
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
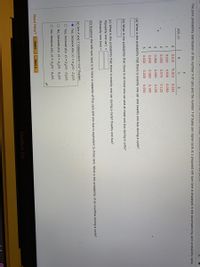
Transcribed Image Text:The joint probability distribution of the number X of cars and the number Y of buses per signal cycle at a proposed left-turn lane is displayed in the accompanying joint probability table.
y
P(x, y)
1
2
0.010
0.015
0.025
1.
0,020
0.030
0.050
0.050
0.075
0.125
3
0.060
0.090
0.150
0.040
0.060
0.100
5
0.020
0.030
0.050
(a) What is the probability that there is exactly one car and exactly one bus during a cycle?
(b) What is the probability that there is at most one car and at most one bus during a cycle?
(c) What is the probability that there is exactly one car during a cycle? Exactly one bus?
P(exactly one car) =
P(exactly one bus) =
(d) Suppose the left-turn lane is to have a capacity of five cars and one bus is equivalent to three cars. What is the probability of an overflow during a cycle?
(e) Are X and Y independent rv's? Explain.
O Yes, because p(x, y) = px(x)•PylY).
O Yes, because p(x, y) # P(x) Py(Y).
O No, because p(x, y) = P(x)•Py(Y).
O No, because p(x, y) # Px(x) Py(Y).
Need Help?
Watch It
Read It
MacBook Pro
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2 3. Consider the joint probability distribution of X and Y: x = -2 0.25 x = 0 x = 2 y = -4 y = 0 0.25 0.5 In this example, X and Y are not independent, correlated not independent, uncorrelated independent, correlated independent, uncorrelated In this example, X and Y are 4. Consider the joint probability distribution of X and Y: x = 0 x = 1 y = 0 0.2 0.2 y= 1 0.1 0.5 In this example, X and Y are not independent, correlated not independent, uncorrelated independent, correlated independent, uncorrelated In this example, X and Y arearrow_forwardData were collected from a survey given to graduating college seniors on the number of times they had changed majors. From that data, a probability distribution was constructed. The random variable X is defined as the number of times a graduating senior changed majors. It is shown below: xx 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 P(X=x)P(X=x) 0.244 0.234 0.233 0.16 0.068 0.039 0.017 0.003 0.002 What is the probability that a randomly selected student changed his or her major at least once? What is the probability that a randomly selected student changed his or her major at most twice? What is the probability that a randomly selected student changed his or her major exactly twice? What is the mean number of times students changed majors? What is the standard deviation of X?arrow_forwardThe joint probability distribution of the number X of cars and the number Y of buses per signal cycle at a proposed left-turn lane is displayed in the accompanying joint probability table. p(x, у) 1 2 0.015 0.010 0.025 1 0.030 0.020 0.050 2 0.075 0.050 0.125 3 0.090 0.060 0.150 4 0.060 0.040 0.100 0.030 0.020 0.050 (a) What is the probability that there exactly one car and exactly one bus during a cycle? (b) What is the probability that there is at most one car and at most one bus during a cycle? (c) What is the probability that there is exactly one car during a cycle? Exactly one bus? P(exactly one car) P(exactly one bus) = (d) Suppose the left-turn lane is to have a capacity of five cars and one bus is equivalent to three cars. What is the probability of an overflow during a cycle? (e) Are X and Y independent rv's? Explain. Yes, because p(x, y) = Px(x) · Py(y). Yes, because p(x, y) ± Px(x) · py(y). No, because p(x, y) = Px(x) · Py(Y). No, because p(x, y) # Px(x) · Py(y).arrow_forward
- Find the variance for the probability distribution 4 0 1 2 3 P(X=x) 0.04 0.18 0.34 0.23 0.21 Select one: а. 1.12 b. 1.26 с. 1.59 d. 3.79arrow_forwardLet X be the discrete r.v. that represents the number of Boys in a three-child family. Assume that the outcomes boys and girls are equally likely. What is the expected value of this discrete probability distribution? What is the variance?arrow_forwardOxygen demand is a term biologists use to describe the oxygen needed by fish and other aquatic organisms for survival. The Environmental Protection Agency conducted a study of a wetland area. In this wetland environment, the mean oxygen demand was μ = 9.9 mg/L with 95% of the data ranging from 7.3 mg/L to 12.5 mg/L. Let x be a random variable that represents oxygen demand in this wetland environment. Assume x has a probability distribution that is approximately normal. (a) Use the 95% data range to estimate the standard deviation for oxygen demand.arrow_forward
- In the probability distribution to the right, the random variable X represents the number of marriages an individual aged 15 years or older has been involved in. Compute and interpret the mean of the random variable X. Hx = marriages (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) X 0 1 2 3 4 5 P(x) 0.264 0.567 0.136 0.029 0.003 0.001arrow_forwardSuppose we are interested in the relationship between an individual's brown hair and skin color. Based on a random sample of LIU students, we have the following joint probability distribution given by: X-degree of brown hair color 2 3 4 0.12 0.01 0.05 0.07 0.07 0.12 0.09 0.16 Y- degree of skin color 2 0.12 3 0.16 | 0.03 The probability that an individual with degree of brown hair 2 has a degree of skin color 1 is: None of these 0.263 0.167 0.3arrow_forwardLet X = {Email, In Person, Instant Message, Text Message}; P(Email) = 0.06 P(In Person) = 0.55 P(Instant Message) = 0.24 P(Text Message) = 0.15 Is this model a probability distribution? A. Yes. B. No. C. Maybe.arrow_forward
- The joint probability distribution of the number X of cars and the number Y of buses per signal cycle at a proposed left-turn lane is displayed in the accompanying joint probability table below. y P(xy) 1 2. 0. .025 .015 .010 .050 .030 020 2. .125 .075 050 3. 150 090 060 4. 100 .060 040 050 .030 .020 Suppose the left-turn lane is to have a capacity of six cars, and that one bus is equivalent to three cars. What is the probability of an overflow duringa cycle? Select one: O 48 O 28 O38 0.18arrow_forwardPlease calculate the covariance and the correlation coefficient for the two random variables and briefly comment on the resulting correlation between the variables.arrow_forwardA survey of almost 44,000 two-child families yielded the accompanying table. The probability distribution of x, the number of boys in a two-child family is given below. Find E(x) and give a practical interpretation of its value. Gender Configuration Proportion D Girl-girl (GG) Boy-girl (BG) Girl-Boy (GB) 0.215 0.267 0.256 P(x) 0.215 0.523 0.262 Boy-boy (BB) 0.262 Choose the correct answer below and fill in the answer box to complete your choice. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) O A. If a very large number of households were sampled, on average, there would be E(x) = boys. O B. If a very large number of two-child households were sampled, on average, there would be E(x) = boys. of getting a family with a boy. %3D O C. If a very large number of two-child households were sampled, there would be a probability of E(x) = O D. In the sample of 44,000 households, each household had E(x) = boys.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman