Question
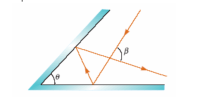
The reflecting surfaces of two intersecting flat mirrors are at an angle θ (0° < θ < 90°) as shown in the figure below. For a light ray that strikes the horizontal mirror, show that the emerging ray will intersect the incident ray at an angle β = 180° - 2θ. Assume that all angles are expressed in degrees and define the angles of incidence for the two reflections to be α and δ with respect to the normals.
(a)Calculate β in terms of α and δ
(b) Now calculate θ in terms of α and δ.
(c) Combine the previous two results in order to obtain an expression for β in terms of θ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Consider a convex lens having a thickness d whose sides have radii of curvature R1 and R2. a. Find the 2x2 matrix describing this lensb. What is the change in focal length for the case where the two radii equal R and d =0.1R, compared to the case where the lens thickness is neglected?arrow_forwardA light beam reflects off two parallel reflecting surfaces that are = 202 cm long and separated by a distance of s = 65.0 cm. If the beam of light enters this region as shown, with the angle 0 = 25.1°, determine the following. Ꮎ (a) the number of times the light beam reflects off the left surface Have you redrawn the figure with all angles and distances labeled? How is the entrance angle related to the angle of Incidence and the angle of reflection for the mirrors? times (b) the number of times the light beam reflects off the right surface timesarrow_forwardIn the diagram below, a person uses a laser pointer to illuminate a spot below the surface of a body of water. The beam originates 1.8m above the surface of the water, and is incident to the water 2.4m horizontal away from its origin point. (a) What is the incident angle, θ1? Given the indices of refraction of air and water, (b) what is the angle from the normal of the ray in the water, θ2? (c) How far horizontally from the point of incidence to the bottom of the body of water does the beam land? (What is x?)arrow_forward
- Light rays in a material with index of refrection 1.39 can undergo total internal reflection when they strike the interface with another material at a critical angle of incidence. Find the second material's index of refraction n when the required critical angle is 73.3°. n =arrow_forwardA ray of light crosses the boundary between some substance with n = 1.54 and air, going from the substance into air. If the angle of incidence is 29◦ what is the angle of refraction? Calculate to 1decimal.arrow_forwardConsider a refracting prism shown below. The face opposite the apex (top of the prism) is called the base. The total angle by which light changes direction is called the angle of deviation D. I A to a. Show that nprism = sin(A+D)/2/ sin (A/2) when light passes through the prism symmetrically such that the angles of incidence (1) and emergence (E) are equal (Assume the angle A is 60°) b. Find the deviation angles for blue and red light having indices of refraction 1.652 and 1.618 respectively. c. Sketch what happens when white light is incident on the prism. Iarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios