
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
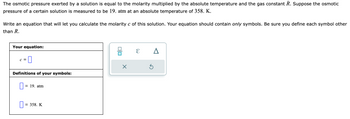
Transcribed Image Text:The osmotic pressure exerted by a solution is equal to the molarity multiplied by the absolute temperature and the gas constant R. Suppose the osmotic
pressure of a certain solution is measured to be 19. atm at an absolute temperature of 358. K.
Write an equation that will let you calculate the molarity c of this solution. Your equation should contain only symbols. Be sure you define each symbol other
than R.
Your equation:
-0
C =
Definitions of your symbols:
0 = 19. atm
0 = 358. K
010
X
ε Δ
S
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 304. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.0501 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardA 0.32 M aqueous solution of an unknown solute has a density of 1.08 g/mL. The molar mass of the solute is 146.8 g/mol. What is the molality of this solution? Report your answer in mol/kg and round to the second decimal place.arrow_forward114. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.0231 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. molarrow_forward
- 107. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.0197 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. mol Xarrow_forward203. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.149 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 0 mol x10 X Sarrow_forward458. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.0903 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. mol x10arrow_forward
- 45. A solution is prepared by dissolving 35.0 mg of hemoglobin in enough water to make up 15.0 mLin volume. The osmotic pressure of the solution is found to be 10.0 torr at 25.0 °C. Calculatethe molar mass of hemoglobin.arrow_forward140. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.133 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. g mol x10arrow_forward391. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.240 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forward
- Osmotic pressure data for a solution containing an unknown sugar are given below. Determine the molar mass of the sugar. T (atm) 2.59 5.06 7.61 12.75 18.13 23.72 density (g/L) 33.5 65.7 96.5 155 209 259arrow_forward296. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.0580 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forward454. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.119 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. bo molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY