
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The ladder in the picture has a mass of 34 kilograms and a length 3.2 meters.
Fn=333.2N
a.Assume that the ladder's weight is evenly distributed, so it can be treated as a single force through the middle. If the ladder is at a 69° angle from the ground, what is the torque exerted by the weight (using the floor as the pivot point)?
b.The torque from the ladder must be balanced by the torque caused by the normal force on the wall. Calculate this force.
c.The normal force from the wall must be balanced by the friction force from the floor. Determine the minimum coefficient of friction to keep the ladder from slipping.
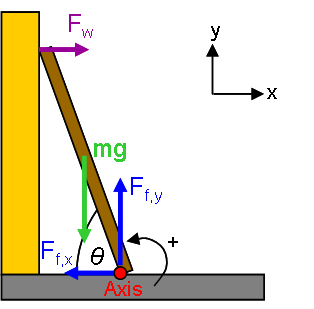
Transcribed Image Text:F
W
mg
AF
Ff.y
Fixe
Axis
+
L
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A flagpole has a uniform mass density and total mass of M and length L. It is hinged at the ground and makes an angle of U with respect to the horizontal, as shown. To support the pole, a horizontal cable is attached to the pole at a point L from the bottom of the pole. 3 What is the correct sum of torque equation for the axis perpendicular to the page and passing through the bottom of the pole? cable 2L/3 0-Mg + 흙LT=0 O-Mgcos0 +LTsin0 = 0 ○ 들Mgsind + 능TCOS6) +Tcose = 0 Mgsino + LTcos0 = 0 O- Mgsin0+LTcos0 = 0arrow_forwardYou open a door by applying a force 1/2 m away from the hinge. The torque you applied was 100 N⋅m. However, the angle at which you pushed the door was 30 degrees from the face of the door. What amount of force did you apply? Please answer in units of newtons and your answer should be exact.arrow_forwardPlease ASAParrow_forward
- A seesaw has length 11.0 m and uniform mass 11.3 kg and is resting at an angle of 30° with respect to the ground (see the following figure). The pivot is located at 8.3 m from the end of the seesaw. What magnitude of force (in N) needs to be applied perpendicular to the seesaw at the raised end so as to allow the seesaw to barely start to rotate? F=? 30 N tarrow_forward(a) A person opens a 1.20 m wide door by pushing on it with a force of 57.5 N applied at the center of the door, at an angle perpendicular to the door's surface. What magnitude of torque (in N · m) is applied about an axis through the hinges? _________N · m (b) A man opens the same door, using the same force, again directed perpendicular to the surface, but now the force is applied at the edge of the door. What magnitude of torque (in N · m) is applied about the axis through the hinges now? _________N · marrow_forwardThe angle between the beam and the floor is 15.0 degrees. The angle between the rope and the horizontal is 31.0 degrees. The beam is 4.10-m long and has a mass of 6.10 kg. The box sits a distance of d = 0.770 m from the upper end of the beam and has a mass of 9.60 kg.What is the torque due only to the weight of the box if the axis is at the hinge?arrow_forward
- (a) A woman opens a 1.35 m wide door by pushing on it with a force of 44.5 N applied at the center of the door, at an angle perpendicular to the door's surface. What magnitude of torque (in N · m) is applied about an axis through the hinges? (b) A girl opens the same door, using the same force, again directed perpendicular to the surface, but now the force is applied at the edge of the door. What magnitude of torque (in N · m) is applied about the axis through the hinges now?arrow_forwardA uniform 10.0 m ladder of weight WL=375 N leans against a frictionless wall. There is a force of static friction between the floor and the bottom of the ladder. A person weighing Wp stands 7.4 m between the bottom of the ladder. Draw a free body diagram for the ladder. Draw a torque diagram for the ladder. Determine the force that the wall exerts on the top of the ladder. Determine the force of static friction exerted on the ladder by the floor.arrow_forwardWhen the palmaris longus muscle in the forearm is flexed, the wrist moves back and forth. If the muscle generates a force of 39.5 N39.5 N and it is acting with an effective lever arm of 2.55 cm, what is the torque that the muscle produces on the wrist?arrow_forward
- A rectangular bar is hinged at point O. The bar is 3.00 m long and 2.00 m wide. Find the torque resulting from the following force about an axis through point O: F1 = 1 N. Use a positive for a counterclockwise torque and a negative for a clockwise torque.arrow_forwardA 3.0-m rod is pivoted about its left end. A force of 6.0 N is applied perpendicular to the rod at a distance of 1.2 m from the pivot causing a counter clockwise torque, and a force of 5.2 N is applied at the end of the rod 3.0 m from the pivot. The 5.2 N is at an angle of 30° to the rod and causes a clockwise torque. What is the net torque about the pivot? A 15 N.m B 0 N.m -6.3 N.m -0.6 Nxm Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON