
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
A random sample of 76 eighth grade students' scores on a national mathematics assessment test has a
Assume that the population standard deviation is 33.
At α=0.11, is there enough evidence to support theadministrator's claim? Complete parts (a) through (e).
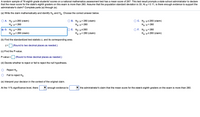
Transcribed Image Text:A random sample of 76 eighth grade students' scores on a national mathematics assessment test has a mean score of 267. This test result prompts a state school administrator to declare
that the mean score for the state's eighth graders on this exam is more than 260. Assume that the population standard deviation is 33. At a = 0.11, is there enough evidence to support the
administrator's claim? Complete parts (a) through (e).
(a) Write the claim mathematically and identify Ho and Ha. Choose the correct answer below.
Ο Α. H: μ2 260 (claim)
O B. Ho: µ= 260 (claim)
Ha:µ > 260
O C. Ho: µs 260 (claim)
Ha: µ> 260
Ha:µ<260
O D. Ho: µ = 260
Ha: µ> 260 (claim)
O E. Ho: µs260
Ha: µ> 260 (claim)
O F. Ho: µ<260
Ha: µ2 260 (claim)
(b) Find the standardized test statistic z, and its corresponding area.
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
(c) Find the P-value.
P-value =|(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
(d) Decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Reject Ho
Fail to reject Ho
(e) Interpret your decision in the context of the original claim.
At the 11% significance level, there
V enough evidence to
the administrator's claim that the mean score for the state's eighth graders on the exam is more than 260.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose babies born after a gestation period of 32 to 35 weeks have a mean weight of 2500 grams and a standard deviation of 700 grams while babies born after a gestation period of 40 weeks have a mean weight of 2700 grams and a standard deviation of 340 grams. If a 34-week gestation period baby weighs 2275 grams and a 40-week gestation period baby weighs 2475 grams, find the corresponding z-scores. Which baby weighs less relative to the gestation period?arrow_forwardSuppose babies born after a gestation period of 32 to 35 weeks have a mean weight of 3000 grams and a standard deviation of 1000 grams while babies born after a gestation period of 40 weeks have a mean weight of 3500 grams and a standard deviation of 545 grams. If a 35-week gestation period baby weighs 3300 grams and a 41-week gestation period baby weighs 3800 grams, find the corresponding z-scores. Which baby weighs more relative to the gestation period? ..... Find the corresponding z-scores. Which baby weighs relatively more? Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) A. The baby born in week 41 weighs relatively more since its z-score, is larger than the z-score of for the baby born in week 35. O B. The baby born in week 35 weighs relatively more since its z-score, is larger than the z-score of for the baby born in week 41. C. The baby born in week 41 weighs relatively more since its z-score, is…arrow_forwardSuppose the mean and standard deviation of the GPAs at Tulane are Xbar = 2.899; and s = -0.753Charlie's GPA has a z-score of -0.140. What is Charlie's GPA?(Leave your answer to 2 decimals: ex: 1.23)arrow_forward
- A sample of size 50 will be drawn from a population with mean 76 and standard deviation 14. Find the 69th percentile of x.arrow_forwardAlthough the two lines are exactly the same length, the vertical line appears to be much longer. To examine the strength of this illusion, a researcher prepares an example in which both lines are exactly 10 inches long. The example is shown to individual participants who are told that the horizontal line is 10 inches long and then are asked to estimate the length of the vertical line. For a sample of n = 25 participants, the average estimate is M = 12.2 inches with a standard deviation of s = 1.00. Use a one-tailed hypothesis test with α = .01 to demonstrate that the individual participants in the sample significantly overestimate the true length of the line. (Note: Accurate estimation would produce a mean μ = 10 inches.) (Use three decimal places.) t-critical = t = The results indicate: Failure to reject the null hypothesis; there is not significant evidence that the true length of the vertical line is overestimated Failure to reject the null…arrow_forwardGn. don't provide handwriting solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman