
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
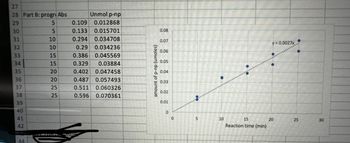
The purpose of the progress curve is to determine if an enzymatic reaction rate remains constant for given concentrations of enzyme and substrate, for a given assay time (20 min). How long did the rate of reaction of WGAP remain constant in your experiments? How do you know? What would cause the reaction rate to not be constant and plateau after some time?
Transcribed Image Text:27
28 Part B: progr Abs
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
44
5
5
10
10
15
15
20
20
25
25
Unmol p-np
0.109 0.012868
0.133 0.015701
0.294 0.034708
0.29 0.034236
0.386 0.045569
0.329 0.03884
0.402 0.047458
0.487 0.057493
0.511 0.060326
0.596 0.070361
"Mur
amount of p-np (umoles)
0.08
0.07
0.06
0.05
0.04
0.03
0.02
0.01
0
0
5
10
15
Reaction time (min)
y=0.0027x
20
25
30
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of proteins in a cell extract provides a qualitative way to compare proteins with respect to intra- cellular abundance. Describe a quantitative approach to the deter- mination of number of molecules of an enzyme per cell.arrow_forwardIf the higher value of KM resulting in the new plot ( red curb ) is due to the presence of an enzyme inhibitor is inhibitor reversible or irreversible? And why?arrow_forwardYou design an enzyme assay and choose a substrate concentration equal to the Km of the enzymatic reaction. You measure the rate of the reaction at this substrate concentration to be 75.0 μmol/min. Calculate the Vmax of this reaction in μmol/min. Express your answer with one decimal place. Your previous attempt suffered from low signal-to-noise ratio when you used a substrate concentration equal to the Km. So you decide to increase the substrate concentration to 0.45 mM. You remeasure the rate of the reaction at this new substrate concentration and find it to be 135.0 μmol/min. Using the same Vmax value found above, calculate the Km value of this enzymatic reaction. Express your answer in μM with one decimal place. Considering the previous two questions, what would be the rate of the reaction at a substrate concentration of 0.01 mM? Express your answer in μmol/min with one decimal place.arrow_forward
- The IAP kinetics assay was preformed at a basic pH. What does this tell you about the reaction environment ?arrow_forwardAn uncatalyzed reaction progresses at a rate of 20micromoles per minute while the same reaction in the presence of an enzyme progresses at a rate of 100micromoles per second. What is the rate enhancement achieved by the presence of the enzyme? At 25oC, how much energy is required to produce a 10-fold rate enhancement? At the same temperature, how much energy is required to produce a million-fold rate acceleration?arrow_forwardIf 10 µM enzyme was used to obtain the data in the summary plot below, k-cat = ________________ sec-1 and efficiency = _________________ sec-1 M-1 for this enzyme. (Enter numeric answers to the nearest integer; Do NOT write unts.)arrow_forward
- A protein (PrX) was heated in vitro to 45C for 15 min, in the presence or absence of Hsp40, Hsc70, and ATP. The amount of PrX in aggregated (P, pellet) and soluble (S) fractions was then quantified (Bars, 1 SD). Based on these data, answer the following questions. In all cases, give brief justification for your answer. a) How does Hsp40 alone influence the solubility of PrX? b) How does Hsc70 alone influence the solubility of PrX? c) Do Hsp40 and Hsc70 co-operate in this experiment? d) Which components combined provide maximal solubility of PrX after heat shock?arrow_forwardMichaelis Menton Plot and a Lineweaver-Burke plot using this dataarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON