Question
thumb_up100%
Good morning, could you help me with this exercise of creating linear graphs ?
Beforehand thank you very much.
The masses and volumes of eight bodies of the same material are measured. To do this, a balance that appreciates up to the tenth of a gram (o.1 g) and a graduated cylinder that appreciates up to two tenths of a cubic centimeter (0.2 cm^3) were used. The results are (see image)
Calculate the density of the material using the method of least squares, and the value of the
(Remember: plot of volume (abscissa) versus mass (ordinate), remembering that m=ρV.)
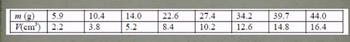
Transcribed Image Text:m (g)
5.9
V(cm³) 2.2
10.4
3.8
14.0
5.2
22.6
8.4
27.4
10.2
34.2
12.6
39.7
14.8
44.0
16.4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A group of students wish to determine, experimentally, the bulk density of an unknown material. To determine this amount, the students measured the diameter, height, and mass of various cylinders. These values appear in the table below. Determine: a) The volume of the cylinders that appears in the following table. b) The graph of mass vs. volume.arrow_forwardWhat is the volume of a hat box (cylinder) in liters, which is 60.0cm in diameter and 38.5cmtall ? (V = πr2h) Explain how you got your answer.arrow_forwardProblem 2. 1-3arrow_forward
- You are making a sculpture that is a pyramid with a square base . You want the height of the pyramid to be 4 inches less than the length of a side of the base . You want the volume of the sculpture to be 200 cubic inches . a . Let x represent the length ( in inches ) of a side of the sculpture's base . Draw a diagram of the sculpture , and label the dimensions in terms of x . b . Write a function that gives the volume V of the sculpture in terms of x .arrow_forwardA hot tub with a surface area of 28 ft2 is filled with water to a depth of 29 in . Hint: volume is calculated as area × height (A × h). A) What is the volume of water in the tub, in liters? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. B) How many kilojoules are needed to heat the water from 59∘F to 103 ∘F? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. C) If the hot-tub heater provides 5900 kJ/min, how long, in hours, will it take to heat the water in the hot tub from 59∘F to 103∘F? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardYou will be using these rules in your calculations. As an example of a sample calculation, find the volume of a rectangular solid: V = Lx W x H V = (25.95 cm)(5.87 cm)(83 cm) V = 13000 cm³ = 1.3 x 10“ cm3 Note that when you do this calculation in your calculator, you will have an answer of 12643.0995. However, the 83 cm limits your answer to 2 significant figures, so you must round the final answer to 2 significant figures. Remember you need to keep the place value of the significant figures! The scientific notation helps clarify that none of the zeros are significant.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios