
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
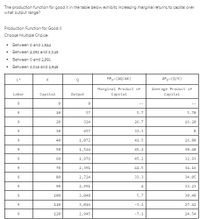
Transcribed Image Text:The production function for good X in the table below exhibits increasing marginal returns to capital over
what outout range?
Production Function for Good X
Choose Multiple Choice:
Between o and 1,524
Between 2391 and 3,048
Between o and 2,991
• Between 3,016 and 2,945
L*
MPx= (AQ/AK)
AP=(Q/K)
Marginal Product of
Average Product of
Labor
Capital
Output
Capital
Capital
10
57
5.7
5.70
20
324
26.7
16.20
30
657
33.3
40
1,072
41.5
26.80
50
1,524
45.2
30.48
60
1,976
45.2
32.93
70
2,391
41.5
34.16
2,724
33.3
34.85
9e
2,991
A
33.23
10e
3,048
5.7
30.48
11e
3,016
-3.2
27.42
120
2,945
-7.1
24.54
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Units of fixed input K Labor Hours (L) Output (Q) TFC TVC TC AFC AVC ATC MC 3 0 0 3 1 4 3 2 90 3 3 160 3 4 200 3 5 230 3 6 250 3 7 260 3 8 265 A firm has the following production function: Q=f (L/K). It must pay $20 per hour of labor and rents its fixed inputs (K) for $30 per unit. Complete the following table and answer the questions that follow:arrow_forward6arrow_forward1. The following production function is used to produce wheat, q, from capi- tal, K, and labour, L: q = f(K, L) = «³K/3 + B³L/3 a) Describe the role of a and B in this production function. b) Derive the slope of an isoquant for this production function and in- terpret your result. Draw the isoquant in (K L) space, labeling where appropriate. The drawing does not need to be exact, but the curvature needs to be approximately correct. Explain why under- standing the curvature is so important. | c) Does this production function follow the "Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns"? Show your work and explain your answer.arrow_forward
- Consider the production function from earlier: Quantity of Haircuts 20 15 10 0+0 0 N 2 8 14 O Increasing marginal productivity O Constant marginal productivity O Decreasing marginal productivity 3 19 23 Labor (hours) 27 26 Total Product Curve From 1 labor hour up to 7 labor hours, what sort of marginal productivity does this production function have?arrow_forwardConsider the following production function for shirts: q = v6 L3/4K/4, where L is worker-hours, and K is sewing machine-hours. a. Compute the marginal products of labor and capital, the average product of labor, and the marginal rate of technical substitution of labor for capital (i.e. how many units of capital are needed to make up for the loss of one unit of labor)? b. Are there diminishing returns to labor (that is, does the marginal product of labor decrease when labor L increases)? What about to capital? Is there diminishing marginal rate of technical substitution (MRTS)? с.arrow_forwardQUESTION 39 The folllowing table shows data for a simple production function. Capital (K). Labor (L) 10 0 10 1 10 2 3 4 5 6 10 10 10 10 TP or Q AP MP 6 14 20 14 8 Assume that the cost of capital, PK, is $50 per unit, and the cost of labor, PL, is $100 per unit. Marginal cost, MC, is at minimum when labor, L, is equal to O2 units. O4 units. O 3 units. 5 units.arrow_forward
- 13. Suppose you have a production technology given by f(x1, x2) = min{2x₁, x2} and you are producing at the point where x₁ = 10 and x₂ = 20. (a) Explain in words what we mean (generally) by the ‘marginal product' of an input in production. (b) For the production technology in this question and the initial point x₁ = 10 and x2 = 20, what is the marginal product of a small increase in input 1? (c) Suppose input 2 increases and you are now at the initial point x₁ = 10 and x2 = 30. Relative to your answer in part (b), does the marginal product of input 1 decrease, increase, or stay constant? Explain briefly.arrow_forward***PLEASE NOTE - An answer is NOT needed for parts A, B and C; these are included to assist with answering part D. Only an answer for part D is required, but it is derived from the previous answers*** Given: A farmer raises peaches using land (K) and labor (L), and has an output of ?(?,?)= ?0.5?0.5 bushels of apples. a. Find several input combinations that give the farmer 6 bushels of apples. Sketch the associated isoquant on a graph, with L on the x-axis and K on the y-axis. b. In the short run, the farmer only has 4 units of land. What is his short-run production function? Graph it for values of L from 0 to 16, with L on the x-axis and output on the y-axis. What is the name of the slope of this curve? c. Assuming the farmer still only has 4 units of land, how much extra output does he get from adding 1 extra unit of labor if he is already using only 1 unit of labor? How much extra output does he get from adding 1 extra unit of labor if he is already using 4 units of labor?…arrow_forwardF. None of the above 4) Please indicate whether the following production function has the characteristic of CRS, IRS and DRS. (b) F(K, L)=[aKP +(1-a)Le ]1/e, (1>a>0, 1>p) 1. CRS 2. IRS 3. DRS 4. None of the abovearrow_forward
- dien There are two factors in a production function y = x 113 x₂¹1³. The market price of each unit ofy is p=3, and the factor prices are w₁=1 and W₂=2 for x₁ and X₂ respectively. variable (a). Calculate your cost function as a function of y if X, and x₂ are both barible factors. (b). Now derive the functions of average and marginal cost and plot them against quantity (C). Solve for your optional output of y. Calculate the ratio of two factors (X₁/X₂) (d). In the short run the fixed factor is set at X₂=1. What is the new optimal output level now?arrow_forwardConstrained Optimization: Cobb-Douglas Production Function:1. Based from the factor shares of the two inputs, what will happen to the number of output if it the firm decides to triple both the amount of labor and capital?2. State the optimization problem of the firm.3. Solve for the formulas of the Marginal Product of Labor (MPL), and Marginal product ofCapital (MPK)4. Using your knowledge of the tangency condition in Producer’s theory, find the combinationof K and L that the firm should use to produce the maximum possible output. Do not solvethe problem using the Lagrangian method.Note: The tangency conditions just states that the slope of the production function must beequal to the slope of the isocost function.5. What is the maximum possible output that the firm could earn given the constraint it faces?arrow_forwardProblem 5 Suppose that a firm has a production function f(K, L) = 12L¹/3 K¹/3 and that w and r are input prices and p is output price. The firm does not change those prices. a) Show that the firm's profit π is a concave function of (K, L). b) Find (K*, L*) that maximizes the profit, as a function of (w,r, p).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education