
Principles of Accounting Volume 2
19th Edition
ISBN: 9781947172609
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: OpenStax College
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I NEED ANSWER
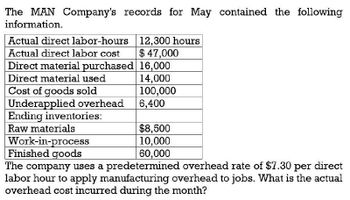
Transcribed Image Text:The MAN Company's records for May contained the following
information.
Actual direct labor-hours
Actual direct labor cost
12,300 hours
$ 47,000
Direct material purchased 16,000
Direct material used
14,000
Cost of goods sold
100,000
Underapplied overhead
6,400
Ending inventories:
$8,500
10,000
60,000
Raw materials
Work-in-process
Finished goods
The company uses a predetermined overhead rate of $7.30 per direct
labor hour to apply manufacturing overhead to jobs. What is the actual
overhead cost incurred during the month?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- SCHEDULE OF COST OF GOODS MANUFACTURED The following information is supplied for Sanchez Welding and Manufacturing Company. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured for the year ended December 31, 20--. Assume that all materials inventory items are direct materials. Work in process, January 1 20,500 Materials inventory, January 1 11,000 Materials purchases 12,000 Materials inventory, December 31 13,000 Direct labor 9,500 Overhead 5,500 Work in process, December 31 10,500arrow_forwardSCHEDULE OF COST OF GOODS MANUFACTURED The following information is supplied for Maupin Manufacturing Company. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured for the year ended December 31, 20--. Assume that all materials inventory items are direct materials. Work in process, January 1 77,000 Materials inventory, January 1 31,000 Materials purchases 35,000 Materials inventory, December 31 26,000 Direct labor 48,000 Overhead 20,000 Work in process, December 31 62,000arrow_forwardAmounts for materials Big Timber Furniture Company manufactures furniture. Big Timber Furniture uses a job order cost system. Balances on June 1 from the materials ledger are as follows: The materials purchased during June are summarized from the receiving reports as follows: Materials were requisitioned to individual jobs as follows: The glue is not a significant cost, so it is treated as indirect materials (factory overhead). a.Determine the total purchase of materials in June. b.Determine the amounts of materials transferred to Work in Process and Factory Overhead during June. c.Determine the June 30 balances that would be shown in the materials ledger accounts.arrow_forward
- The following data summarize the operations during the year. Prepare a journal entry for each transaction. A. Purchase of raw materials on account: $1,500 B. Raw materials used by Job 1: $400 C. Raw materials used as indirect materials: $50 D. Direct labor for Job 1: $200 E. Indirect labor Incurred for Job 1: $30 F. Factory utilities Incurred on account: $500 G. Adjusting entry for factory depreciation: $200 H. Manufacturing overhead applied as percent of direct labor: 100% I. Job 1 is transferred to finished goods J. Job 1 is sold: $1,000 K. Manufacturing overhead is under applied: $100arrow_forwardSelected information from Skylar Studios shows the following: Prepare journal entries to record the following: raw material purchased direct labor incurred depreciation expense (hint: this is part of manufacturing overhead) raw materials used overhead applied on the basis of $0.50 per machine hour the transfer from department 1 to department 2arrow_forwardDuring the year, a company purchased raw materials of $77,321, and incurred direct labor costs of $125,900. Overhead is applied at the rate of 75% of the direct labor cost. These are the inventory balances: Compute the cost of materials used in production, the cost of goods manufactured, and the cost of goods sold.arrow_forward
- JOURNAL ENTRIES FOR MATERIAL, LABOR, AND OVERHEAD Rich Manufacturing Corporation had the following transactions for its job order costing operation. Prepare general journal entries to record these transactions. Jan. 1 Purchased materials on account, 22,000. 15 Issued direct materials to Job No. 1, 18,000. 20 Issued indirect materials (factory overhead), 3,000. 31 Incurred direct labor, Job No. 1, 11,000. 31 Incurred indirect labor (factory overhead), 4,000. 31 Incurred other indirect costs (factory overhead; credit Accounts Payable), 1,500.arrow_forwardJOURNAL ENTRIES FOR MATERIAL, LABOR, AND OVERHEAD Hilburn Manufacturing Corporation had the following transactions for its job order costing operation. Prepare general journal entries to record these transactions. Jan.1 Purchased materials on account, 17,000. 15 Issued direct materials to Job No. 104, 11,000. 20 Issued indirect materials (factory overhead), 5,000. 31 Incurred direct labor, Job No. 104, 9,000. 31 Incurred indirect labor (factory overhead), 2,500. 31 Incurred other indirect costs (factory overhead; credit Accounts Payable), 2,000.arrow_forwardA company calculated the predetermined overhead based on an estimated overhead of $70.000, and the activity for the cost driver was estimated as 2,500 hours. If product A utilized 1,350 hours and product 8 utilized 1,100 hours, what was the total amount of overhead assigned to the products? A. $35000 B. $30.800 C. $37,800 D. $68,600arrow_forward
- The records of Burris Inc. reflect the following data: Work in process, beginning of month2,000 units one-half completed at a cost of 1,250 for materials, 675 for labor, and 950 for overhead. Production costs for the monthmaterials, 99,150; labor, 54,925; factory overhead, 75,050. Units completed and transferred to stock38,500. Work in process, end of month3,000 units, one-half completed. Compute the months unit cost for each element of manufacturing cost and the total per unit cost.arrow_forwardRecording issuing of materials Materials issued for the current month are as follows a. Determine the amount of materials transferred lo Work in Process and Factory Overhead for the current month. b.Illustrate (he effect on the accounts and financial statements of the materials transferred in (a).:arrow_forwardThe following data summarize the operations during the year. Prepare a journal entry for each transaction. Purchase of raw materials on account: $3000 Raw materials used by Job 1: $500 Raw materials used as indirect materials: $100 Direct labor for Job 1: $300 Indirect labor incurred: $50 Factory utilities incurred on account: $700 Adjusting entry for factory depreciation: $250 Manufacturing overhead applied as percent of direct labor: 200% Job 1 is transferred to finished goods Job 1 is sold: $3,000 Manufacturing overhead is over applied: $100arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning  Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172609
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:9781337794756
Author:HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:9781305961883
Author:Carl Warren
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:South-Western College Pub