
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I've done simmlar problems before but I can't figure out how to factor in the top part of the pendulum can you show me what I am missing here?
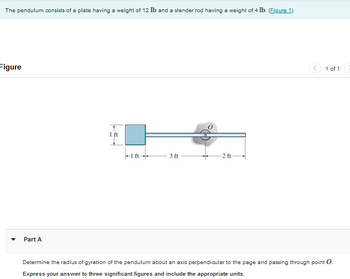
Transcribed Image Text:The pendulum consists of a plate having a weight of 12 lb and a slender rod having a weight of 4 lb. (Figure 1)
Figure
Part A
1 ft
3 ft
2 ft-
1 of 1
Determine the radius of gyration of the pendulum about an axis perpendicular to the page and passing through point O.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Please fast vey fast please pleasearrow_forwardDetermine the radius of gyration kx (in inches) of the homogeneous body (shown in the image below) about the x axis. The specific weight of the material is g = 400 Ib/ft°, the length /= 10 in., and the exponent in the equation a = 1.9. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 3 places after the decimal point. ya = x Your Answer: Answerarrow_forwardwheel with a mass of 20 kg and a radius of inertia of 300mm, moves under the influence of a torque of 100Nm. Find the angular acceleration of the wheel, the linear acceleration of its center O, the wheel pressure n the ground N, and the mass moment of inertia J. Give the result to 2 decimal places.arrow_forward
- Find the moments of inertia in kg-m2 of the pendulum shown in the figure below about the z-axis. The x and y axes are in the plane of the pendulum. Ris a slender rod of 1.0 kg, and D is a semicircular disk of 2.0 kg. L = 1.1 m and r = 0.25 m. R L D Figure is from "Engineering Mechanic An Introduction to Dynamics", McGill and King.arrow_forwardDetermine equivalent inertia and equivalent stiffness of the system shown in Figure. Mass of the bar is M. Use rotation of the bar (0) as the generalized coordinate. L L/4 2m k₁ m 2karrow_forwardThe mass of the gear is 48 kg and it has a radius of gyration of ko = 125 mm. The mass of the gear rack is 22 kg. Assume that the contact surface between the gear rack and the horizontal plane is smooth. (Figure 1) Figure 150 mm- 75 mm vira 1 of 1 P = 150 N Part A If the cord is subjected to a horizontal force of P = 150 N, and gear is supported by a fixed pin at O, determine the angular velocity of the gear in 1 s, starting from rest. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Enter positive value if the angular velocity is counterclockwise and negative value if the angular velocity is clockwise. Submit Part B V = μÀ Value Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Determine the velocity of the gear rack in 1 s, starting from rest. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Enter positive value if the velocity is rightward and negative value if the velocity is leftward. Value μA Units Request Answer www…arrow_forward
- Please write out the problem on paper and provide all steps and units.arrow_forwardThe material has a specific weight y = 70 lb/ft². (Figure 1) Figure 0.5 ft 0.25 ft/ 2 ft 1 ft 0.25 ft 1 of 1 Part A Determine the moment of inertia of the wheel about an axis which is perpendicular to the page and passes through point O. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Io = Submit LO Value Request Answer Units < Return to Assignment Provide Feedback ?arrow_forwardA pleasearrow_forward
- Consider the assembly shown in (Figure 1). Suppose that a = 1.3 ft , b = 0.4 ft , r= 1 ft , and d = 0.15 ft . The material has a specific weight of γ = 90 lb/ft3 Determine the moment of inertia of the assembly about an axis that is perpendicular to the page and passes through point O.arrow_forward4. Please explain the answer.arrow_forwardExample 3-3: Parallel-Axis theorem and composite bodies A clock pendulum consists of a slender rod and a circular disc with a hole in it as shown. The rod 20 cm has a density of 7000 kg/m3 and cross sectional area of 50 mm2 he disc has a density of 8000 kg/m3 and a thickness of 5 mm. 5 ст 10 ст Compute the moment of inertia of the pendulum about O.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY