Question
B.) What is the current in the middle resistor
c.) imagine the resistors are lightbulbs, rank them from brightest to dimmest using leftmost as L then M for middle and R for right
Transcribed Image Text:**Text Transcription and Diagram Explanation for Educational Website**
---
**Problem Statement:**
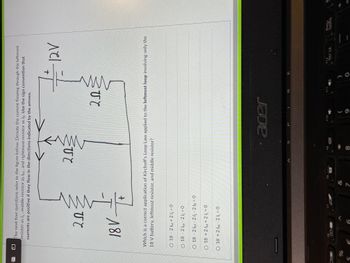
The next four questions refer to the figure below. Denote the current flowing through the leftmost resistor as \( I_L \), middle resistor as \( I_M \), and rightmost resistor as \( I_R \). Use the sign convention that currents are positive if they flow in the directions indicated by the arrows.
**Circuit Diagram:**
- There is a series circuit with the following components:
- An 18 V battery with the positive terminal connected to a 2 Ω resistor on the left.
- The leftmost 2 Ω resistor follows the 18 V battery.
- A middle 2 Ω resistor is connected after the leftmost resistor.
- The current flow is indicated by arrows pointing counter-clockwise through these two resistors.
- A separate loop on the right consists of a 12 V battery connected to a 2 Ω resistor on the right.
- The arrows indicate the current direction from the positive terminal of the 12 V battery, flowing clockwise through the rightmost resistor.
**Question:**
Which is a correct application of Kirchhoff's Loop Law applied to the leftmost loop involving only the 18 V battery, leftmost resistor, and middle resistor?
1. \( 18 - 2I_M + 2I_L = 0 \)
2. \( 18 - 2I_M - 2I_L = 0 \)
3. \( 18 + 2I_M + 2I_L = 0 \)
4. \( 18 + 2I_M - 2I_L = 0 \)
**Diagram Explanation:**
The circuit diagram illustrates a basic schematic with two loops. The left loop includes the 18 V battery and two resistors (both 2 Ω), while the right loop involves a 12 V battery and a single 2 Ω resistor. Arrows in the diagram specify the presumed direction of current flow for solving the problem using Kirchhoff’s Loop Law, which involves summing the electromotive forces and voltage drops around a closed circuit loop.
---
This transcription provides a clear and detailed understanding of the problem and diagram, facilitating educational use of the content related to Kirchhoff's laws in electrical circuits.
Transcribed Image Text:The image features an electrical circuit consisting of two voltage sources and three resistors. Here's a detailed description:
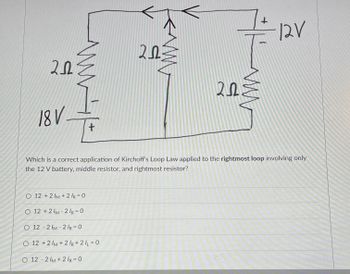
**Circuit Diagram:**
- There are two voltage sources in the circuit: an 18V battery on the left and a 12V battery on the right.
- Three resistors, each labeled as 2Ω, are positioned within the circuit: one on the left, one in the middle, and one on the right.
- The circuit is closed, forming two loops. Arrows indicate the current direction in each loop.
**Question:**
The challenge involves applying Kirchhoff's Loop Law to the rightmost loop of the circuit, which includes the 12V battery, the middle resistor, and the rightmost resistor. The goal is to determine which of the provided equations correctly represents Kirchhoff's Loop Law for this section of the circuit.
**Options:**
1. \(12 + 2I_M + 2I_R = 0\)
2. \(12 + 2I_M - 2I_R = 0\)
3. \(12 - 2I_M - 2I_R = 0\)
4. \(12 + 2I_M + 2I_R + 2I_L = 0\)
5. \(12 - 2I_M + 2I_R = 0\)
Here, \(I_M\) represents the current through the middle resistor, \(I_R\) represents the current through the rightmost resistor, and \(I_L\) might indicate current related to a left section of the circuit, but only options specific to the rightmost loop apply.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given Data:
Let all the resistance =
Voltage on left side
Voltage on right side
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Problem 8: Consider a circuit shown in the figure. Ignore the internal resistances of the batteries. A) Express the current I1 going through resistor R1 in terms of the currents I2 and I3 going through resistors R2 and R3. Use the direction of the currents as specified in the figure. B) Write the equation of potential change in loop EBAF in terms of the circuit elements. C) Write the equation of potential change in loop DCAF in terms of the circuit elements. D) Solve the three equations to get I3 as expression NOT a numerial valuearrow_forwardHOW and/or then) 1. a) The circuit below has three resistors with values R₁-10 S2, R2-20 2, R3-30 S2, one initially (t=0) uncharged 0.001 F capacitor, and a 30 V battery. Find all the currents at t=0 (right after the switch is closed,) all the currents a long time after the switch is closed (at steady state), and the charge on the capacitor at t→∞0. At time t₁, once steady state with the switch close has been effectively reached, the switch is reopened. Find the currents at this time, right after reopening the switch. Make sure to make your reasoning clear! T=t₁ 4+ ww R₁ b JE S R₂ www www. R3 30 0.001 D₁ I₂ Iz 1+²0 12 O +=2arrow_forwardPart A) Too much current can be a bad thing. When too much current flows through a wire, the wire heats up and either melts or causes a fire. Turning on too many appliances at the same time can cause a large amount of current to flow through the wiring in your home. Since this can be a dangerous thing, most homes are protected by a circuit breaker. A circuit breaker monitors the amount of current and shuts it down if the current becomes larger than a specified value. Suppose the circuit in your kitchen is protected by a circuit breaker that shuts off the current when it reaches 10 amperes. A new toaster oven that you have just purchased has a resistance of 8 ohms. When you plug the toaster into the 120-volt electric outlet, does the circuit breaker shut off? yes / no. Why or why not? Part B) What is the power rating of the toaster? In other words, how much power does the toaster normally consume? Show your work below:arrow_forward
- Need Help with #2arrow_forwardHow would the value of each of the four following physical quantities change over time after the switch is closed? Explain why for each case in 1 or 2 sentences. (You may assume that the resistance of the batteries, the wires, and the switch are negligibly small for this question). a. The voltage across the capacitor, VCAP b. The voltage across the light bulb, VBULB c. The current through light bulb, IBULB d. VBULB + VCAParrow_forwardFor all of the following, we're considering parallel plate capacitors. Select all the true statements. If none of them are true, select "None of the above." A. Capacitance is the property of a device that enables it to store current.B. Charge is stored in the dielectric medium between the plates of a capacitor.C. The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor depends on the charge stored on the plates.D. The charges on the two plates of a capacitor are equal in magnitude and sign.E. Adding a dielectric between the plates of an isolated air-filled charged capacitor reduces the charge stored on the device.F. None of the above.arrow_forward
- In the circuit below, if R5 is replaced by a resistor that is a third of R5, which one of the following statement about the currents in each branch is correct? R4 in RS O The only thing that will change is the current flowing through R5. O Changing R5 does not affect the currents in the circuit. O The only thing that will change is 1. O Current 11 will change, as well as currents flowing through R2, R3 and R5. O Currents flowing in R3 and in R2 will change but 11 will remain constant.arrow_forward14. (C2, 4, 31, 32, 38) Rank the following quantities (ie tell me which is larger or if they are equal,) for the circuit to the right. Explain your reasoning. The wires have resistivity PB-5PA, length LB-2LA, and radius RB=3RA. The current density though wires A and B The resistance of wires A and B 6Varrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios