
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
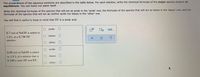
Transcribed Image Text:The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major specles present at
equilibrium. You can leave out water itself.
Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the
formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row.
You will find it useful to keep in mind that HF is a weak acid.
ロ□ロ
acids:
00..
0.7 mol of NaOH is added to
bases:|
1.0 L of a 0.7M HF
solution.
other:
acids:
0.09 mol of NaOH is added
to 1.0 L of a solution that is
bases:
0.5M in both HF and KF.
O other:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Order these chemical species by increasing pH of an 0.1 M aqueous solution of each. That is, imagine making an 0.1 M solution of each species. Select 1 next to the species that makes the solution with the lowest pH. Select 2 next to the species that makes the solution with the next higher pH, and so on. Notice that some of the rankings have been filled in for you already. Also notice that water is on the list. For that particular case, just compare the pH of pure water to the pH of the other solutions. Note for advanced students: for all charged species, you may assume the necessary counterions act as neither acids nor bases. relative pH of 0.1 M aqueous solution species NO2 |(Choose one) HNO, 2 H,O 4 103 5 НСООН (Choose one) ▼ OH (Choose one) HIO3 (Choose one) НСОО 7arrow_forwardIdentify whether each species functions as a Brønsted-Lowry acid or a Brønsted-Lowry base in this net ionic equation. HF (aq) + SO32- ⇌ F- + HSO3- Brønsted-Lowry Brønsted-Lowry Brønsted-Lowry Brønsted-Lowry In this reaction: The formula for the conjugate of HF is The formula for the conjugate of SO32- isarrow_forwardOrder these chemical species by increasing pH of an 0.1 M aqueous solution of each. That is, imagine making an 0.1 M solution of each species. Select 1 next to the species that makes the solution with the lowest pH. Select 2 next to the species that makes the solution with the next higher pH, and so on. Notice that some of the rankings have been filled in for you already. Also notice that water is on the list. For that particular case, just compare the pH of pure water to the pH of the other solutions. Note for advanced students: for all charged species, you may assume the necessary counterions act as neither acids nor bases. species so 103 OH F 2- HSO4 HIO3 H₂O HF relative pH of 0.1 M aqueous solution 6 (Choose one) ▼ 8 (highest) 7 (Choose one) 1 (lowest) (Choose one) ▼ (Choose one) X ? 圖 olaarrow_forward
- Type your anSwers in all of the Let's consider two dilute acid solutions that are both made at a concentration of 0.010 M. One solution is made with HCl and one solution is made with HClO. Complete the following sentences based on these two solutions. HCl is a Type your answer here acid while HCIO is a Type your answer here acid. (strong, weak) The pH of the HCl solution is Type your answer here Due to the difference in acid strength, HCIO dissociates Type your answer here than HCl. (more, less) This means that there is Type your answer here (more, less) Htor H.0t produced in the HCIO solution than in the HCl solution. Higher hydronium ion concentration corresponds to a Type your answer here pH value. (higher, lower) Altogether, this means that the pH of the HCIO solution is Type your answer here than the HCl solution. (higher, Fullscreen lower) 10:40 PM a の 5/8/2021 hp enter pause ↑ shift endarrow_forwardO ACIDS AND BASES Identifying the major species in weak acid or weak base.. 0/5 The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that NH, is a weak base. acids: 0.8 mol of HCl is added to 1.0 L of a 0.8 M NH3 bases: solution. other: 0.2 mol of NAOH is added to acids: 1.0 L of a solution that is bases: U 0.4M in both NH, and NH,C1. O other: O O O Oarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- O ACIDS AND BASES Identifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria Ryan The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that HCH,CO, is a weak acid. O, acids: 0 ol 0.4 mol of NAOH is added to 0,0,.. 1.0 L of a 0.2 M HCH;CO2 O bases: CH,CO,OH 18 Ar solution. other: Na 0.58 mol of HI is added to acids: I 1.0 L of a solution that is 1.3 M in both HCH;CO2 bases: and KCH;CO,. other: Explanation Check 2020 McGraw-Hill Education. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy MacBook Pro 1IIarrow_forwardThe pH of an aqueous solution at 25°C was found to be 9.20. The pOH of this solution is | The hydronium ion concentration is M. The hydroxide ion concentration is M.arrow_forwardFor the reaction: H2CO3 (aq) + CN- (aq) ⇌ HCN )aq) + HCO3- (aq) label each species as an acid or a base. For the base on the left, what is the conjugate acid?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY