
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
8.20 The piston diameter of a certain hand pump is 0.6 inch. The manager determines that the diameters are
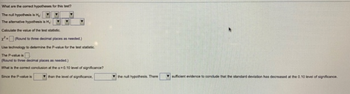
Transcribed Image Text:**Hypothesis Test for Standard Deviation**
**What are the correct hypotheses for this test?**
- **The null hypothesis is \( H_0: \)**
- \(_\square\) \( \sigma \leq \)
- \(_\square\) \( \sigma \geq \)
- \(_\square\) \( \sigma = \)
- **The alternative hypothesis is \( H_1: \)**
- \(_\square\) \( \sigma < \)
- \(_\square\) \( \sigma > \)
- \(_\square\) \( \sigma \neq \)
**Calculate the value of the test statistic.**
- \( \chi^2 = \_\_ \) (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
**Use technology to determine the P-value for the test statistic.**
- **The P-value is \_\_** (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
**What is the correct conclusion at the \(\alpha = 0.10\) level of significance?**
- Since the P-value is \(_\square\) than the level of significance, \(_\square\) the null hypothesis. There \(_\square\) sufficient evidence to conclude that the standard deviation has decreased at the 0.10 level of significance.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A synthetic fiber used in manufacturing carpet has tensile strength that is normally distributed with mean 75.5 psi and standard deviation 3.5 psi. How is the standard deviation of the sample mean changed when the sample size is increased from n = 4 ton = 48 Round all intermediate calculations to four decimal places (e.g. 12.3456) and round the final answer to three decimal places (e.g. 98.768). The standard deviation is reduced ✓by i 1.25 psi. Statistical Tables and Chartsarrow_forwardA state school administrator says that the standard deviation OT SAI critical reading test scores is 114. A random sample of 19 SAT critical reading test scores has a standard deviation of 143. At α = 0.10, is there enough evidence to reject the school administrator's claim? Assume the population is normally distributed.arrow_forwardSony would like to test the hypothesis that the average age of a PlayStation user is different from the average age of an Xbox user. A random sample of 32 PlayStation users had an average age of 33.7 years while a random sample of 36 Xbox users had an average age of 35.6 years. Assume that the population standard deviation for the age of PlayStation and Xbox users is 3.7 and 3.5 years, respectively. Sony would like to set α = 0.05. The p-value for this hypothesis test would bearrow_forward
- An engineer working for a tire manufacturer investigates the average life of a new material to be used in the manufacturing process. For this purpose, he builds a sample of 13 tires and tests them in a laboratory until the end of their useful life is reached. The data obtained from the sample are as follows: average of 60897.9 km and standard deviation of 2734.8 km. The engineer would like to demonstrate that the average service life of the tire with the new material exceeds 60,000 km. a) State the null and alternative hypothesis to be stated in this experiment. Test the stated hypotheses using an α = 0.05 What conclusions are reached? b) Find a 95% confidence interval for the average tire life with the new material. Interpret your answer. (RESPOND MANUALLY) (RESPOND MANUALLY)arrow_forwardA light bulb manufacturer guarantees that the mean life of a certain type of light bulb is at least 754 hours. A random sample of 30 light bulbs has a mean life of 732 hours. Assume the population is normally distributed and the population standard deviation is 62 hours. At a = 0.05, do you have enough evidence to reject the manufacturer's claim? Complete parts (a) through (e). Zo = - 1.65 (Use a comma to separate answers as needed. Round to two decimal places as needed.) Identify the rejection region(s). Choose the correct answer below. O A. B. O C. Fail to reject H- Fail to reject Ho Fail to reject Ho- Reject Ho Reject Ho Reject Ho Reject H,- -4arrow_forwardSuppose babies born after a gestation period of 32 to 35 weeks have a mean weight of 2600 grams and a standard deviation of 600 grams while babies born after a gestation period of 40 weeks have a mean weight of 2900 grams and a standard deviation of 440 grams. If a 35-week gestation period baby weighs 2775 grams and a 40-week gestation period baby weighs 3075 grams, find the corresponding z-scores. Which baby weighs more relative to the gestation period? Find the corresponding z-scores. Which baby weighs relatively more? Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) A. The baby born in week 40 weighs relatively more since its z-score, is smaller than the z-score of for the baby born in week 35. B. The baby born in week 40 weighs relatively more since its z-score, is larger than the z-score of for the baby born in week 35. O C. The baby born in week 35 weighs relatively more since its z-score, is larger…arrow_forward
- The blood platelet counts of a group of women have a bell-shaped distribution with a mean of 264.8264.8 and a standard deviation of 60.960.9. (All units are 1000 cells/muμL.) Using the empirical rule, find each approximate percentage below. a. What is the approximate percentage of women with platelet counts within 11 standard deviationdeviation of the mean, or between 203.9203.9 and 325.7325.7? b. What is the approximate percentage of women with platelet counts between 82.182.1 and 447.5447.5?arrow_forwardIn a certain country the heights of adult men are normally distributed with a mean of 69.7 inches and a standard deviation of 2.5 inches. The country's military requires that men have heights between 65 inches and 76 inches. Determine what percentage of this country's men are eligible for the military based on height. The percentage of men that are eligible for the military based on height is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) %. (1) U +arrow_forwardAn obstetrician read that a newborn baby loses on average 7 ounces in the first two days of his or her life. He feels that in the hospital where he works, the average weight loss of a newborn baby is less than 7 ounces. A random sample of 30 newborn babies has a mean weight loss of 6.4 ounces. The population standard deviation is 1.6 ounces. Is there enough evidence at =α0.01 to support his claim? Assume that the variable is normally distributed. Use the critical value method with tables. hello the question askas to find the critical value compute the test value and select the hypothesisarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman