
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
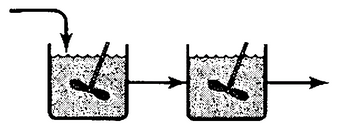

Transcribed Image Text:The reaction A → B takes place in two reactors in series as shown in the image. The reactors are
well-mixed but are not at steady-state. The unsteady-state mass balance for each stirred tank reactor is
shown below:
dC
A1
dt
dC
B1
dt
dC
A2
dt
dC
B2
=
dt
=
=
1
-+-+-(CA0 - CA1) - KC A1
T
AO
=
+/+CB₁+kC
KC
B1
T
1
+(CB₁ - CB2) - KC B2
B1
where CAO concentration of A at the inlet of the first reactor
A1
+-+-+-(CA₁ - CA₂) - KC A2
A1
CAL = concentration of A at the outlet of the first reactor (and inlet of the second)
CA2= concentration of A at the outlet of the second reactor
CBI concentration of B at the outlet of the first reactor (and inlet of the second)
=
CB2= concentration of B in the second reactor
T = residence time for each reactor
k
=rate constant for reaction of A to produce B
If CAO is equal to 20 mol/L, find the concentrations of A and B in both reactors during their first 10
minutes of operation using 4th order Runge-Kutta Method, with At = 0.10. Use k = 0.12/min and
T = 5 minutes, and assume that the initial conditions of all the dependent variables are zero. In
addition, make concentration profiles by plotting all the concentrations as a function of time for each
chemical species.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 15. A 500L reactor initially holds 200L of a solution containing A. "A" decomposes into "B" by the following equation: with the rate of A decomposition being given by: RA = -kc. where k is in min. Throughout this problem, the reactor is well-mixed and the concentrations of A and B are sufficiently low so that all solution densities are identical. Inadvertently, a batch of material is made without any A. Thus, after the reactor has been operating at steady-state for some time, stream 1 suddenly shifts to a solution having no A. How much time will pass before the concentration of A in the reactor decreases below 10 mmol/L? A. less than 5 min B. 5- 10 min C. 10– 20 min D. 20- 30 min E. More than 30 minarrow_forwardPlease help me with this.arrow_forwardA constant volume batch reactor undergoes the series reaction ki , k2 A BC The rates of disappearance per unit reactor volume are -TA = kı Cử ; -Ts = k2 C3 + kı C? Develop the mass balance equations for a constant density batch reactor and find closed-form solutions for CA(t), CB(t) and Cc(t) for the case where Ca = CA0 and CB = CBo and Cc = Cco = 0 at t = 0. Prove that the solutions are correct by substituting %3D back into the origianl set of ODES.arrow_forward
- 4.53 We wish to produce B in the reaction A → B in a continuous reactor at = 5 liter/min with CAo = 4 moles/liter. However, we find that there is a second reaction B → C that can also occur. We find that both reactions are first order and irreversible with k₁ = 1.0 min-¹ and k₂= 0.1 min-¹. Find T, V, CB.SB, and YB for 95% conversion of A in a PFTR and in a CSTR.arrow_forwardI have a reactor which is operating at steady state. The balanced reaction is shown below: 1A + 5 B => 2 M + 1 N The feed to the reactor contains only A and B, and B is fed in excess by 29 % of what is required to react all of the A. The reactor has a single outlet stream, and all unused reactants and all products leave the reactor in the same stream. The fractional conversion of the A in the reactor is 0.36. Calculate the mole fraction of M in the outlet from the reactor. Place your answer in the blank below, rounded to two decimal places.arrow_forwardA → B is carried out isothermally in a continuous reactor. Calculate both the CSTR and PFR reactor volumes necessary to consume 99% of A (i.e. CA = 0.01 CAO) when the entering molar flow rate is nA0 = 5 mol/h assuming the reaction -TA is 1. -TA = k 2. -TA = KCA 3. -TA = KC² The entering volumentric flow rate is V = 10 dm³/h. (Hint: Make use of equality n 40 No consider a Batch Reactor (BR) with a volume of V = 1000 dm³. Take the three reaction O rates from above and caclulate the times necessary to consume 99.9% of species A if the initial concentration is CAO 0.5 mol/dm³. with k = 0.05 mol h-dm3 with k = 0.0001 with k=3 dm³ mol-h :CAO V) =arrow_forward
