
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The reflecting surfaces of two intersecting flat mirrors are at an angle of 59 ◦ , as shown in the figure. A light ray strikes the horizontal mirror at an angle of 53◦ with respect to the mirror’s surface
(Figure is not drawn to scale)
Calculate the angle φ. Answer in units of ◦.
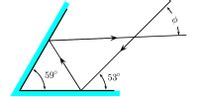
Transcribed Image Text:59°
53°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 110. The two mirrors shown meet at a right angle. The beam of light in the vertical plane P strikes mirror 1 as shown. (a) Mirror Light beam Determine the 40.0% distance the reflected light beam travels before striking mirror 2. (b) In what direction does the 1.25 m Mirror 1 light beam travel after reflecting from mirror 2?arrow_forwardA plane mirror and a concave mirror (f = 7.50 cm) are facing each other and are separated by a distance of 17.0 cm. An object is placed between the mirrors and is 8.50 cm from each mirror. Consider the light from the object that reflects first from the plane mirror and then from the concave mirror. Find the location of the image that this light produces in the concave mirror. Specify this distance relative to the concave mirror. Number i Object (-²) Units ◄►arrow_forwardI need help with part a and b of this question! Thanks! For an independent study project, you design an experiment to measure the speed of light. You propose to bounce laser light off a mirror that is 51.0 km due east and have it detected by a light sensor that is 129 m due south of the laser. The first problem is to orient the mirror so that the laser light reflects off the mirror and into the light sensor. (a) Determine the angle that the normal to the mirror should make with respect to due west. ANS:____º Since you can read your protractor only so accurately, the mirror is slightly misaligned and the actual angle between the normal to the mirror and due west exceeds the desired amount by 0.003°. Determine how far south you need to move the light sensor in order to detect the reflected laser light. ANS:_____ marrow_forward
- A ray of light strikes a flat block of glass at an incidence angle of 01 = 35.0°. The glass is 2.00 cm thick and has an index of refraction that equals n = 1.75. 'g 2.00 cm (a) What is the angle of refraction, 2, that describes the light ray after it enters the glass from above? (Enter your answer in degrees to at least 2 decimal places.) (b) with what angle of incidence, 03, does the ray approach the interface at the bottom of the glass? (Enter your answer in degrees to at least 2 decimal places.) ° (c) with what angle of refraction, 84, does the ray emerge from the bottom of the glass? (Enter your answer in degrees to at least 1 decimal place.) о (d) The distance d separates the twice-bent ray from the path it would have taken without the glass in the way. What is this distance (in cm)? cm (e) At what speed (in m/s) does the light travel within the glass? m/s (f) How many nanoseconds does the light take to pass through the glass along the angled path shown here? ns (g) Is the travel…arrow_forwardYou can see part of the back of your head if you have two mirrors mounted at an acute angle. The picture shows a top view of this with a ray of light that starts at the side of your head, reflects off both mirrors and to your eye. If you are standing equidistant from both mirrors and the angle between the mirrors is 67.4o, what is the angle of reflection from the first mirror? Please give your answer in degrees.arrow_forwardA ray of light travels from air into another medium, making an angle of θ1 = 45.0° with the normal as in the figure below. (A light ray in air is moving down and to the right and is incident on a second medium. It makes an angle θ1 with the vertical. Inside the vertical, it continues to move down and to the right but at a steeper slope than the incident ray. It makes an angle θ2 with the vertical.) (a) Find the angle of refraction θ2 if the second medium is ice. °(b) Find the angle of refraction θ2 if the second medium is flint glass. °(c) Find the angle of refraction θ2 if the second medium is carbon tetrachloride. °arrow_forward
- A small candle is placed on the optical axis upright in front of an unknown spherical mirror. If the magnification of the image is 2.00 and the distance between object and image is 45.0 cm, what kind of mirror is this, concave or convex? What is the focal length of such a mirror?arrow_forwardThe two mirrors illustrated in the figure below meet at a right angle. The beam of light in the vertical plane indicated by the dashed lines strikes mirror 1 as shown. (Let d = 1.40 m and 0 = 42.0°.) Mirror 2 d A Ꮎ Mirror 1 (a) Determine the distance the reflected light beam travels before striking mirror 2. m (b) In what direction does the light beam travel after being reflected from mirror 2? ° above the horizontalarrow_forwardA plane mirror and a concave mirror (f = 8.70 cm) are facing each other and are separated by a distance of 23.0 cm. An object is placed between the mirrors and is 11.5 cm from each mirror. Consider the light from the object that reflects first from the plane mirror and then from the concave mirror. Find the location of the image that this light produces in the concave mirror. Specify this distance relative to the concave mirror. Number i C Object F Unitsarrow_forward
- The focal length of a concave mirror has a magnitude of 20 cm. What is its radius of curvature?arrow_forwardTwo light rays, originating from the same point, have an angle of 35.0° between them and reflect off a plane mirror. Determine the angle between the reflected rays.arrow_forwardAs shown in the figure, a ray of light strikes a plane mirror with some incident angle. The mirror is now rotated by an angle of ? = 19.0° about an axis through the point where N1 contacts the mirror, without altering the incident ray. The new position is shown by the line M2. (a) Determine the angle through which the reflected ray rotates if the incident angle is 40.0°.° (b) Determine the angle through which the reflected ray rotates if the incident angle is 50.0°.°arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON