
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134753119
Author: Sheldon Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
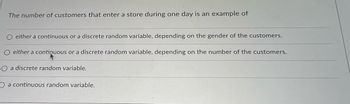
Transcribed Image Text:The number of customers that enter a store during one day is an example of
either a continuous or a discrete random variable, depending on the gender of the customers.
either a continuous or a discrete random variable, depending on the number of the customers.
O a discrete random variable.
O a continuous random variable.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Determine whether the random variable described is discrete or continuous.The total value of a set of coinsarrow_forwardMs. Burke's biology class has 115 students, classified by academic year and major, as illustrated in the table. Ms. Burke randomly chooses one student to collect yesterday's work. Academic Year Biology Majors Non-Biology Majors Freshman 9 16 Sophomore 18 18 Junior 13 9 Senior 16 16 What is the probability that she selects a biology major, given that she chooses randomly from only the freshman?arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Which of the following is not a random variable? The number of heads in ten tosses of a fair coin. The number of passengers in cars passing though a toll booth. The age of the driver in cars passing through a toll booth. The response of randomly-selected people to the question, “Did you eat breakfast this morning?” The response of randomly-selected people to the question, “How many hours of sleep did you get last night?"arrow_forwardA university conducted a survey of 272 Sophomore, Junior, and Senior undergraduate students regarding satisfaction with student government. Results of the survey are shown in the table by class rank. Sophomore Junior Senior Total Satisfied 48 65 59 172 Neutral 16 18 9. 43 Not satisfied 16 14 27 57 Total 80 97 95 272 A survey participant is selected at random. What is the probability that he or she is a Junior or Senior? The probability that a student is a Junior or a Senior is (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardThree students scheduled interviews for summer employment at the Tiket.com. In each case the interview results in either an offer for a position or no offer. Experimental outcomes are defined in terms of the results of the three interviews.a. List the experimental outcomes.b. Define a random variable that represents the number of offers made. Is the random variable continuous?c. Show the value of the random variable for each of the experimental outcomesarrow_forward
- What do we mean when we say that two random variables are independent? (Briefly. You may use an example to illustrate). (Recall that two events A and B are independent if P(A given B) = P(A), or equivalently, P(A and B) = P(A) times P(B) )arrow_forwardThe probability of randomly choosing a tea drinker who has a college degree. Assume that you are choosing from the population of all tea drinkers. The probability of choosing.... a. a tea drinker who is not in college b. a college graduate who does not drink tea c. a tea drinker who is in college d. a tea drinker who does not have a college degreearrow_forwardConsider a game of rolling a single die, with the outcome as the random variable X. A player gains $10 if the outcome is {1, 2, 3} and a player loses $5 if the outcome is (4, 5, or 6}. It does not cost anything to play the game. Calculate o. Round to 2 decimal places.arrow_forward
- determine whether the random variable x is discrete or continuous. let x represent the populations of the 50 U.S. statesarrow_forwardThe fish population of a small lake is has been found and is summarized in the table below. One fish is drawn out of the lake at random. Male Female | Totals. 200 300 400 700 600 1000 What is the probability that the fish is a male and a perch? Perch 100 Trout 300 Totals 400 100/400 400/1000 100/1000 100/300arrow_forwardA grocery store employs cashiers, stock clerks, and deli/bakery workers. The distribution of employees with and without dependents is shown here. Dependents Cashiers Stock Clerks Deli/Bakery Workers Yes 8 12 3 No 5 15 2 If an employee is selected at random, find the probability that the employee is a stock clerk or has dependents. A grocery store employs cashiers, stock clerks, and deli/bakery workers. The distribution of employees with and without dependents is shown here. Dependents Cashiers Stock Clerks Deli/Bakery Workers Yes 8 12 3 No 5 15 2 If an employee is selected at random, find the probability that the employee is a stock clerk or has dependents. 0.8444 0.60 0.5111 0.4889arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:PEARSON
