
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
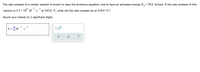
Transcribed Image Text:The rate constant of a certain reaction is known to obey the Arrhenius equation, and to have an activation energy E,= 19.0 kJ/mol. If the rate constant of this
a
8.
- 1
-1
reaction is 2.5 × 10° M
at 343.0 °C, what will the rate constant be at 310.0 °C?
'S
Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
- 1
- 1
k
I| M
•S
x10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Some measurements of the initial rate of a certain reaction are given in the table below. N2|||H2|initial rate of reaction 2.46M 2.06M 0.603M/s 11.3М| 2.06М 12.7M/s 2.46M 5.01М 3.57M/s Use this information to write a rate law for this reaction, and calculate the value of the rate constant k. Round your value for the rate constant to 3 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. rate = k ||| k =arrow_forwardSome measurements of the initial rate of a certain reaction are given in the table below. [N₂] H₂ initial rate of reaction 1.23M | 2.41M 95.0M/s 0.335M 2.41 M 25.9 M/s 1.23 M 6.52M 695. M/s Use this information to write a rate law for this reaction, and calculate the value of the rate constant k. Round your value for the rate constant to 3 significant digits. Also be sure your answer has the correct unit symbol. rate = k x10 k <= 0 Ś ? Xarrow_forwardCalculate the heat change at 0 °C for each of the following, and indicate whether heat was absorbed/released: -calories to melt 65 g of ice -kilojoules to freeze 50.0 g of waterarrow_forward
- TIAarrow_forwardCalculate the average rate of a reaction, given the following data: Reaction Data Time (s) Concentration (mol/L) 60 5.00 × 10-² 85 3.25 x 10-²arrow_forwardThe rate constant k for a certain reaction is measured at two different temperatures: temperature k 142.0 °C 6.1 x 1011 226.0 °C 3.7 x 10¹2 Assuming the rate constant obeys the Arrhenius equation, calculate the activation energy E for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. mol ×arrow_forward
- A certain catalyzed reaction is known to have an activation energy E =39.0 kJ/mol. Furthermore, the rate of this reaction is measured at 278. K and found to be 4.7 × 10² M/s. Use this information to answer the questions in the table below. Suppose the concentrations of all reactants is kept the same, but the temperature is lowered by 10% from 278. K to 250. K. How will the rate of the reaction change? Suppose the concentrations of all reactants is kept the same, but the catalyst is removed, which has the effect of raising the activation energy by 5%, from 39.0 kJ/mol to 41.0 kJ/mol. How will the rate of the reaction change? The rate will The rate will choose one ✓ choose one stay the same rise about 5% rise more than 5% rise less than 5% fall about 5% fall more than 5% fall less than 5%arrow_forwardThe rate constant k for a certain reaction is measured at two different temperatures: temperature 274.0 °C 348.0 °C E = a Assuming the rate constant obeys the Arrhenius equation, calculate the activation energy E for this reaction. a k 4.2 × 10 ¹0 11 1.8 × 10¹ Round your answer to 2 significant digits. kJ mol x10 X Śarrow_forwardThe rate constant k for a certain reaction is measured at two different temperatures: temperature k 70.0 °C 5.6 x 107 -63.0 °C 3.1 × 106 Assuming the rate constant obeys the Arrhenius equation, calculate the activation energy E for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. kJ E = mol O2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Te 43,203 FEB 18 CH.9 PP ASSESS MacBook Airarrow_forward
- Only typed solution.arrow_forwardOne mechanism for the destruction of ozone in the upper atmosphere is Os (9) + NO(g) → NO₂(g) + O2(g) Slow NO₂(g) + 0(g) → NO(g) + O₂(g) Fast Overall reaction O3(g) + O(g) → 20₂ (g) a. Which species is a catalyst? ONO 003 002 O NO2 b. Which species is an intermediate? ONO 003 002 O NO₂ c. E₂ for the uncatalyzed reaction 03 (g) + 0(g) → 20₂ (g) is 14.0 kj. E for the same reaction when catalyzed is 11.9 kJ. What is the ratio of the rate constant for the catalyzed reaction to that for the uncatalyzed reaction at 85°C? Assume the frequency factor A is the same for each reaction. Ratio = [References) Submit Answer Try Another Version frem atempt remaning (Pr Previousarrow_forwardGeneral Chemistry 4th Edition McQuarrie • Rock • Gallogly University Science Books presented by Macmillan Learning The reaction C,H, (g) → 2 C,H,(g) has an activation energy of 262 kJ/mol. At 600.0 K, the rate constant, k, is 6.1 × 10-8 s-1. What is the value of the rate constant at 750.0 K? k = 1.34 x103 Incorrectarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY