
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
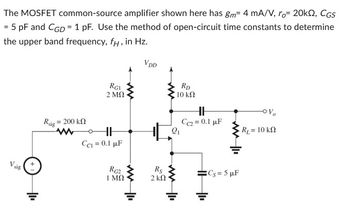
Transcribed Image Text:**Title:** Determining the Upper Band Frequency of a MOSFET Common-Source Amplifier
**Objective:**
To use the method of open-circuit time constants to find the upper band frequency, \( f_H \), of the given MOSFET common-source amplifier circuit.
**Description of the Circuit:**
- **Components:**
- A MOSFET transistor labeled \( Q_1 \) is the central active component.
- The gate of the MOSFET is connected to a voltage signal \( V_{\text{sig}} \) through a resistor \( R_{\text{sig}} = 200 \, \text{k}\Omega \).
- The gate is also connected to two resistors \( R_{G1} = 2 \, \text{M}\Omega \) and \( R_{G2} = 1 \, \text{M}\Omega \), which are connected to \( V_{\text{DD}} \) and ground respectively.
- The drain is connected to \( V_{\text{DD}} \) through a resistor \( R_{D} = 10 \, \text{k}\Omega \).
- The source is grounded through resistor \( R_{S} = 2 \, \text{k}\Omega \).
- A load resistor \( R_L = 10 \, \text{k}\Omega \) is connected from the output node to ground.
- Capacitors \( C_1 = 0.1 \, \mu\text{F} \), \( C_2 = 0.1 \, \mu\text{F} \), and \( C_S = 5 \, \mu\text{F} \) are introduced to block DC components.
- **MOSFET Parameters:**
- Transconductance, \( g_m = 4 \, \text{mA/V} \).
- Output resistance, \( r_o = 20 \, \text{k}\Omega \).
- Gate-source capacitance, \( C_{GS} = 5 \, \text{pF} \).
- Gate-drain capacitance, \( C_{GD} = 1 \, \text{pF} \).
**Objective:**
The exercise is to determine the frequency \( f_H \) above which the amplifier's gain falls below its mid-band value by 3 dB. This is
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- J Vcc 8 Rc - Vout VinoKQ₁ = CL For the circuit above, Q₁ is in active mode and ignore early effect. Let Ic1=1mA, Rc-250ohm, C₁=1nF. Assume V+-25mV, the small-signal voltage gain close to DC should be V/V. It DC gain at the corner frequency is dB and its corner frequency is Mrad/sec.arrow_forwardTrue or False? For good amplifier design, transistors are biased in the knee part of the IV-Curves. The most fundamental parameter in characterizing the small-signal linear operation of a transistor is the transconductance gm. When a resistance is connected in series with the source (or emitter), the Hybrid-Pi model is the most convenient to use. Discrete-circuit amplifiers predominantly employ MOSFETs while IC amplifiers predominantly uses BJTs. The basic gain cell of IC amplifiers is the CS (CE) amplifier with a current-source load. The MOS current mirror has a current transfer ratio of (W/L)1/(W/L)2. The internal capacitances of the MOSFET and the BJT cause the amplifier gain to rise at high frequencies. The internal MOSFET capacitances that must be considered when evaluating the frequency performance are the gate capacitances and the junction capacitances. Channel modulation causes Id to increase in the saturation mode. When Vgs=Vt, the channel charge beneath the gate is inverted.arrow_forwardThree resistors are connected in parallel namely R1, R2 and R3. It is impressed by a source voltage of 120V. If R1 receives 15W while R2 carries a current if 100mA, what should be the value of resistance R3 if the power supplied by the voltage source is 60W? a. 364.4 ohmsb. 436.4 ohmsc. 43.64 ohmsd. none of thesearrow_forward
- Vi RB Vcc Rc our A BJT (B=200) is implemented in an amplifier circuit, with a VCC of 15 volts. One wishes to set the Q point at IC = 5.76 mA and VCE = 6.73 volts (DC). Determine RB.arrow_forwardConsider the circuit depicted in the figure shown below. This circuit is designed using a silicon bipolar junction transistor (BJT) with a forward current gain BF = 100, and two resistances RB = 1kN and Rc = 1kN. The supply voltage is Vcc = 10 volts. The currents Ig and Ic designate the base and collector currents, respectively, whereas the voltage VCẸ denotes the voltage between collector and emitter. Vcc = 10 volts Rc =1 k2 Rg = 1 k2 VCE GND Throughout this question, you will use VBE,on = 0.7 volt and VCE,sat = 0.2 volt. Recall that VBE.on is the threshold voltage of the base-emitter junction, while VCE.sat represents the voltage that is measured between collector and emitter when the BJT is saturated. a) What is the value of the base current In? Please enter the value expressed in milliamperes (mA) in the box below. For instance, if you think that IR = 0.1 A, enter 100 in the box. If you think that Ip = 10 mA, enter 10 in the box. mas-numbas-Iti.ncl.ac.uk Submit part Unanswered b)…arrow_forwardI need the answer as soon as possiblearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,