
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
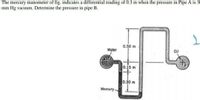
Transcribed Image Text:The mercury manometer of fig. indicates a differential reading of 0.3 m when the pressure in Pipe A is 30
mm Hg vacuum. Determine the pressure in pipe B.
0.50 m
Water
Oil
0.15 m
0.30 m
Mercury.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Water is flowing in a pipeline, the pressure in the inlet pipe is 20 kPa there is a gradual decrease in pipe diameter and the pressure reading in the reduced pipe diameter is 10 kPa, the reading was via manometer connected to the 2 points. Determine the differential pressure head if the gauge liquid is mercury (S=13.62) in m. *arrow_forward5) Determine the value of y in the manometer shown in the figure. 1 m Alr, 5 KPa Oil S = 0.8 3 m 1 m Water 0.5 ml Mercury 6) For a gage reading of -17.1 kPa, determine the (a) elevations of the liquids in the open piezometer columns E, Fand G and (b) the deflection of the mercury in the U-tube manometer neglecting the weight of air. Gage Air El. 15 m S0.70 El. 12 m Water El. 8 m S 1.6 B. 4m YMercuryarrow_forwardINCLINED MONOMETER EXAMPLE tube shown in Fig. than that at B. T 1m Determine the angle of the inclined if the pressure at A is 5KPa greater SG-0.7 SG-1.0 10 marrow_forward
- Compute the pressure @ point n ( Pn ) as shown by the differential manometer in KPa if pressure @ point m ( Pm ) is equal 1027.66 mm Hg. air plpeline where: a= 12" b=3,2 C-4.0 d- 12 m mercury density (16 300 kghm) water pipelinearrow_forward0.5 psi Open Air 0.1 ft Water. Liquid (SG = 0.6) B Mèrcury (SG = 13.6) Figure P2.38 Compartments A and B of the tank shown in Fig. P2.38 are closed and filled with air and a liquid with a specific gravity equalto 0.6. Determine the manometer reading, h, if the barometric pressure is 14.7 psia and the pressure gage reads 0.5 psi. The effect of the weight of the air is negligible.arrow_forwardI need the answer as soon as possiblearrow_forward
- Oil of sp.gr. of 0.750 flows through the nozzle shown and deflects the mercury in the U-tube gage.Determine the value of H in m if the pressure at A is 142 kPa. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.arrow_forward3) A pressure gage at the suction side of a pump shows a vacuum of 25 cm of mercury. Determine the (a) pressure in kPa; (b) pressure head in meter of water; (c) absolute pressure in kPa if the barometer reads 755cm of mercury.arrow_forwardDetermine the pressure difference between pipes A and B for the differential manometer shown in Fig. 2-27.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning