sample which has green eyes. 1. What is the mean of the sampling proportion? 2. What is the standard deviation of the sampling proportion? (Round to the nearest thousandth.) 3. Find the probability that p will be between 0.01 and 0.03. P(0.01 < p < 0.03) = 4. What is the rule of thumb for normalizing the sampling distribution of proportions?arrow_forwardSuppose a random sample of n measurements is selected with probability of success p = . 35. Given n = 200, describe the shape, and find the mean and the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the sample proportion.arrow_forward
- 1. Explain why the mean of the sampling distribution is an unbiased estimator of the population parameter. 2. When do you use the central limit theorem? 3. What are the formulas for μx and Ox?arrow_forwardDescribe the sampling distribution of p. Round to three decimal places when necessary. [ N = 21,000, n = 600, p = 0.6 ]arrow_forwardThe scores of individual students on the American College Testing (ABC) program composite college entrance examination have a normal distribution with a mean 18.6and a standard deviation 6.0. At Northside high, 36 seniors take the test. Assume that the scores at this school have the same distribution as national scores. A) What is the sampling distribution of the sample mean score of randomly selected 36 students?(show work) B) what is the distribution of a randomly selected one student?(show work)arrow_forward
- To estimate the proportion of teen traffic deaths in Texas last year that was caused by speeding, determine the necessary sample size for the estimate to be accurate to within .05 with probability .99. a. Suppose from a previous study, we expect the proportion to be about .30. b. suppose we do not have any prior knowledge about the true proportion.arrow_forward4. You ask an SRS of 1500 college students whether they applied for admission to any other college. Suppose that in fact 35% of all college students applied to colleges besides the one they are attending. The sampling distribution of the proportion of B your sample who say "Yes" is approximately Normal with mean 0.35 and standard deviation 0.01. Sketch this Normal curve and use it to answer the following questions. (You can use the 68-95-99.7 rule for all these questions.) Round to nearest whole percent. (a) What percentage of many samples would have a larger than 0.37? 2.5 (b) What is the probability that your sample will have a less than 0.33?Å (c) what is the probability that your sample result will be either less than 0.33 or greater than 0.35?arrow_forwardSuppose I want to sample the household incomes for EBR parish. Let's say I start with a simple random sample of 100 residents and calculate the sample mean. How would the sampling distribution of change if I increase the sample size to 1,000 residents?arrow_forward
- Answer number 1 to 3 pls. I don't want to waste my money here thanks.arrow_forward8. This question requires you to work z score problems with the sampling distribution of means. For each problem, begin by computing the standard error of the mean, using the formula: OM Then make two diagrams of the problem-one in terms of the actual scores, and one in terms of the z scores; mark the area under investigation on each curve. Show calculation of the appropriate z scores. List the line(s) from the z score table that you use to answer the question. Provide a verbal answer to each question. a. Assume you have a sampling distribution of means of samples of size n=16 from a population distribution in which u = 46 and o = 36. What proportion of sample means fall above M = 48? b. Assume you have a sampling distribution of means of samples of size n=25 from a population distribution in which u = 100 and o = 15. What proportion of sample means fall above M = 96? c. Assume you have a sampling distribution of means of samples of size n=49 from a population distribution in which u =…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman