
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The rod has a diameter of 40 mm. It is subjected to the force system Fx=1100 N, Fy=500 N, Fz=900 N.
A) Determine the normal stress that acts at point A.
B) Determine the shear stress (τA)xy that acts at point A.
C)Determine the shear stress (τA)xz that acts at point A.
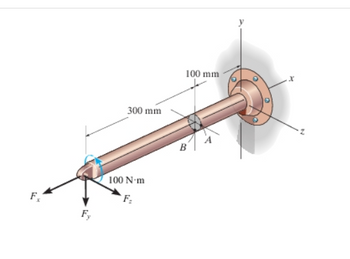
Transcribed Image Text:F
300 mm
100 N-m
F₂
100 mm
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 14 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose that σx = 42 MPa A) Determine the maximum in-plane shear stress. B) Determine the average normal stress.arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution .....arrow_forwardThe state of stress at a point in a member is shown on the element. Take σx= 98 MPa, σy= 50 MPa, τxy= 35 MPa in the directions shown. Solve the problem using the stress transformation equations. A) Determine the normal stress component acting on the inclined plane AB. B) Determine the shear stress component acting on the inclined plane AB.arrow_forward
- F₁ = 250 N 45% 60¹¹ 60 Mad 45 40° 120 F₁ = 800 N 60° F2=100N y An anchor is subjected to the stresses shown determine the magnitude and coordinate angles of direction of the resulting force a F= B=arrow_forwardSolve the problem using the stress transformation equations. Suppose that σx= 92 MPa, σy= 46 MPa, τxy= 36 MPa in the directions shown. A) Determine the normal stress component acting on the plane AB. B) Determine the shear stress component acting on the plane AB.arrow_forwardThe beam is supported by a pin at B and a short link AC. All pins are in double shear as shown in and each has a diameter of 40 mm assume P1=98 kN and P2= 49 kN. A) Determine the average shear stress developed in the pin at A B) Determine the average shear stress developed in the pin at B C) Determine the average shear stress developed in the pin at Carrow_forward
- Q5) A material is subjected to two mutually perpendicular linear strains together with a shear strain. Given that this system produces principal strains of 1x 104 compressive and 3x 104 tensile and that one of the linear strains is 2.5x 104 tensile, determine the magnitudes of the other linear strain and the shear strain by using Mohr's strain circle. Also, find the values of the principal stresses present in the material by using Mohr's stress circle. For the material, take E=208GN/m² and v=0.3arrow_forwardA) A circular rod with a gage length of 3.6 mm and a diameter of 2.3 cm is subjected to an axial load of 51 kN . If the modulus of elasticity is 200 GPa , what is the change in length? B)A circular rod with a length of 4 mm and a diameter of 2.4 cm is subjected to an axial load of 61 kN . If the resulting change in length is 3.34 mm , what is the modulus of elasticity? C)A circular rod with a length of 3.7 mm and a diameter of 2.7 cm is subjected to an axial load and increases in length by 3.26 mm . The initial portion of the stress-strain curve of the material is given. What is the applied load?arrow_forward- The below figure shows a simple model of the loading on the lower jaw (mandible) a) Determine the shear force diagram and the moment diagram using sectioning method b) Determine the shear force diagram and the moment diagram using the graphical method c) If the jaw can be assumed as a uniform rectangle 3cm×1cm, determine the maximum normal stress due to bending in the lower jaw 60N 50N 10N 2cm 10cm 1cm Muscle force Fulcrum Load 3cm 12cm (Answers: c) Omax ~ 0.667MPA)arrow_forward
- MENG222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS P=1000arrow_forwardThe state of stress shown to the left was produced by a combination of loadings on a body that is not shown. Determine the following via Mohr's circle: A) Draw Mohr's Circle for the x-y plane. B) Determine the principal stresses - All 3. C) Sketch a properly oriented differential element showing the principal stresses in the x-y plane. D) Determine the magnitude of the maximum shear stress in the x-y plane. E) Sketch a properly oriented differential element showing the maximum shear stress state in the x-y plane. F) Determine the magnitude of the absolute maximum shear stress (and include the two out of plane circles on your original figure). Use the following values for the magnitudes of the stresses: x = 0₂ Txy Ox X X 10 ksi, σy = 4 ksi, σ₂ = 3 ksi, Txy = 4 ksiarrow_forwardThe state of stress at a point in a member is shown on the element. Suppose that σx= 25 MPa, σy= 100 MPa, and τxy= 53 MPa. A) Determine the normal stress acting on the plane AB. B) Determine the shear stress acting on the plane AB.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY