
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
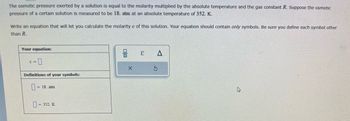
Transcribed Image Text:The osmotic pressure exerted by a solution is equal to the molarity multiplied by the absolute temperature and the gas constant R. Suppose the osmotic
pressure of a certain solution is measured to be 18. atm at an absolute temperature of 352. K.
Write an equation that will let you calculate the molarity c of this solution. Your equation should contain only symbols. Be sure you define each symbol other
than R.
Your equation:
c = 0
Definitions of your symbols:
= 18. atm
= 352. K
00
X
E
A
Ś
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 205. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.137 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. mol Xarrow_forward304. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.0501 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forward114. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.0231 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. molarrow_forward
- 107. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.0197 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. mol Xarrow_forward203. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.149 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 0 mol x10 X Sarrow_forward458. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.0903 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. mol x10arrow_forward
- 140. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.133 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. g mol x10arrow_forward228. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.0572 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. alo g x10 mol Ararrow_forward391. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.240 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forward
- Osmotic pressure data for a solution containing an unknown sugar are given below. Determine the molar mass of the sugar. T (atm) 2.59 5.06 7.61 12.75 18.13 23.72 density (g/L) 33.5 65.7 96.5 155 209 259arrow_forward296. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.0580 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forward454. mg of an unknown protein are dissolved in enough solvent to make 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution is measured to be 0.119 atm at 25.0 °C. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. bo molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY