
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
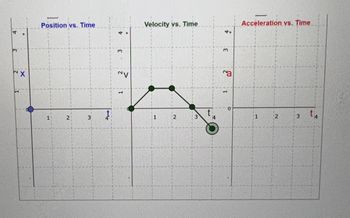
The
- Describe the motion of the bicyclist (direction of velocity and whether the velocity is constant, increasing and decreasing) during each 1s interval from 0-4 s using the graph.
- Draw the position – time (x-t) graph of this motion. This is qualitative only, showing the shapes of the x-t curves in each interval and need not be drawn to scale.
- Draw the acceleration – time graph (a-t graph) for this motion. Draw this graph showing the values of acceleration in m/s2.
- What is the displacement of the bicyclist from 0-4 s. What physics principle did you use? Show your work.
Transcribed Image Text:B
NX
Position vs. Time
1
2
3
4
NV
Velocity vs. Time
1
2
4
3
Na
Acceleration vs. Time
1
2
3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Figure below shows the position of a cart moves along the x-axis. What is the object's velocity at 2.0 s, in m/s? Your answer needs to have 2 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement. x (m) 2 1 A K 0 T -1 -2 B 2 4 6 8 10 C D 12 14 X6 E 18 -t (s)arrow_forwardThe equation for the motion of an object with constant acceleration is d= do + vt + at, where d is distance from a given point in meters, do is the initial distance from the starting point in meters, v is the starting velocity in meters per second, a is acceleration in meters per second squared, and t is time in seconds. A car is stopped at a traffic light. When the light turns green, the driver begins to drive, accelerating at a constant rate of 4 meters squared. A bus is traveling at a speed of 15 meters per second in another lane. The bus is 7 meters behind the car as it begins to accelerate. per second Find when the bus passes the car, when the car passes the bus, and how far each has traveled each time they pass one another. it lad wodarrow_forwardThe velocity - time graph of the journey of a person is shown in the attached graph. How much distance, in meters, did the person cover during the whole journey, from time = 0 to time = 50 seconds? Round your answer to the nearest integer. Speed (m/s) 25 20 15 10 5 0 0 10 20 Time (s) 30 40 50arrow_forward
- A particular rabbit accelerates from rest to a speed of 11.7 m/s in 1.2 seconds. What is the rabbit's average acceleration during that time interval? (Assume the acceleration is positive in our coordinate system, and give your answer in m/s2 .)arrow_forwardPlease box all answersarrow_forwardAn individual at the edge of a cliff drops a ball meanwhile another human at the base of a cliff throws a ball straight upward. When the 2 balls meet, the one thrown from the base of the cliff is descending. Sketch the y versus t graph showing the motion of the balls please.arrow_forward
- sketch what you think the speed time graph would look like for a vehicle that begins at 10 m/hr. and remains at that speed for 10 minutes. Label this section A. Then the vehicle (over a five-minute interval) increases speed from 10 to 20 m/hr. Label this section B. Then immediately the vehicle begins to slow down. It takes the vehicle 10 minutes to slow down from 20 m/hr. to zero. Label this section C. This graph would have 3 intervals. The first interval (A) is from 0 to 10 minutes. The second interval (B) is from 10 minutes to 15 minutes. The third interval (C) is from 15 minutes to 25 minutes. The x-axis needs to go from zero to 25 minutes. The y axis needs to go from zero to 20 m/hr. Describe the motion of the vehicle in each interval as increasing, decreasing, constant, or at rest.arrow_forwardPlease box both answers.arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution .....arrow_forward
- This position time graph describes an object's motion. Use it to predict the position (in m) of the object at a time of 24.0 seconds.arrow_forwardA boulder starting from rest rolls down a hill in a straight line, which we shall call the xx axis. A graph of its position xx as a function of time tt is shown in the figure. (Figure attached) 1) Find the distance the boulder rolled between the end of the first second and the end of the third second. Express your answer in meters to one significant figure. 2) Find the boulder’s average speed during the first second. Express your answer in meters per second to one significant figure. 3) Find the boulder’s average speed during the second second. Express your answer in meters per second to one significant figure. 4) Find the boulder’s average speed during the third second. Express your answer in meters per second to one significant figure. 5) Find the boulder’s average speed during the fourth second. Express your answer in meters per second to one significant figure. 6) Find the boulder’s average speed during the first 4 seconds. Express your answer in meters per…arrow_forwardQ1: A dolphin in an aquatic show jumps straight up out of the water at a velocity of 13.0 m/s. (a) List the knowns in this problem. (b) How high does his body rise above the water? To solve this part, first note that the final velocity is now a known and identify its value. Then identify the unknown, and discuss how you chose the appropriate equation to solve for it. After choosing the equation, show your steps in solving for the unknown, checking units, and discuss whether the answer is reasonable. (c) How long is the dolphin in the air? Neglect any effects due to his size or orientation.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON