
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
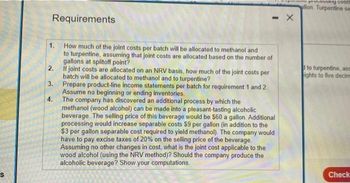
Transcribed Image Text:Requirements
1.
2.
3.
4.
- X
How much of the joint costs per batch will be allocated to methanol and
to turpentine, assuming that joint costs are allocated based on the number of
gallons at splitoff point?
If joint costs are allocated on an NRV basis, how much of the joint costs per
batch will be allocated to methanol and to turpentine?
Prepare product-line income statements per batch for requirement 1 and 2.
Assume no beginning or ending inventories.
The company has discovered an additional process by which the
methanol (wood alcohol) can be made into a pleasant-tasting alcoholic
beverage. The selling price of this beverage would be $60 a gallon. Additional
processing would increase separable costs $9 per gallon (in addition to the
$3 per gallon separable cost required to yield methanol). The company would
have to pay excise taxes of 20% on the selling price of the beverage.
Assuming no other changes in cost, what is the joint cost applicable to the
wood alcohol (using the NRV method)? Should the company produce the
alcoholic beverage? Show your computations.
more processing costs
allon. Turpentine sem
to turpentine, ase
ights to five decim
Check
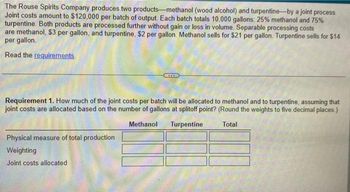
Transcribed Image Text:The Rouse Spirits Company produces two products-methanol (wood alcohol) and turpentine-by a joint process.
Joint costs amount to $120,000 per batch of output. Each batch totals 10,000 gallons: 25% methanol and 75%
turpentine. Both products are processed further without gain or loss in volume. Separable processing costs
are methanol, $3 per gallon, and turpentine, $2 per gallon. Methanol sells for $21 per gallon. Turpentine sells for $14
per gallon.
Read the requirements.
Requirement 1. How much of the joint costs per batch will be allocated to methanol and to turpentine, assuming that
joint costs are allocated based on the number of gallons at splitoff point? (Round the weights to five decimal places.)
Methanol
Turpentine
Total
Physical measure of total production
Weighting
Joint costs allocated
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Elsa Products processes Chem-Z into two products: Chem-A and Chem-B. Chem-Z costs $42,000 per batch. The joint process produces 11,250 units of Chem-A with a market value of $135,000, and 20,000 units of Chem-B with a market value of $33,750. The conversion cost of the joint process is $13,400 per batch. Elsa Products allocates joint costs using the physical quantities method. The company never holds any inventory. Required: What cost (total, not unit) and profit will be reported for each product using the current method for allocating joint costs? If the costs of the joint process are allocated on the basis of the net realizable value of the products, what cost (total, not unit) and profit will be reported for each product? How much will profit at Elsa Products increase or decrease if the company switches to the net realizable value method for allocating joint process costs?arrow_forwardIn a joint processing operation, Nolen Company manufactures three grades of sugar from a common input, sugar cane. Joint processing costs up to the split-off point total $41,800 per year. The company allocates these costs to the joint products on the basis of their total sales value at the split-off point. These sales values are as follows: raw sugar, $21,000; brown sugar, $21,000; and white sugar, $23,100. Each product may be sold at the split-off point or processed further. Additional processing requires no special facilities. The additional processing costs and the sales value after further processing for each product (on an annual basis) are shown below: Product Raw sugar Brown sugar White sugar Additional Processing Costs $ 21,200 $ 14,600 $ 5,300 Sales Value $40,500 Incremental profit (loss) $37,300 $44,400 Required: a. Compute the Incremental profit (loss) for each product. (Loss amounts should be indicated by a minus sign.) Raw Sugar Brown Sugar White Sugararrow_forwardLongwood Corporation processes a liquid into three outputs: K-2, K-4, and K-5. The sales value of each of these products for a single batch follows: K-2 $ 579,600 K-4 428,400 K-5 192,000 The joint costs total $850,000. There are no separable production costs. If K-5 is accounted for as a by-product, its sales are credited to the joint manufacturing costs using method 1 described in the text. Required: a-1. What are the allocated joint costs for the three outputs, if K-5 is accounted for as a joint product? a-2. What are the allocated joint costs for the three outputs, if K-5 is accounted for as a by-product?arrow_forward
- In a joint processing operation, Scarecrow Gardens Ltd. manufactures three varieties of products from a common input, corn. Joint processing costs up to the split-off point total $90,000 per year. The company allocates these costs to the joint products on the basis of their total sales value at the split-off point. These sales values are as follows: whole corn $57,000; dried corn kernels $65,000; and ground corn meal $74,500. Each product may be sold at the split-off point or processed further. Additional processing requires no special facilities. The additional processing costs and the sales value after further processing for each product (on an annual basis) are shown below: Product Additional Processing Costs Sales Value Whole Corn $27,175 $95,250 Dried Corn Kernels $29,760 $104,470 Ground Corn Meal $20,400 $92,300 REQUIRED: Which product or products should be sold at the split-off point, and which product or products should be processedfurther. Explain why…arrow_forwardStoney Brook Company produces two products (X and Y) from a joint process. Each product may be sold at the split-off point or processed further. Additional processing requires no special facilities, and production costs of further processing are entirely variable and traceable to the products involved. Joint manufacturing costs for the year were $81,000. Sales values and costs were as follows: Product Units Made Sales Price at Split-Off If Processed Further Sales Value Separable Cost X 12,000 $ 43,000 $ 81,000 $ 10,500 Y 4,000 86,000 96,000 7,500 If the joint production costs are allocated based on the relative-sales-value method, what woukd be the amount of joint cost assigned to product X ?arrow_forwardPlease answer in text form without imagearrow_forward
- A company manufactures three products, L-Ten, Triol, and Pioze, from a joint process. Each production run costs $13,000. None of the products can be sold at split-off, but must be processed further. Information on one batch of the three products is as follows: Product Gallons L-Ten Triol Pioze 3,400 4,000 2,400 Total Revenue Total Costs Further Processing Cost per Gallon $0.50 Total Gross Profit 1.00 1.50 Eventual Market Price per Gallon $2.00 Required: 1. Calculate the total revenue, total costs, and total gross profit the company will earn on the sale of L-Ten, Triol, and Pioze. 5.00 6.00 2. Allocate the joint cost to L-Ten, Triol, and Pioze using the constant gross margin percentage method. Round the gross margin percentage to four decimal places and round all other computations to the nearest dollar.arrow_forwardPacheco, Inc., produces two products, overs and unders, in a single process. The joint costs ofthis process were $50,000, and 14,000 units of overs and 36,000 units of unders were produced.Separable processing costs beyond the split-off point were as follows: overs, $18,000; unders,$23,040. Overs sell for $2.00 per unit; unders sell for $3.14 per unit.Required:1. Allocate the $50,000 joint costs using the estimated net realizable value method.2. Suppose that overs could be sold at the split-off point for $1.80 per unit. Should Pacheco sellovers at split-off or process them further? Show supporting computations.arrow_forwardQw.69.arrow_forward
- Alpesharrow_forwardThe Marshall Company has a joint production process that produces two joint products and a by-product. The joint products are Ying and Yang, and the by-product is Bit. Marshall accounts for the costs of its products using the net realizable value method. The two joint products are processed beyond the split-off point, incurring separable processing costs. There is a $1,500 disposal cost for the by- product. A summary of a recent month's activity at Marshall is shown below: Ying 75,000 75,000 $ 210,000 $ 15,000 $ 6.00 Total joint costs for Marshall in the recent month are $211,000, of which $90,730 is a variable cost. Units sold Units produced Separable processing costs-variable Separable processing costs-fixed Sales price Manufacturing cost per unit Total gross margin Yang 60,000 60,000 $ 65,000 $ 10,000 $ 12.50 Required: 1. Calculate the manufacturing cost per unit for each of the three products. (Round manufacturing cost per unit answers to 2 decimal places.) 2. Calculate the total…arrow_forwardDifferential Chemical produced 10,500 gallons of Preon and 14,000 gallons of Paron. Joint costs incurred in producing the two products totaled $8,000. At the split-off point, Preon has a market value of $8.00 per gallon and Paron $4.00 per gallon. Compute the portion of the joint costs to be allocated to Preon if the value basis is used.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education