
The lower surface of a flat Teflon plate (k=0.35 W/(m.K),ρ=2200 kg/m3 and cp=1500 J/(kg.K) with 2 m long and 60 mm thick is heated by radiation from infrared lamps that emit a constant flux over this surface, while its opposite surface exchanges heat by convection with an air stream at 15oC flowing parallel to its length, with speed of 15 m/s. The temperature of surface 1 (T1) is maintained at 60oC by lamp irradiation and surface temperature 2 (T2) is not known. Under steady-state conditions for heat transfer, it is requested:
(a) Estimate the film coefficient for convection heat exchange (consider the free current temperature to estimate the physical properties);
(b) Estimate the temperature T2 and the heat flux provided by the
heating lamps
Table below about the physical properties of air at 1 atm
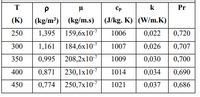
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

- A 10.0 m by 3.0 m by 1.3 m barge (495 kg) is floating in water (SG=1.05) and being loaded with a 0.32 m diameter dredging liquid stream (SG = 1.41) with a velocity of 15.5 m/s. If the minimum permissible freeboard during loading (boat edge above the waterline) is 0.35 m, what is the maximum time (seconds) that the barge can be 'filled'. +0.32 m BARGE 10.0 m 1.3 marrow_forwardConsider a thin sheet of 20 cm (width) x 20 cm (length) × 1 cm (thickness) with its top surface covered by a coating layer (thickness 2 mm). The water is flowing over the coating layer with a free stream temperature of 20 °C and velocity of 10 m/s. All the other surfaces are well insulated, and the sheet and the coating have a uniform initial temperature of 95 °C (at t=0). U∞ = 10 m/s Too=20°C 2 mm Coating 1 cm Sheet T=95°C 20 cm m 20 cm P assume: steady state external flow •uniform initial teme @ coating (a) At t = 0, determine the heat transfer rate from the coating surface to the water. average (b) Determine the Biot number of the sheet. (c) How long does it take for the top surface of the sheet to be cooled to 30 °C? Properties of water: v₁ = 4.97×104 m²/s, k = 0.65 W/m K, d=0.143×10-6 m²/s, and Prw = 3.15. Properties of the sheet: ps = 8400 kg/m³, Cp.s= 420 J/kg K, and ks = 10 W/m K. Properties of the coating: kc = 0.04 W/m.K.arrow_forwardWind flows over a flat plate of length L = 25 mm and width W = 8 mm. The plate is maintained at a constant temperature of 32 °C on both sides. using an electric heater generating heat at a rate of Q = 0.5 W which is dissipated to air from both sides of the plate. Consider the temperature of the wind/air as 20 °C and assume that the wind speed does not exceed 100 m/s. The properties of air at this temperature are given as; specific heat capacity Cp = 1.005 kJ/kg-K, thermal conductivity k = 0.0253 W/m-K, Density p = 1.19 kg/m³, and kinematic viscosity v = 1.522 x 10 5 m²/s.arrow_forward
- The wall of a furnace has an inner temperature of 500 F. The wall has a thickness of 2 inches and has a thermal conductivity of 0.02 Btu/(h·ft·F). On the outside, air at 30 F flows over the 10 ft x 10 ft wall at a speed of 10 ft/s. Determine the rate of heat loss from the furnace to the environment.arrow_forwardQ3/Air at 0.5 atm pressure and 27 C flows across a 34-cm-square plate at a velocity of 20 m/s. The plate temperature is maintained at 127 C. Calculate the heat lost by the plate.arrow_forwardAir at a temperature of 20 oC flows at a speed of 10 m/s through a rectangular duct made of wrought iron with a cross section of 30 cm x 50 cm and a length of 20 m. Calculate the required fan powerarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