- You are designing a reactor for a process that has the following decomposition reaction: A →D + 2F The rate law for this reaction is unknown and must be determined by an experiment. Since the reaction takes place in the liquid phase, you choose to build a CSTR reactor. You allow the reactor to fill to a certain volume, V, and then adjust the inlet and outlet volumetric flow rates to equal values, vo, to allow the system to reach steady state. Once the system is at steady state you measure the outlet concentration, CA. The residence time (t = V/v.) is increased by turning off the outlet flow, which allows the volume to increase, then setting the outlet flow to its original value and waiting until steady state is reached. You measure the concentration again and repeat this procedure multiple times to obtain the following table. Measurement 1 2 (ii) 234 in 3 5 Residence Time (min) 15.0 38.0 100 300 1200 Concentration (mol/L) 1.50 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 The inlet concentration (containing…arrow_forwardThe liquid phase reaction A + B → C follows an elementary law of velocity and occurs isothermally in a flow-through system. The rules for the feed streams of A and B are 2.0 mol/L before mixing. The volumetric flow rate of each stream is 5 dm3/min, and the inlet temperature is 300 K. The streams are mixed just before entering. Two reactors are available. One is a 200 dm3 CSTR, which can be heated to 77oC or cooled to 0oC; another is an 800 dm3 PFR, operated at 300 K, which cannot be heated or cooled. Note that k = 0.07 dm3 / mol.min at 300K and E = 20 kcal / mol. (A) What conversion would be achieved if the CSTR and PFR were operated at 300K and connected in series? And in parallel with 5 mols/min each? (B)Knowing that the operating times (loading, unloading, heating, cleaning, etc.) of the batch reactor is around 3 h, what volume of batch reactor would be necessary to process, per day, the same amount of species A as in reactors with Flow so as to achieve 90% conversion?arrow_forwardThere is heavier traffic in the L.A. basin in the mornings and in the evenings as workers go to and from work in downtown L.A. Consequently, the flow of CO into the L.A. basin might be better repre- sented by the sine function over a 24-hour period. P1-5, The reaction A → B is to be carried out isothermally in a continuous-flow reactor. The entering volumetric flow rate vo is 10 dm/h. (Note: FA = C,v. For a constant volumetric flow rate v=v,, then FA = C,vo. Also, CAo = FA/vo = ([5 mol/h\/[10 dm³/h]) 0.5 mol/dm³.) Calculate both the CSTR and PFR reactor volumes necessary to consume 99% of A (i.e., CA = 0.01CA0) when the entering molar flow rate is 5 mol/h, assuming the reaction rate –ra is mol (a) -ra = k with k = 0.05 [Ans.: VesTR = 99 dm³] h-dm3 (b) -ra = kCA with k = 0.0001 s-! dm3 (c) -ra = kC with k = 300 mol ·h [Ans.: VesTr = 660 dm³] (d) Repeat (a), (b), and/or (c) to calculate the time necessary to consume 99.9% of species A in a 1000 dm³ constant-volume batch reactor with CA0…arrow_forward
- please work out all the partsarrow_forwardA 1000 m3 lake is found to be contaminated with TCE (trichloroethane) that is potentially toxic to organisms. The concentration of TCE is 1.5 mg/L under steady-state conditions. Assume the lake behaves as a CSTR (completely stirred tank reactor). The decay of TCE is a first-order reaction with the rate constant of 2×10-6 s-1. If the source of TCE is closed off and the lake is to be flushed with clean water at a rate of 0.15 m3/s, how long will it take to lower the TCE concentration to 0.15 mg/L? Hint: You need to write the mass balance equation (VdC/dt=input rate-output rate-reaction rate) for this flushing (dilution) process and derive the concentration over time. The reaction rate for the first order kinetics is dC/dt= -kCV, where C is the pollutant concentration in the lake, t is the time, V is the lake water volume and k is the reaction rate constant. Group of answer choices A. 3 h B. 4.2 h C. 5.3 h D. 6.4 harrow_forwardillustrates an endothermic reactor applied in the production of methanol. Design a P&ID for this reactor by considering that the reactor temperature and pressure are needed to be maintained at a specific value.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The